HTML 事件属性
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB原创
- 2024-09-04 16:17:27743浏览
在本文中,我们将详细讨论 HTML 事件属性。事件是由于用户操作而执行的操作。例如,当用户按下键盘读取数据时,就称为键盘事件。当用户查看网站并单击按钮或按下刷新按钮加载页面(其中浏览器对页面进行操作)时,就会完成这些活动;所有这些动作都被称为一个事件。在这里,我们将基本了解事件以及它如何在浏览器中处理用户操作。整个浏览器窗口中会发生不同类型的事件,以下部分将对此进行说明。
前 5 个 HTML 事件属性
HTML 中提供了不同的事件变体。所有这些事件都有一个名为事件处理程序的小代码块,该代码块在执行事件操作时触发。它们附加到 HTML 元素。事件处理程序或事件侦听器在 HTML 事件属性中发挥着重要作用。让我们看看全局声明并应用于 HTML 元素的不同类型的事件属性以及它们的详细工作。主要使用四个主要事件属性。他们是:
- 窗口事件
- 表单事件
- 鼠标事件
- 键盘事件
- 拖放事件
我们将通过示例一一描述所有这些属性。首先,我们一起去。
1.窗口事件
- onafterprintEvent: 所有 Html 标签都支持此属性,并且在页面开始打印并且具有单值脚本时起作用。这是 HTML 代码的示例。此示例显示了按下按钮时的情况;它打印一条在对话框消息中打印的消息。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Windows onafterprint Event
</title>
</head>
<body onafterprint="myfun()">
<h1>Windows onafterprint Event </h1>
<p>This attribute works in IE and Mozilla</p>
<body style = "text-align:center">
<script>
function myfun() {
alert("Document is being printed");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:

- onbeforeprint:它在打印之前起作用。该事件在打印过程后被触发。以下是示例代码。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: #9370DB;
background-color: #BC8F8F;
text-align: center;
padding: 20px;
}
p {
font-size: 2rem;
}
</style>
</head>
<body onbeforeprint="get()">
<h1> Attribute Demo</h1>
<p style="color:#0000FF;">trigger to print.</p>
<div class="show"></div>
<script>
function get() {
document.body.style.background = "#00BFFF";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:

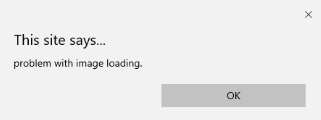
- onerror: 当没有元素存在时抛出错误时会触发此函数。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<img src="p.jpg" onerror="myFun()">
<p>hello world.</p>
<script>
function myFun() {
alert("problem with image loading.");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
- onload:此函数有助于加载对象,并且可以很好地查看网页是否正确加载。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>onload event demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="pic.jpg" onload="ldImg()" width="50" height="92">
<script>
function ldImg() {
alert("image loaded without error");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
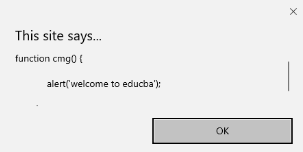
- onresize:当浏览器窗口大小调整时触发该事件,任何元素在resize属性下都可以触发。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<title>onresize event</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function cmg() {
alert('welcome to educba');
}
window.onresize = cmg;
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="Click the button"
onclick="alert(window.onresize);">
</body>
</html>
输出:

- onunload:当网页窗口关闭或用户离开网页时触发此事件。下面的代码会在用户离开时卸载页面,并发出感谢搜索的警报。此事件有时适用于所有浏览器。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body onunload="onfunc()"><h1>Welcometo educba tutorial</h1>
<p>Leave the page .</p>
<script>
function onfunc() {
alert("Thank you for searching!");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
2.表单事件
它与表单控件一起使用。以下是用户与浏览器交互时发生的属性。
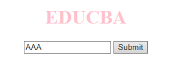
- onblur:当用户的注意力离开表单窗口时发生此事件。以下示例采用小写形式输入,单击提交按钮时,会将输出转换为大写形式。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> Form onblur </title>
<style>
body {
text-align:center;
}
h1 {
color:pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EDUCBA</h1>
<input type="text" name="fname" id="aaa"
onblur="myfunc()">
<button type="button">Submit</button>
<script>
function myfunc() {
var a = document.getElementById("aaa");
a.value = a.value.toUpperCase();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:


