使用 Spring Security 保护微服务:实施 JWT
- PHPz原创
- 2024-08-24 06:42:38667浏览
JSON 网络令牌 (JWT)
JWT(JSON Web Token)是一种以 JSON 对象的形式在两方(例如客户端和服务器)之间安全传输信息的方法。它的设计紧凑且 URL 安全,可以轻松地在 URL、标头中传递。
- 标题
- 有效负载
- 签名
标题
标头通常由两部分组成:令牌的类型 (JWT) 和所使用的签名算法,例如 HMAC SHA256 或 RSA。
{
"alg":"HS256",
"typ":"JWT"
}
有效负载
这是实际数据存储的地方。它可以包含用户 ID、角色、过期时间和其他声明(有关用户或会话的数据)等信息。
{
"电子邮件":"ayushstwt@gmail.com",
"name":"阿尤什"
}
签名
确保令牌的完整性。这是一项安全功能,可确保令牌不被更改。它是通过使用指定算法将编码的标头和有效负载与密钥组合起来创建的。签名帮助服务器验证令牌是否合法且未被篡改。
智威汤逊的优势
无需重复发送凭据:使用 JWT,您不必在每次请求时都发送用户名和密码。相反,您登录一次,服务器就会给您一个令牌。然后,您可以在每个请求中发送此令牌来证明您的身份,从而使该过程更加安全和高效。
内置过期时间:每个 JWT 都有一个过期时间,这意味着它仅在特定期限内有效。如果令牌以某种方式被拦截,这可以降低长期滥用的风险。过期后,用户需要重新登录才能获取新的令牌,增加了额外的安全层。
JWT 与 Spring Boot 通过在登录后颁发令牌来安全地管理用户身份验证。这些令牌随每个请求一起发送,确保安全、无状态的通信,而无需重复发送凭据。
无状态通信意味着服务器不记得过去的请求。每个请求都携带所需的一切(如 JWT),因此服务器不会存储会话信息。
在 Java Spring Boot 应用程序中实现 JWT 涉及几个步骤。以下是帮助您入门的简化大纲:
1。添加依赖项
在 pom.xml 文件中包含必要的依赖项
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.12.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-impl</artifactId>
<version>0.12.5</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-jackson</artifactId>
<version>0.12.5</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
我们使用 JWT 创建 spring-boot 应用程序所需的所有依赖项
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.3.3</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.tier3Hub</groupId>
<artifactId>user-auth-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>user-auth-service</name>
<description>The user-auth-service is a microservice responsible for handling user authentication and authorization within a distributed system. It is designed to manage user login, registration, and secure access to various services using robust security practices. This service implements authentication mechanisms like JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and integrates with OAuth 2.0 for third-party authentication. Built with Spring Boot, it ensures scalability, reliability, and easy integration with other microservices in the system.</description>
<url/>
<licenses>
<license/>
</licenses>
<developers>
<developer/>
</developers>
<scm>
<connection/>
<developerConnection/>
<tag/>
<url/>
</scm>
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.12.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-impl</artifactId>
<version>0.12.5</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-jackson</artifactId>
<version>0.12.5</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.modelmapper</groupId>
<artifactId>modelmapper</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
我们正在使用不同类型的依赖项,例如
- Spring Boot Starter Actuator:3.3.3 - 添加生产就绪功能,例如监控和运行状况检查。
- Spring Boot Starter Data JPA:3.3.3 - 通过 JPA 支持简化数据库交互。
- Spring Boot Starter Security:3.3.3 - 提供身份验证和授权等安全功能。
- Spring Boot Starter Web:3.3.3 - 支持构建 Web 应用程序,包括 RESTful 服务。
- JJWT API:0.12.5 - 处理 JWT 创建和解析以实现安全令牌管理。
- JJWT Impl:0.12.5 - 实现核心 JWT 功能。
- JJWT Jackson:0.12.5 - 使用 Jackson 启用 JWT JSON 解析。
- MySQL 连接器:运行时 - 将您的应用程序连接到 MySQL 数据库。
- Lombok:未指定 - 通过注释减少样板代码。
- Spring Boot Starter Test:3.3.3 - 为 Spring Boot 应用程序提供测试支持。
- Spring 安全测试:3.3.3 - 帮助测试安全配置。
- Spring Boot Starter 验证:3.3.3 - 添加对请求和响应对象的验证支持。
- SpringDoc OpenAPI Starter WebMVC UI:2.5.0 - 集成 Swagger UI 以获取 API 文档。
- ModelMapper:3.1.1 - 简化不同层之间的对象映射。
*2。项目结构*
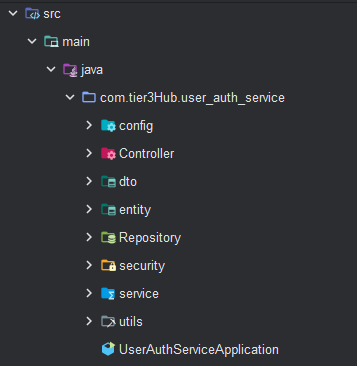
3。在application.properties文件中添加配置
spring.application.name=user-auth-service server.port=8000 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/auth_services spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=ayush@123 spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update spring.jpa.show-sql=true #debug logs logging.level.org.springframework.security=debug spring.main.allow-circular-references=true
4。创建 USER 实体
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
@Builder
@Table
@Entity(name = "User")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String email;
private String phoneNumber;
private List<String> roles;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
private LocalDateTime updatedAt;
}
** 5. 创建服务和存储库类和接口**
Repository.java
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.Repository;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface AuthRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findByUsername(String username);
}
service.java
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.service;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto.LoginResponse;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto.RegisterDTO;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto.RegisterResponse;
public interface AuthService {
RegisterResponse register(RegisterDTO registerDTO);
}
6。创建用于登录、登录请求和响应的 DTO
