In this article, we will analyze ErrorBoundary class component in Zustand’s test case. Error handling is a crucial part of any React application.
Overview of the Test Case
Here’s the test case we’ll be exploring:
// Picked from https://github.com/pmndrs/zustand/blob/v4.5.5/tests/basic.test.tsx#L378
it('can throw an error in equality checker', async () => {
console.error = vi.fn()
type State = { value: string | number }
const initialState: State = { value: 'foo' }
const useBoundStore = createWithEqualityFn(() => initialState, Object.is)
const { setState } = useBoundStore
const selector = (s: State) => s
const equalityFn = (a: State, b: State) =>
// @ts-expect-error This function is supposed to throw an error
a.value.trim() === b.value.trim()
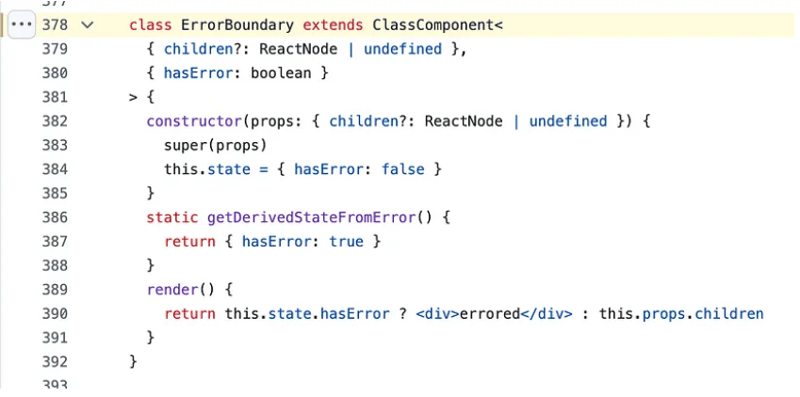
class ErrorBoundary extends ClassComponent<
{ children?: ReactNode | undefined },
{ hasError: boolean }
> {
constructor(props: { children?: ReactNode | undefined }) {
super(props)
this.state = { hasError: false }
}
static getDerivedStateFromError() {
return { hasError: true }
}
render() {
return this.state.hasError ? <div>errored</div> : this.props.children
}
}
function Component() {
useBoundStore(selector, equalityFn)
return <div>no error</div>
}
const { findByText } = render(
<StrictMode>
<ErrorBoundary>
<Component />
</ErrorBoundary>
</StrictMode>,
)
await findByText('no error')
act(() => {
setState({ value: 123 })
})
await findByText('errored')
})
This test verifies that when an error occurs inside an equality checker, the error is caught and handled gracefully by an ErrorBoundary component.
Key Concepts in the Test Case
1. Zustand’s createWithEqualityFn
Zustand allows you to define stores with custom equality functions using createWithEqualityFn. In this test, the initial state is defined as:
const initialState: State = { value: 'foo' }
The createWithEqualityFn function is used to create a store where the equality function is defined to compare states based on whether the value property is equal. In this case, the equality checker is intentionally set to throw an error when value is of a type other than string:
You can intentionally throw errors in your test cases to ensure your code handles errors as expected.
const equalityFn = (a: State, b: State) => a.value.trim() === b.value.trim() // Throws error if 'value' is not a string
The test case expects this equality function to fail when value becomes a number, causing the error handler to come into play.
2. Custom ErrorBoundary Component
React’s ErrorBoundary component is a common pattern used to catch JavaScript errors in a component tree, and Zustand has taken this approach to test how errors within their state management are handled. This particular test case defines a custom ErrorBoundary component directly inside the test. I mean, how often do you come across a test case that has the custom ErrorBoundary with in a “test case”?
class ErrorBoundary extends ClassComponent<
{ children?: ReactNode | undefined },
{ hasError: boolean }
> {
constructor(props: { children?: ReactNode | undefined }) {
super(props)
this.state = { hasError: false }
}
static getDerivedStateFromError() {
return { hasError: true }
}
render() {
return this.state.hasError ? <div>errored</div> : this.props.children
}
}
How it works:
The component uses the lifecycle method getDerivedStateFromError() to catch errors and update its state (hasError) to true.
If an error is detected, the component renders
errored. Otherwise, it renders its children.
In typical production use, ErrorBoundary components are created as reusable elements to catch and display errors across the application. However, embedding the ErrorBoundary directly inside a test case like this provides fine-grained control over error testing, allowing you to assert that the component reacts correctly when errors occur in specific parts of the application.
3. Testing Error Handling with Vitest
In this test case, Vitest is used as the testing framework. Here’s how it works with Zustand:
- Rendering the Component: The Component that uses the useBoundStore hook is rendered inside the ErrorBoundary within a React StrictMode block. This ensures that errors inside the equality checker can be caught.
const { findByText } = render(
<StrictMode>
<ErrorBoundary>
<Component />
</ErrorBoundary>
</StrictMode>,
)
await findByText('no error')
At this point, the test verifies that no error has been thrown yet and checks for the text no error.