- onchange: 当用户更改表单中的现有元素时,会发生此事件。当元素失去焦点时就会发生这种情况。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>HTML onchange</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="example" action=""> <input type="text" name="rahul" onchange="alert('input is changed')"><br>
<label>select the dress color</label>
<select onchange="alert('You have changed the selection!');">
<option>pink</option>
<option>Yellow</option>
<option>White</option>
</select>
<p><strong>Note:</strong> Select any option </p>
<label>Describe yourself in short : </label> <br/><textarea cols="15" rows="7" name="details" onchange="alert('description has changed')"> </textarea><br>
<button type="button" name="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
输出:
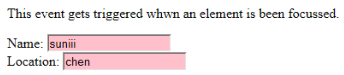
- onfocus: 当用户关注网页上的元素或输入获得焦点时,会启用此属性。下面的示例突出显示了我们在字段中输入的内容。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>This event gets triggered whwn an element is been focussed.</p>
Name: <input type="text" id="name" onfocus="onfoc(this.id)"><br>
Location: <input type="text" id="loc" onfocus="onfoc(this.id)">
<script>
function onfoc(a) {
document.getElementById(a).style.background = "pink";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
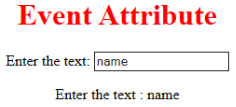
- oninput: This event triggers when the input is entered in the input field. It has been activated when the value in the text field is changed. It reflects once the value of the element is changed.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> HTML oninput </title>
</head>
<style>
body {
text-align:center;
}
h1 {
color:red;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1> Event Attribute </h1>
Enter the text:
<input type="text" id="EDUCBA" oninput="myon()">
<p id= "sid"></p>
<script>
function myon()
{
var x = document.getElementById("EDUCBA").value;
document.getElementById("sid").innerHTML = "Enter the text : " +x;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
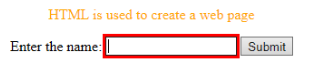

- oninvalid: This attribute calls the events when the text entered in the input type is invalid or remains empty. This event attribute must fill the input element.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> example oninvalid Event </title>
<style>
p {
color:orange;
}
body {
text-align:center;
}
</style> </head>
<body>
<p> HTML is used to create a web page</p>
<form method="get">
Enter the name:
<input type="text" oninvalid="alert('Fill the text form!');" required>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form> </body>
</html>
Output:

- onreset: It is fired when a form is a rest. The following example says when you submit the button, a form is processed, and again when you click to reset, the form is being reset.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
body {font-family:calibri;}
label {font-variant:small-caps;}
ol {background-color:#610000; margin-top:35px;}
li {margin-top:3px; padding:3px; background-color:rose; font-size:15px;}
div {position:absolute;top:250px;left:70px; font-size:1.5em;
}
</style>
<body>
<ol>
<li>Form with input to reset and submit</li>
</ol>
<form action="" method="get" onreset="onRes()" onsubmit="onSub()">
<label>Enter input:<br /><input type="text" id="iv" oninvalid="onInva()" oninput="onInp()"></label><br /><br />
<input type="submit" value="press"> <input type="reset">
</form>
<div id="a_box"></div>
<script>
function onInva() {
alert("Input field cannot be empty!");
}
function onInp() {
var input_value = document.getElementById("iv").value;
document.getElementById("a_box").innerHTML = "Input value: <br />" + iv;
}
function onRes() {
alert("form is reset!");
}
function onSubmitEvent() {
alert("Form is loading");
location.reload();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

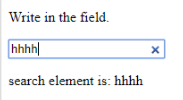
- onsearch: It works when a user presses an enter button.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Write in the field.</p>
<input type="search" id="value1" onsearch="myF()">
<p id="sample"></p>
<script>
function myF() {
var k = document.getElementById("value1");
document.getElementById("sample").innerHTML = "search element is: " + k.value;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
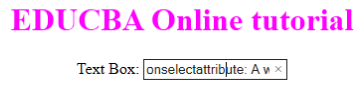
- onselect: It is triggered when a text has been selected in an input box. It throws a dialog box printing an alert message.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>onselect demo</title>
<style>
h1 {
color:magenta;
}
body {
text-align:center;
}
</style>
<script>
function eduhtml() {
alert("text highlighted!");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EDUCBA Online tutorial</h1>
Text Box: <input type="text" value="onselectattribute: A well defined portal" onselect="eduhtml()">
</body>
</html>
</html>
Output:
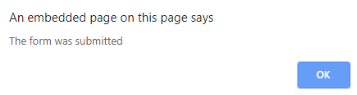
- onsubmit: The purpose of this event is to execute the action performed while pressing the submit button.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<head>
<title> Onsubmit Example</title>
</head>
<form action="demo_form.asp" onsubmit="myF()">
Enter name: <input type="text" name="fname">
<label>Email :</label>
<input id="email" name="email" type="text">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<script>
function myF() {
alert("The form was submitted");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
3. Key Board Attributes
- OnKeyDown: It is triggered when a user presses a down Arrow key.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Example for Onkeydown.</p>
<input type="text" onkeydown="mykedwn()">
<script>
function mykedwn() {
alert("key press is activated");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

- OnKeyPress: This event gets triggered when the user presses any key on the keyboard. Note: some browser doesn’t support pressing any key.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p> This example shows when a user type in the text area it triggers an event </p>
<form>
<textarea onkeypress="alert('triggering onkeypress event.')" placeholder="Place the cursor inside the textarea and press a key." " cols="30" rows="4" style="background-color:pink;">> </textarea> </form>
</body>
</html>
Output:

- OnKeyUp: This attribute gets triggered when a user releases a cursor from the text field. Below comes the demonstration.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p> This example transforms the character to lower case.</p>
Fill the name: <input type="text" id="jjj" onkeyup="mykey()">
<script>
function mykey() {
var g = document.getElementById("jjj");
g.value = g.value.toLowerCase();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

