图的最小生成树是总权重最小的生成树。
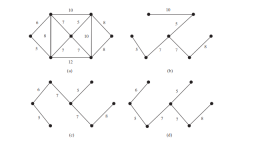
一个图可能有许多生成树。假设边缘被加权。最小生成树的总权重最小。例如,下图 b、c、d 中的树是图 a 中图的生成树。图c和d中的树是最小生成树。
寻找最小生成树的问题有很多应用。考虑一家在许多城市设有分支机构的公司。该公司希望租用电话线将所有分支机构连接在一起。电话公司对连接不同的城市收取不同的费用。有很多方法可以将所有分支连接在一起。最便宜的方法是找到总费率最小的生成树。
最小生成树算法
如何找到最小生成树?有几种众所周知的算法可以做到这一点。本节介绍Prim算法。 Prim 的算法从包含任意顶点的生成树 T 开始。该算法通过重复添加具有与树中已有顶点相关的最低成本边的顶点来扩展树。 Prim的算法是一种贪心算法,其代码如下所示。
Input: A connected undirected weighted G = (V, E) with non-negative weights
Output: MST (a minimum spanning tree)
1 MST minimumSpanningTree() {
2 Let T be a set for the vertices in the spanning tree;
3 Initially, add the starting vertex to T;
4
5 while (size of T
<p>算法首先将起始顶点添加到<strong>T</strong>中。然后,它不断地将一个顶点(例如 <strong>v</strong>)从 <strong>V – T</strong> 添加到 <strong>T</strong> 中。 <strong>v</strong> 是与 <strong>T</strong> 中的顶点相邻且边权重最小的顶点。例如,<strong>T</strong> 和 <strong>V – T</strong> 中的顶点有 5 条边连接,如下图所示,并且 (<strong>u</strong>, <strong>v</strong> ) 是权重最小的一个。</p>
<p><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/000/172557408574612.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Minimum Spanning Trees"></p>
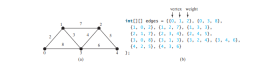
<p>考虑下图中的图表。该算法按以下顺序将顶点添加到 <strong>T</strong>:</p>
<p><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/000/172557408660759.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy" alt="Minimum Spanning Trees"></p>
<ol>
<li>将顶点 <strong>0</strong> 添加到 <strong>T</strong>。</li>
<li>将顶点 <strong>5</strong> 添加到 <strong>T</strong>,因为 <strong>Edge(5, 0, 5)</strong> 在与 T<strong>,如图a所示。从 </strong>0<strong> 到 </strong>5<strong> 的箭头线表示 </strong>0<strong> 是 </strong>5<strong> 的父级。</strong>
</li>将顶点 <li>1<strong> 添加到 </strong>T<strong>,因为 </strong>Edge(1, 0, 6)<strong> 在与 T</strong>,如图b.<strong>
</strong>将顶点 </li>6<li> 添加到 <strong>T</strong>,因为 <strong>Edge(6, 1, 7)</strong> 在与 T<strong>,如图c.</strong>
<strong>将顶点</strong>2</li>添加到<li>T<strong>,因为</strong>边(2,6,5)<strong>在与T</strong>,如图d.<strong>
</strong>将顶点<strong>4</strong>添加到</li>T<li>,因为<strong>边(4,6,7)</strong>在与T<strong>,如图e.</strong>
<strong>将顶点</strong>3<strong>添加到</strong>T</li>,因为<li>边(3,2,8)<strong>在与T</strong>,如图f.<strong>
</strong>
<strong>最小生成树不是唯一的。例如,下图中的 (c) 和 (d) 都是图 a 中的图的最小生成树。但是,如果权重不同,则该图具有唯一的最小生成树。</strong>
<strong></strong>
</li>
</ol>假设图是连通且无向的。如果图没有连通或有向,则该算法将不起作用。您可以修改算法来查找任何无向图的生成林。生成森林是一个图,其中每个连接的组件都是一棵树。<p>
</p><h2>
Refining Prim’s MST Algorithm
</h2>
<p>To make it easy to identify the next vertex to add into the tree, we use <strong>cost[v]</strong> to store the cost of adding a vertex <strong>v</strong> to the spanning tree <strong>T</strong>. Initially <strong>cost[s]</strong> is <strong>0</strong> for a starting vertex and assign infinity to <strong>cost[v]</strong> for all other vertices. The algorithm repeatedly finds a vertex <strong>u</strong> in <strong>V – T</strong> with the smallest <strong>cost[u]</strong> and moves <strong>u</strong> to <strong>T</strong>. The refined version of the alogrithm is given in code below.<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">Input: A connected undirected weighted G = (V, E) with non-negative weights
Output: a minimum spanning tree with the starting vertex s as the root
1 MST getMinimumSpanngingTree(s) {
2 Let T be a set that contains the vertices in the spanning tree;
3 Initially T is empty;
4 Set cost[s] = 0; and cost[v] = infinity for all other vertices in V;
5
6 while (size of T w(u, v)) { // Adjust cost[v]
11 cost[v] = w(u, v); parent[v] = u;
12 }
13 }
14 }
Implementation of the MST Algorithm
The getMinimumSpanningTree(int v) method is defined in the WeightedGraph class. It returns an instance of the MST class, as shown in Figure below.