CreateloginDTO.java
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Size;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class LoginDTO {
@NotBlank(message = "Username is required")
@Size(min = 3, max = 20, message = "Username must be between 3 and 20 characters")
private String username;
@NotBlank(message = "Password is required")
private String password;
}
loginResponse.java
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class LoginResponse {
private String accessToken;
private String tokenType = "Bearer";
}
注册DTO.java
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Email;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Size;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class RegisterDTO {
@NotBlank(message = "Username is required")
@Size(min = 3, max = 20, message = "Username must be between 3 and 20 characters")
private String username;
@NotBlank(message = "Password is required")
@Size(min = 8, message = "Password must be at least 8 characters")
private String password;
@NotBlank(message = "Email is required")
@Email(message = "Email should be valid")
private String email;
}
RegisterResponse.java
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class RegisterResponse {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String email;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
private LocalDateTime updatedAt;
}
*7。为了从 API 发送自定义响应,我们使用 ResponseHandler.java *
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.utils;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ResponseHandler {
public static ResponseEntity<Object> generateResponse(String message, HttpStatus status, Object responseObj) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("message", message);
map.put("status", status.value());
map.put("data", responseObj);
return new ResponseEntity<Object>(map, status);
}
}
8. for storing some constants we create the class inside the utils package that is ApplicationConstants.java
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.utils;
public class AppConstants {
public static final String[] PUBLIC_URLS = { "/v3/api-docs/**", "/swagger-ui/**", "/api/auth/register/**", "/api/auth/login/**","/api/auth/registerAdmin/**" };
}
9. for converting the object one to another we use the dependency that is model mapper for configuration that we create the class inside the config package that is ApplicationConfigs.java
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.config;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ApplicationConfigs {
@Bean
public ModelMapper modelMapper()
{
return new ModelMapper();
}
}
**
This is the basic setup that we do for every spring-boot application we create now securing the rest endpoint with JWT we started.
**
now inside the security package we create the class called JWTFilter.java
The JWTFilter is a custom Spring Security filter that intercepts HTTP requests to validate JWTs. It checks for the "Authorization" header, extracts the token, and retrieves the username. If the token is valid, it creates an authentication token with user details and sets it in the security context, allowing the application to recognize the authenticated user for further processing.
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.security;
import jakarta.servlet.FilterChain;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetailsSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
@Service
public class JWTFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private JWTUtil jwtUtil;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException {
String authorizationHeader = request.getHeader("Authorization");
String username = null;
String jwt = null;
if (authorizationHeader != null && authorizationHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
jwt = authorizationHeader.substring(7);
username = jwtUtil.extractUsername(jwt);
}
if (username != null) {
UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
if (jwtUtil.validateToken(jwt)) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken auth = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails, null, userDetails.getAuthorities());
auth.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(auth);
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
create the class JWTUtil.java
The JWTUtil class manages JWT operations, including extracting usernames and expiration dates from tokens. It generates new tokens using a secret key and validates existing tokens by checking their expiration. The class uses HMAC for signing and includes methods to parse claims and determine if tokens are expired, ensuring secure authentication and authorization in the application.