4. Mouse Event Attributes
This action triggers a mouse event when a mouse is pressed either from a computer or any external devices like a smartphone or tablet. Some of the mouse events are given below:
- onclick: It is triggered when a user presses the button over the mouse. An input example is given below to show the event while clicking the mouse.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>HTML onclick Event</h1>
<p> Event plays a vital role in HTML.</p>
<button onclick="oncf()">Click </button>
<p id="sample"></p>
<script>
function oncf() {
document.getElementById("sample").innerHTML = "Hello World";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

- onmousemove: It is fired when a mouse is moved over an image in any direction.
Code:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head><title> Event onmousemove demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This event is activated when the pointer drags its direction.</p>
<body style="width:200px;height:80px;border:2px solid;" onmousemove="javascript:alert('mouse action');">Sample text</body>
</body>
</html>
Output:

- Onmouseup: This event gives a notification when a user releases a button on an output.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
color: "#ff0000";
height: 120vh;
background-color: #610000;
text-align: center;
}
.polygon {
float: right;
shape-inside: polygon(0 0, 0 200px, 100px 200px);
clip-path: polygon(0 0, 0 250px, 100px 300px);
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background: linear-gradient(to bottom left, #7CFC00, #8B008B);
}
p {
margin: 30px auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML onmouseup Demo</h1>
<div class="polygon" onmouseup="mupfn()"></div>
<p> click below object</p>
<script>
function mupFn() {
document.querySelector('.polygon').style.transform = 'scale(2.2)';
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

- Onmouseover: Execute a JavaScript when moving the mouse pointer over an image
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<title>Example demonstrating Onmouseover.</title>
<h1 id="sample" onmouseover="A()" onmouseout="B()">Mouse over </h1>
<script>
function A() {
document.getElementById("sample").style.color = "yellow";}
function B() {
document.getElementById("sample").style.color = "green";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
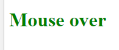
5. Drag Event Attributes
This application helps in the HTML window when the user drags the input element. Below are the different event listeners used in HTML to store dragged data.
- Ondrag: This is used when an element is being dragged from the web page.
- Ondragstart: This fires when the user begins to drag from the input field. The below example demonstrates about dragging the two-target area.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style type = "text/css">
#b1, #b2 {
float:left;padding:11px;margin:11px; -moz-user-select:none;
}
#b1 { background-color: #FF6699; width:65px; height:85px; }
#b2 { background-color: #808000; width:180px; height:180px; }
</style>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function dStart(e) {
e.dataTransfer.effectAllowed = 'move';
e.dataTransfer.setData("Text", e.target.getAttribute('id'));
e.dataTransfer.setDragImage(e.target,0,0);
return true;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h2>Drag demo</h2>
<div> Drag the box.</div>
<div id = "b1" draggable = "true"
ondragstart = "return dStart(e)">
<p>Drag it</p>
</div>
<div id = "b2">welcome</div>
</center>
</body>
</html>
Output:
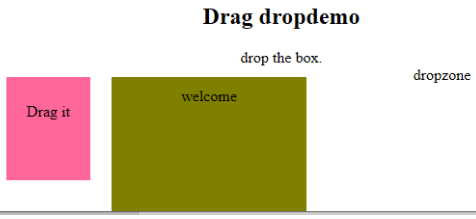
-
ondrop: Execute this attribute when a draggable element is dropped in element.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <style type = "text/css"> #b1, #b2 { float:left;padding:11px;margin:11px; -moz-user-select:none; } #b1 { background-color: #FF6699; width:65px; height:85px; } #b2 { background-color: #808000; width:180px; height:180px; } </style> <script type = "text/javascript"> function dStart(e) { e.dataTransfer.effectAllowed = 'move'; e.dataTransfer.setData("Text", e.target.getAttribute('id')); e.dataTransfer.setDragImage(e.target,0,0); return true; } </script> </head> <body> <center> <h2>Drag dropdemo</h2> <div> drop the box.</div> <div id = "b1" draggable = "true" ondragstart = "return dStart(e)"> <p>Drag it</p> </div> <div class="droptarget" ondrop="drop(event)" ondragover="allowDrop(event)"> </div> <div id = "b2">welcome</div> <span> dropzone </span> </center> </body> </html>Output:

Conclusion
This event attribute helps to make a web application very easier and attractive. The different occurrence of actions generates various events. Even though this approach is generally avoided, the programmer likes to learn the function assigned for the HTML attributes events. These event handlers are still executed to beautify the web pages.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to the HTML Event Attributes. Here we discuss the Introduction to HTML Event Attributes along with Code implementation and Output. you can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –
- HTML Frames
- HTML Style Attribute
- Applications of HTML
- HTML vs HTML5
以上是HTML 事件属性的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
JavaScript html5 html Object if for while Error Attribute Event pointer function this alert input windows声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系admin@php.cn