Java 中的文本文件
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB原创
- 2024-08-30 15:54:181314浏览
程序员在使用需要读写文件的 Java 应用程序时使用 Java 中的文本文件。 文本文件是存储信息、代码或任何其他数据的通用方式。文本文件被视为水平组织的字符序列。 Java 中的文本文件具有扩展名,例如包含 Java 代码的 .java。 Java 提供了不同的实用程序,允许您通过读取或写入纯文本文件来处理它们。您可以根据您的理解选择任何读/写实用程序。

主要亮点
- 文本文件由不同的字符组成,可以使用java.io.package进行读写操作。
- 要阅读,您可以使用 Reader 类或实用程序类。一些实用程序类是 - File Class、FileReader、BufferedReader 和 Scanner 类。
- 要在 Java 中写入文件,您可以使用 Java 7 Files、FileWriter、BufferedWriter 和 FileOutputStream。
- 使用不同的方法,您可以有效地处理 Java 中的文本文件。
如何用Java读取文本文件?
- 在文本文件中,每一行都有纯字符,并且每行都由一个不可见的“行尾”符号标记,代表该特定行的结尾。
- 为了用 Java 读取文本文件,可以使用不同的实用程序。每个实用程序都有自己的读取文本文件的方式,并提供一些与其他替代方案不同的功能。
- 这里我们将通过一个很好的例子来解释不同的方法,以便更好地理解。
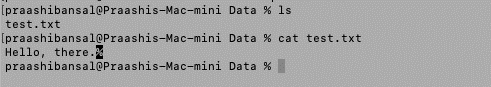
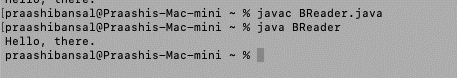
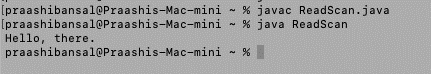
在开始使用这些方法之前,我们正在考虑路径“/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt”处的文本文件“test.txt”,其内容为“Hello,there”。
广告 该类别中的热门课程 JAVA 掌握 - 专业化 | 78 课程系列 | 15 次模拟测试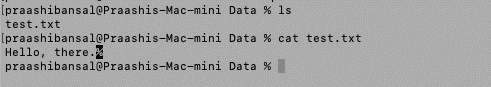
方法 1 – 使用 BufferedReader 类
- 您可以使用此方法从字符输入流中读取文本。您可以使用默认缓冲区大小 (8KB) 或指定您自己的缓冲区大小。它支持编码。
- 每个请求都有一个 Reader,它创建由底层字符流或字节流组成的读取请求。
- 因此,许多开发人员建议使用其 read() 操作将 BufferedReader 包装在任何 Reader 周围。
- 它非常适合处理大文件。该方法是同步的,因此可以在多个线程中使用。
代码:
import java.io.*;
public class BReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
File f = new File(
"https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
// Creating an object
BufferedReader b
= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
// Declaring a string variable
String s;
// Condition holds till
// there is a character in a string
while ((s = b.readLine()) != null)
// Print the string
System.out.println(s);
}
}
输出:
方法 2 – 使用 FileReader 类
- 您可以使用 FileReader 获取 BufferedReader 并开始读取文件。
- 与 BufferedReader 不同,它不支持编码,而是使用系统默认的编码。
- 这只是一种简单的读字方式。
- 该类使用三个构造函数。
- FileReader(File file):创建一个新的 FileReader。该文件是您将从中读取内容的文件。
- FileReader(FileDescriptor fd):创建一个新的 FileReader,从指定为 FileDescriptor 的文件中读取。
- FileReader(String fileName):创建一个新的 FileReader,将从名为 fileName 的文件中读取内容。
代码:
import java.io.*;
public class RFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Passing the file’s path
FileReader f = new FileReader(
"https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
// declaring loop variable
int i;
while ((i = f.read()) != -1)
// Print the content of a file
System.out.print((char)i);
}
}
输出:
方法 3 – 使用 Scanner 类
- 它是一个简单的文本扫描器,它能够通过正则表达式解析原始类型和字符串。
- 它通过分隔符模式将输入分解为标记。默认情况下,分隔符是空格。
- 然后令牌转换成不同类型的值。
代码:
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadScan
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// passing the file’s path
File file = new File("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
Scanner s = new Scanner(file);
while (s.hasNextLine())
System.out.println(s.nextLine());
}
}
输出:
方法 4 – 使用 Files 类方法
- Files 类使用以下方法来读取文件。
- readAllBytes(Path path):从文件中读取所有字节,并返回包含文件中字节的字节数组。
- readAllLines(Path path, Charsetcs):从文件中读取所有行并返回包含文件中的行的列表。
代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
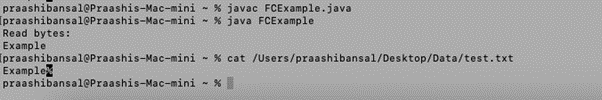
public class FCExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path path = Paths.get("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
try {
byte[] b = Files.readAllBytes(path);
System.out.println("Read bytes: \n"+new String(b));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
输出:
How to Write a Text File in Java?