Triggering the Error: After the component is initially rendered without errors, the test triggers an error by updating the store’s state to a number:
act(() => { setState({ value: 123 }) })
This causes the equality function to throw an error, as value.trim() is no longer valid for a number type.
Asserting the Error Handling: Once the error is thrown, the ErrorBoundary catches it, and the test waits for the UI to render the errored message:
await findByText('errored')
- This assertion confirms that the error was properly caught and displayed by the ErrorBoundary
Why This Approach is Unique
What makes this test case particularly interesting is the use of an inline ErrorBoundary component within a unit test. Typically, error boundaries are part of the main React app, wrapping components in the main render tree. However, Zustand's approach to create an error boundary in the test suite itself offers a more flexible and isolated way to test how errors are handled under specific conditions.
By directly controlling the boundary within the test, Zustand ensures:
Granularity: The test can focus on how errors in a particular part of the application (like the equality checker) are handled, without needing to rely on global error boundaries.
Test Isolation: The ErrorBoundary exists only within the scope of this test, reducing potential side effects or dependencies on the app’s broader error-handling logic.
About us:
At Think Throo, we are on a mission to teach the advanced codebase architectural concepts used in open-source projects.
10x your coding skills by practising advanced architectural concepts in Next.js/React, learn the best practices and build production-grade projects.
We are open source — https://github.com/thinkthroo/thinkthroo (Do give us a star!)
Up skill your team with our advanced courses based on codebase architecture. Reach out to us at hello@thinkthroo.com to learn more!
References:
- https://github.com/pmndrs/zustand/blob/v4.5.5/tests/basic.test.tsx#L378
以上是Here’s how Zustand’s test-case uses ErrorBoundary.的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 JavaScript数据类型:浏览器和nodejs之间是否有区别?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
JavaScript数据类型:浏览器和nodejs之间是否有区别?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript核心数据类型在浏览器和Node.js中一致,但处理方式和额外类型有所不同。1)全局对象在浏览器中为window,在Node.js中为global。2)Node.js独有Buffer对象,用于处理二进制数据。3)性能和时间处理在两者间也有差异,需根据环境调整代码。
 JavaScript评论:使用//和 / * * / * / * /May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript评论:使用//和 / * * / * / * /May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript:开发人员的比较分析May 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:开发人员的比较分析May 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMPython和JavaScript的主要区别在于类型系统和应用场景。1.Python使用动态类型,适合科学计算和数据分析。2.JavaScript采用弱类型,广泛用于前端和全栈开发。两者在异步编程和性能优化上各有优势,选择时应根据项目需求决定。
 Python vs. JavaScript:选择合适的工具May 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:选择合适的工具May 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM选择Python还是JavaScript取决于项目类型:1)数据科学和自动化任务选择Python;2)前端和全栈开发选择JavaScript。Python因其在数据处理和自动化方面的强大库而备受青睐,而JavaScript则因其在网页交互和全栈开发中的优势而不可或缺。
 Python和JavaScript:了解每个的优势May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python和JavaScript:了解每个的优势May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython和JavaScript各有优势,选择取决于项目需求和个人偏好。1.Python易学,语法简洁,适用于数据科学和后端开发,但执行速度较慢。2.JavaScript在前端开发中无处不在,异步编程能力强,Node.js使其适用于全栈开发,但语法可能复杂且易出错。
 JavaScript的核心:它是在C还是C上构建的?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript的核心:它是在C还是C上构建的?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMjavascriptisnotbuiltoncorc; saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninc.1)javascriptwasdesignedAsalightweight,解释edganguageforwebbrowsers.2)Enginesevolvedfromsimpleterterterpretpreterterterpretertestojitcompilerers,典型地提示。
 JavaScript应用程序:从前端到后端May 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript应用程序:从前端到后端May 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript可用于前端和后端开发。前端通过DOM操作增强用户体验,后端通过Node.js处理服务器任务。1.前端示例:改变网页文本内容。2.后端示例:创建Node.js服务器。
 Python vs. JavaScript:您应该学到哪种语言?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:您应该学到哪种语言?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM选择Python还是JavaScript应基于职业发展、学习曲线和生态系统:1)职业发展:Python适合数据科学和后端开发,JavaScript适合前端和全栈开发。2)学习曲线:Python语法简洁,适合初学者;JavaScript语法灵活。3)生态系统:Python有丰富的科学计算库,JavaScript有强大的前端框架。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

mPDF
mPDF是一个PHP库,可以从UTF-8编码的HTML生成PDF文件。原作者Ian Back编写mPDF以从他的网站上“即时”输出PDF文件,并处理不同的语言。与原始脚本如HTML2FPDF相比,它的速度较慢,并且在使用Unicode字体时生成的文件较大,但支持CSS样式等,并进行了大量增强。支持几乎所有语言,包括RTL(阿拉伯语和希伯来语)和CJK(中日韩)。支持嵌套的块级元素(如P、DIV),

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具