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.security;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.security.Keys;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class JWTUtil {
private String SECRET_KEY = "TaK+HaV^uvCHEFsEVfypW#7g9^k*Z8$V";
private SecretKey getSigningKey() {
return Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(SECRET_KEY.getBytes());
}
public String extractUsername(String token) {
Claims claims = extractAllClaims(token);
return claims.getSubject();
}
public Date extractExpiration(String token) {
return extractAllClaims(token).getExpiration();
}
private Claims extractAllClaims(String token) {
return Jwts.parser()
.verifyWith(getSigningKey())
.build()
.parseSignedClaims(token)
.getPayload();
}
private Boolean isTokenExpired(String token) {
return extractExpiration(token).before(new Date());
}
public String generateToken(String username) {
Map<String, Object> claims = new HashMap<>();
return createToken(claims, username);
}
private String createToken(Map<String, Object> claims, String subject) {
return Jwts.builder()
.claims(claims)
.subject(subject)
.header().empty().add("typ","JWT")
.and()
.issuedAt(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()))
.expiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + 1000 * 60 * 50)) // 5 minutes expiration time
.signWith(getSigningKey())
.compact();
}
public Boolean validateToken(String token) {
return !isTokenExpired(token);
}
}
*configure the Spring security and add some modifictaion we create the class SecurityConfig.java *
The SecurityConfig class sets up security for the application using Spring Security. It defines access rules, allowing public endpoints while restricting others based on user roles. The class incorporates a JWT filter to validate tokens and uses BCrypt for password encoding. It also configures an authentication manager with a custom user details service for secure user authentication.
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.config;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.security.JWTFilter;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.service.UserInfoConfigManager;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.utils.AppConstants;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.configuration.AuthenticationConfiguration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configurers.AbstractHttpConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Autowired
private JWTFilter jwtFilter;
@Autowired
private UserInfoConfigManager userInfoConfigManager;
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
return http.authorizeHttpRequests(request -> request
.requestMatchers(AppConstants.PUBLIC_URLS).permitAll()
.requestMatchers("/api/test/public/hello/**").hasAnyRole("USER","ADMIN")
.requestMatchers("/api/test/private/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest()
.authenticated())
.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.addFilterBefore(jwtFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.build();
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userInfoConfigManager).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager(AuthenticationConfiguration auth) throws Exception {
return auth.getAuthenticationManager();
}
}
The securityFilterChain method configures access rules for different API endpoints in the Spring application. It permits public URLs and applies role-based access control for user and admin roles. Role-based authentication restricts resource access based on user roles (e.g., USER, ADMIN). In Spring Boot, you define roles and configure security settings in the SecurityConfig class to specify access permissions. During user registration, assign roles, and use annotations like @PreAuthorize to enforce role checks in controllers. This approach enhances security, allows easy permission management, and simplifies user access rights as the application scales. Implementing role-based auth provides flexibility and maintainability for your user management system. CSRF protection is disabled, and a custom JWT filter is added to authenticate requests based on JSON Web Tokens, ensuring secure and controlled access to resources.
configureGlobal method handle configures global authentication settings in a Spring application. It uses a custom user details service for loading user data and a BCrypt password encoder for secure password hashing. Additionally, it provides an AuthenticationManager bean for handling authentication processes, ensuring a secure and efficient user authentication system that leverages strong password management practices.
