Java.net URI
- PHPz原创
- 2024-08-30 16:04:58463浏览
Java.net 包提供了一个类 URI,其中包含从其组件创建 URI 实例的方法或解析这些组件的字符串形式以访问和检索 URI 实例的多个组件的方法。
广告 该类别中的热门课程 JAVA 掌握 - 专业化 | 78 课程系列 | 15 次模拟测试开始您的免费软件开发课程
网络开发、编程语言、软件测试及其他
什么是 URI?
统一资源标识符具有有助于特定资源识别的字符序列。此外,它还有助于在某些协议的帮助下通过网络进行资源表示的交互。有关此特定类的更多详细信息将在以下部分中讨论。
语法
下面是 java.net URI 类的语法。
scheme:[//[user:password@]host[:port]][/]path[?query][#fragment]
- 方案:此组件列出了与 URI 链接的特定协议。尽管某些方案需要“//”,但在其他方案中则不使用。
- 权限:该组件由不同的组件组成,例如身份验证部分、主机和前面带有冒号“:”的端口号。在第一部分中,身份验证部分由用户名和密码组成。同时,第二段Host可以是任意的ip地址。第三部分端口号是可选的。
- 路径:具有字符串的组件,该字符串由服务器中存在的特定资源的地址组成。
- 查询:该组件是非分层数据,其中查询用于通过前一部分中的“?”问号查找特定资源。
- 片段:标识辅助资源的组件。它可以是页面上出现的标题和副标题等。
Java.net URI 类如何工作?
正如已经讨论过的,URI 被称为统一资源定位器,它可以通过使用位置和名称来帮助识别 Web 资源,例如图像、级联样式表文件、视频等。这里,位置是访问或检索特定资源的机制。例如,HTTP://、FTP:// 等都是位置。除此之外,“名称”是特定资源的全局特定名称。让我们看一个示例,其中以下网址:https://samplepath/path/to/video.mkv 检索视频。在这里,这个特定地址的sample-path/path/to/video.mkv部分是URN或名称。
构造函数
以下是 URI 的五种不同的构造函数。
- URI(String st): 通过解析字符串 st 构造一个 URI。
- URI( String schema , String str, String frag): 将根据给定的组件构造 URI。
- URI( String schm, String userinf, String host, int portnum, String path, String query, String frag): 将根据给定的组件构建分层 URI。
- URI( String schm, String host, String path, String frag): 将根据给定的组件构建分层 URI。
- URI(String schm、String suthorty、String path、String query、String frag):将根据给定的组件构造分层 URI。
Java.net URI 的方法
下面是执行多种操作的 URI 类的不同方法。
- compareTo(URI ur): This URI will be compared with another URI.
- create(String str): A URI will be created on parsing the string str
- equals(Object obj): The URI will be tested for equality with the object obj
- getAuthority(): Returns the URI’s authority component, which is decoded.
- getFragment(): Returns the URI’s fragment component, which is decoded.
- getHost(): Returns the URI’s host component, which is decoded.
- getPath(): Returns the URI’s path component, which is decoded.
- getPort(): URI port number will be returned.
- getQuery(): Returns the URI’s query component, which is decoded.
- getRawAuthority(): Returns the URI’s raw authority component.
- getRawFragment(): Returns the URI’s raw fragment component.
- getRawPath(): Returns the URI’s raw path component.
- getRawQuery(): Returns the URI’s raw query component.
- getRawSchemeSpecificPart(): Returns the URI’s raw scheme-specific part.
- getRawUserInfo(): Returns the URI’s raw user information component.
- getScheme(): Returns the URI’s scheme component.
- getSchemeSpecificPart(): Returns the URI’s scheme-specific part which is decoded.
- getUserInfo(): Returns the URI’s user information component which is decoded.
- hashCode(): Returns URI hash code value.
- isAbsolute(): Checks whether the URI provided is absolute or not.
- isOpaque(): Checks whether the URI provided is opaque or not.
- normalize(): URI path gets normalized on calling this method.
- parseServerAuthority(): This method parses the authority component into user information, port, and host components.
- relativize(URI uri): Given URI gets relativized to the URI specified.
- resolve(String str): A new URI is constructed by parsing the string mentioned and resolving the same against the URI.
- resolve(URI uri): The given URI is resolved against the URI.
- toASCIIString(): Content of the URI mentioned is returned as a US-ASCII string.
- toString(): Content of the URI mentioned is returned as a string.
- toURL(): A URL gets constructed from the URI mentioned.
Examples to Implement Java.net URI
Now, let us see a sample program of java.net uri class.
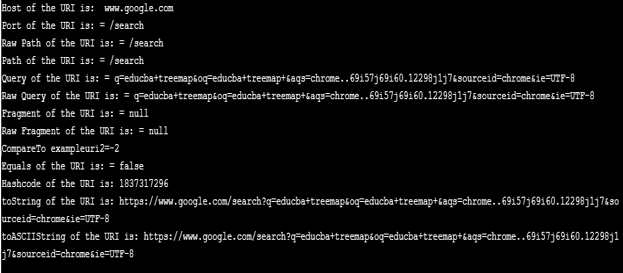
Java program to demonstrate several methods in the class java.net.uri. //Java Program to demonstrate methods of URI class
Code:
import java.net.*;
class URIexample
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String str = "https://www.google.com/search?q=educba+treemap&oq=educba+treemap+&aqs=chrome..69i57j69i60.12298j1j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8";
// Creation of new URI by parsing the string
URI exampleuri = new URI(str);
//different methods of <u>uri</u> class
System.out.println("Host of the URI is: " + exampleuri.getHost());
System.out.println("Port of the URI is: = " + exampleuri.getPath());
System.out.println("Raw Path of the URI is: = " + exampleuri.getRawPath());
System.out.println("Path of the URI is: = " + exampleuri.getPath());
System.out.println("Query of the URI is: = " + exampleuri.getQuery());
System.out.println("Raw Query of the URI is: = " + exampleuri.getRawQuery());
System.out.println("Fragment of the URI is: = " + exampleuri.getFragment());
System.out.println("Raw Fragment of the URI is: = " + exampleuri.getRawFragment());
//another uri in order to demonstrate the method compareTo and equals
URI exampleuri2 = new URI(str + "fr");
System.out.println("CompareTo exampleuri2=" + exampleuri.compareTo(exampleuri2));
System.out.println("Equals of the URI is: = " + exampleuri.equals(exampleuri2));
System.out.println("Hashcode of the URI is: " + exampleuri.hashCode());
System.out.println("toString of the URI is: " + exampleuri.toString());
System.out.println("toASCIIString of the URI is: " + exampleuri.toASCIIString());
}
}
Output: In this program, different methods of java.net.uri class are used and displayed results based on that.
以上是Java.net URI的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