- Writing a text file in Java is also a simple process. Java offers different utilities to help write the lines to the file.
- Now for this process, we are assuming a file at the location- C:\\Users\\Data\\Desktop\\write.txt to which we are writing.
Method 1 – Using FileWriter Method
- This all-in-one method allows you to write int, byte array, and String to the File.
- It allows you to write directly into Files and is used in case of the less writes.
- Using the FileWriter method, you can write part of the String or byte array.
Code:
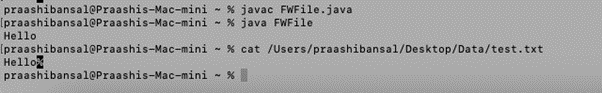
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class FWFile {
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
FileWriter f=new FileWriter("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
f.write("Hello");
f.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
Output:
Method 2 – Using BufferedWriter Method
- BufferedWriter is similar to FileWriter, but BufferedWriter uses an internal buffer to write data into File.
- It works well if you need to do more write operations and to ensure performance.
Code:
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BRExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String data = "data for output file";
try {
// Creates a FileWriter
FileWriter file = new FileWriter("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
try ( // Creates a BufferedWriter
var o = new BufferedWriter(file)) {
// Writes the string to the file
o.write(data);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output:

Method 3 – Using FileOutputStream Method
- For writing text to the file, you can simply use FileWriter and BufferedWriter.
- But, if you want the raw stream data to be written directly into a file, it is recommended to use the FileOutputStream utility.
- With this method, you must create the class object with the specific filename to write data into a file.
- The following example converts the string content into the byte array we will write into the file using the write() method.
Code:
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
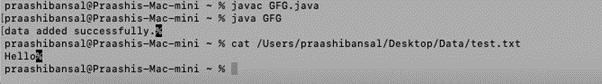
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String f = "Hello";
FileOutputStream o = null;
// starting Try block
try {
// creating an object of FileOutputStream
o = new FileOutputStream("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
// storing byte content from string
byte[] str = f.getBytes();
// writing into the file
o.write(str);
// printing success message
System.out.print(
"data added successfully.");
}
// Catch block for exception handling
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
finally {
// closing the object
if (o != null) {
// checking if the file is closed
try {
o.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
// showing exception message
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
Method 4 – Using Files Class
- In Java 7, you will get another utility, Files class, allowing you to write to a text file using its write function.
- Internally, this class uses the OutputStream utility to write a byte array into the file.
Code:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
/**
* Java Files write file example
*
* @author pankaj
*
*/
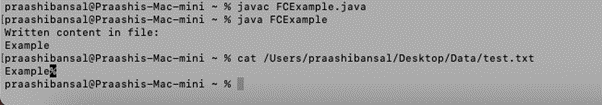
public class FCExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path path = Paths.get("https://cdn.educba.com/Users/praashibansal/Desktop/Data/test.txt");
try {
String str = "Example";
byte[] bs = str.getBytes();
Path w = Files.write(path, bs);
System.out.println("Written content in file:\n"+ new String(Files.readAllBytes(w)));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
Reading and writing a file in Java is a straightforward process. With the availability of different methods and utilities in Java, you can choose a specific way to read from and write to a file. Each utility has its functionality that makes it different from others.
FAQs
Q1. What are the different methods to read a text file in Java?
Answer: To read, you can use Reader Class or utility class. Some utility classes are- File Class, FileReader, BufferedReader, and Scanner class.
Q2. What are the different methods for writing a text file in Java?
Answer: To write a file in Java, you can use FileWriter, BufferedWriter, java 7 Files, FileOutputStream, and many other methods.
Q3. What package to use for handling files in Java?
Answer: You can easily import the File class from the java.io package to work with files.
以上是Java 中的文本文件的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