create the endpoints for register and login
package com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.Controller;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto.LoginDTO;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto.LoginResponse;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.dto.RegisterDTO;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.security.JWTUtil;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.service.AuthService;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.service.UserInfoConfigManager;
import com.tier3Hub.user_auth_service.utils.ResponseHandler;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/auth")
public class AuthController {
@Autowired
JWTUtil jwtUtil;
@Autowired
AuthService authService;
@Autowired
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
private UserInfoConfigManager userInfoConfigManager;
@PostMapping("/register")
public ResponseEntity<Object> register(@Valid @RequestBody RegisterDTO registerDTO) {
return ResponseHandler.generateResponse("User registered successfully", HttpStatus.OK, authService.register(registerDTO));
}
@PostMapping("/login")
public ResponseEntity<Object> login(@Valid @RequestBody LoginDTO loginDTO) {
try {
Authentication authenticate = authenticationManager
.authenticate(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginDTO.getUsername(), loginDTO.getPassword()));
UserDetails userDetails = userInfoConfigManager.loadUserByUsername(loginDTO.getUsername());
String jwt = jwtUtil.generateToken(userDetails.getUsername());
LoginResponse loginResponse = LoginResponse
.builder()
.accessToken(jwt)
.build();
return ResponseHandler.generateResponse("User logged in successfully", HttpStatus.OK, loginResponse);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return new ResponseEntity<>("Incorrect username or password", HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}