The MST class is defined as an inner class in the WeightedGraph class, which extends the Tree class, as shown in Figure below.

The Tree class was shown in Figure below. The MST class was implemented in lines 141–153 in WeightedGraph.java.

The refined version of the Prim’s algoruthm greatly simplifies the implementation. The getMinimumSpanningTree method was implemented using the refined version of the Prim’s algorithm in lines 99–138 in Listing 29.2. The getMinimumSpanningTree(int startingVertex) method sets cost[startingVertex] to 0 (line 105) and cost[v] to infinity for all other vertices (lines 102–104). The parent of startingVertex is set to -1 (line 108). T is a list that stores the vertices added into the spanning tree (line 111). We use a list for T rather than a set in order to record the order of the vertices added to T.
Initially, T is empty. To expand T, the method performs the following operations:
- Find the vertex u with the smallest cost[u] (lines 118–123 and add it into T (line 125).
- After adding u in T, update cost[v] and parent[v] for each v adjacent to u in V-T if cost[v] > w(u, v) (lines 129–134).
After a new vertex is added to T, totalWeight is updated (line 126). Once all vertices are added to T, an instance of MST is created (line 137). Note that the method will not work if the graph is not connected. However, you can modify it to obtain a partial MST.
The MST class extends the Tree class (line 141). To create an instance of MST, pass root, parent, T, and totalWeight (lines 144-145). The data fields root, parent, and searchOrder are defined in the Tree class, which is an inner class defined in AbstractGraph.
Note that testing whether a vertex i is in T by invoking T.contains(i) takes O(n) time, since T is a list. Therefore, the overall time complexity for this implemention is O(n3).
The code below gives a test program that displays minimum spanning trees for the graph in Figure below and the graph in Figure below a, respectively.
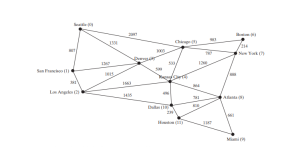
package demo;
public class TestMinimumSpanningTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"};
int[][] edges = {
{0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097},
{1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267},
{2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435},
{3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003},
{4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496},
{5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787},
{6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214},
{7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888},
{8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810},
{9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187},
{10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239},
{11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239}
};
WeightedGraph<string> graph1 = new WeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
WeightedGraph<string>.MST tree1 = graph1.getMinimumSpanningTree();
System.out.println("Total weight is " + tree1.getTotalWeight());
tree1.printTree();
edges = new int[][]{
{0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8},
{1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3},
{2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5},
{3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6},
{4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6}
};
WeightedGraph<integer> graph2 = new WeightedGraph(edges, 5);
WeightedGraph<integer>.MST tree2 = graph2.getMinimumSpanningTree(1);
System.out.println("\nTotal weight is " + tree2.getTotalWeight());
tree2.printTree();
}
}
</integer></integer></string></string>
Total weight is 6513.0
Root is: Seattle
Edges: (Seattle, San Francisco) (San Francisco, Los Angeles)
(Los Angeles, Denver) (Denver, Kansas City) (Kansas City, Chicago)
(New York, Boston) (Chicago, New York) (Dallas, Atlanta)
(Atlanta, Miami) (Kansas City, Dallas) (Dallas, Houston)
Total weight is 14.0
Root is: 1
Edges: (1, 0) (3, 2) (1, 3) (2, 4)
程序为上图第 27 行创建一个加权图。然后调用 getMinimumSpanningTree()(第 28 行)返回一个 MST,它表示图形。在 MST 对象上调用 printTree()(第 30 行)会显示树中的边缘。请注意,MST 是 Tree 的子类。 printTree() 方法定义在 Tree 类中。
最小生成树的图示如下图所示。顶点按以下顺序添加到树中:西雅图、旧金山、洛杉矶、丹佛、堪萨斯城、达拉斯、休斯顿、芝加哥、纽约、波士顿、亚特兰大和迈阿密。
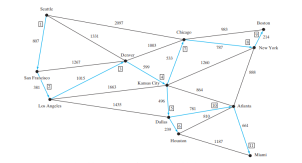
以上是最小生成树的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Java平台是否独立,如果如何?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Java平台是否独立,如果如何?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AMJava是平台独立的,因为其"一次编写,到处运行"的设计理念,依赖于Java虚拟机(JVM)和字节码。1)Java代码编译成字节码,由JVM解释或即时编译在本地运行。2)需要注意库依赖、性能差异和环境配置。3)使用标准库、跨平台测试和版本管理是确保平台独立性的最佳实践。
 关于Java平台独立性的真相:真的那么简单吗?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AM
关于Java平台独立性的真相:真的那么简单吗?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AMJava'splatFormIndenceIsnotsimple; itinvolvesComplexities.1)jvmCompatiblemustbeiblemustbeensurecensuredAcrospPlatForms.2)nativelibrariesandsycallsneedcarefulhandling.3)
 Java平台独立性:Web应用程序的优势May 09, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Java平台独立性:Web应用程序的优势May 09, 2025 am 12:08 AMJava'splatformindependencebenefitswebapplicationsbyallowingcodetorunonanysystemwithaJVM,simplifyingdeploymentandscaling.Itenables:1)easydeploymentacrossdifferentservers,2)seamlessscalingacrosscloudplatforms,and3)consistentdevelopmenttodeploymentproce
 JVM解释:Java虚拟机的综合指南May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JVM解释:Java虚拟机的综合指南May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMthejvmistheruntimeenvorment forexecutingjavabytecode,Cocucialforjava的“ WriteOnce,RunanyWhere”能力
 Java的主要功能:为什么它仍然是顶级编程语言May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Java的主要功能:为什么它仍然是顶级编程语言May 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMJavaremainsatopchoicefordevelopersduetoitsplatFormentence,对象与方向设计,强度,自动化的MememoryManagement和ComprechensivestAndArdArdArdLibrary
 Java平台独立性:这对开发人员意味着什么?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java平台独立性:这对开发人员意味着什么?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AMJava'splatFormIndependecemeansDeveloperScanWriteCeandeCeandOnanyDeviceWithouTrecompOlding.thisAcachivedThroughThroughTheroughThejavavirtualmachine(JVM),WhaterslatesbyTecodeDecodeOdeIntComenthendions,允许univerniverSaliversalComplatibilityAcrossplatss.allospplats.s.howevss.howev
 如何为第一次使用设置JVM?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AM
如何为第一次使用设置JVM?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AM要设置JVM,需按以下步骤进行:1)下载并安装JDK,2)设置环境变量,3)验证安装,4)设置IDE,5)测试运行程序。设置JVM不仅仅是让其工作,还包括优化内存分配、垃圾收集、性能调优和错误处理,以确保最佳运行效果。
 如何查看产品的Java平台独立性?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
如何查看产品的Java平台独立性?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AMtoensurejavaplatFormIntence,lofterTheSeSteps:1)compileAndRunyOpplicationOnmultPlatFormSusiseDifferenToSandjvmversions.2)upureizeci/cdppipipelinelikeinkinslikejenkinsorgithikejenkinsorgithikejenkinsorgithikejenkinsorgithike forautomatecross-plateftestesteftestesting.3)


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

mPDF
mPDF是一个PHP库,可以从UTF-8编码的HTML生成PDF文件。原作者Ian Back编写mPDF以从他的网站上“即时”输出PDF文件,并处理不同的语言。与原始脚本如HTML2FPDF相比,它的速度较慢,并且在使用Unicode字体时生成的文件较大,但支持CSS样式等,并进行了大量增强。支持几乎所有语言,包括RTL(阿拉伯语和希伯来语)和CJK(中日韩)。支持嵌套的块级元素(如P、DIV),

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

WebStorm Mac版
好用的JavaScript开发工具