}
This login method in the AuthController handles user login requests. It takes a LoginDTO containing the username and password, validates them, and attempts authentication using the AuthenticationManager. Upon successful authentication, it retrieves user details and generates a JWT token using the JWTUtil class. The token is then included in a LoginResponse object and returned with a success message. If authentication fails, it catches the exception and returns a "Incorrect username or password" response with a 400 status code.
generateToken(String username): This method creates an empty claims map and calls the createToken method with the username as the subject. It serves as the entry point for token generation.
c*reateToken(Map claims, String subject):* This method builds the JWT using the Jwts.builder(). It sets the claims, subject, and token metadata, such as issue date and expiration time (set to 5 minutes). The token is then signed with a secret key and compacted into a string format for transmission.
Testing
now we run the application
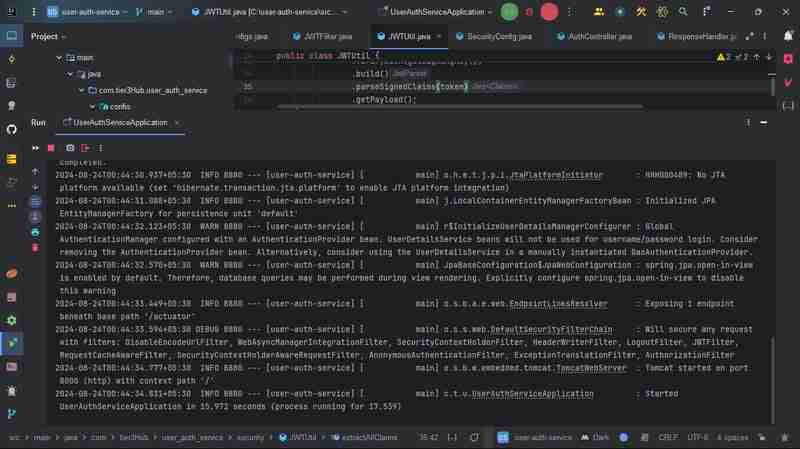
and hit the URL here our application is runing on 8000 port
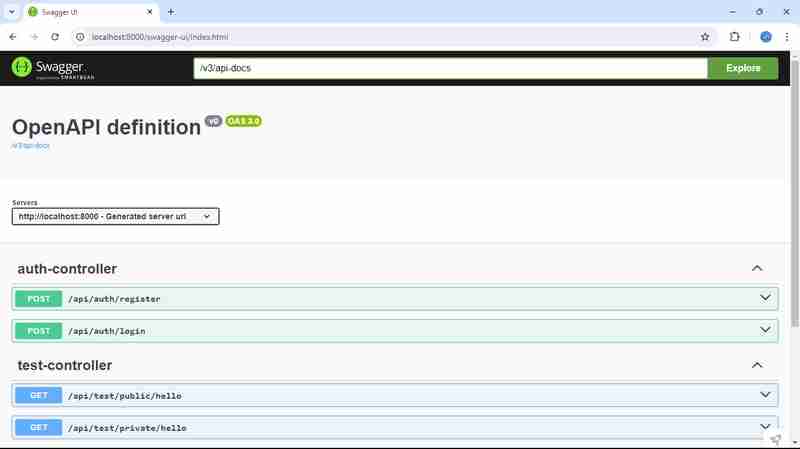
http://localhost:8000/swagger-ui/index.html
在项目中使用 Swagger 可以增强 API 文档和测试。它为开发人员提供了一个用户友好的界面,以探索您的 API、了解请求/响应结构并直接从文档测试端点。通过集成 Swagger,您可以根据代码注释自动生成 API 文档,使前端和后端开发人员更轻松地高效协作。
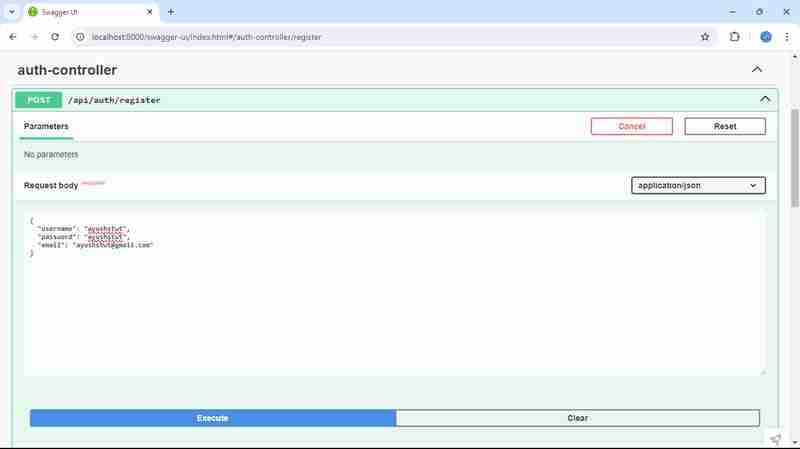
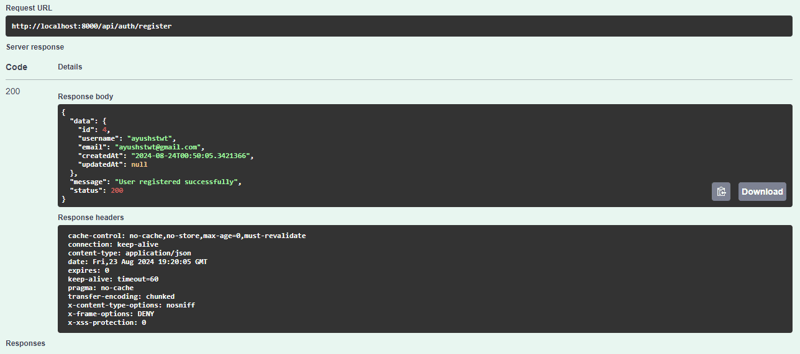
首先我们注册用户
我们得到这样的回复
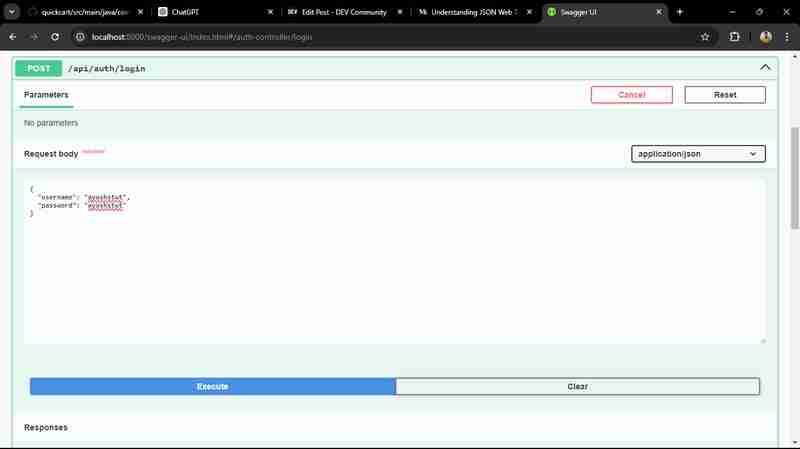
之后我们登录用户
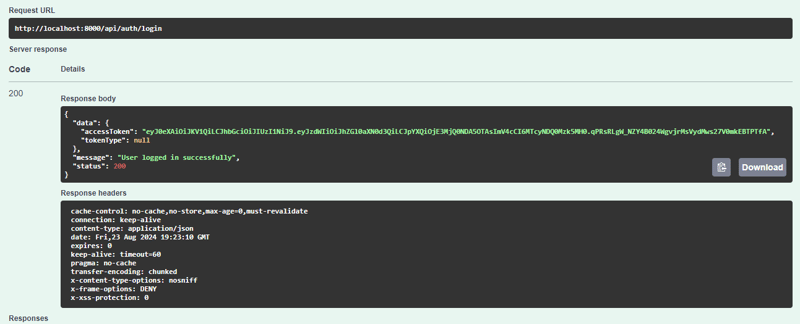
我们得到这样的回复
结论
该项目在 Spring Boot 应用程序中使用 JWT(JSON Web Tokens)实现基于角色的身份验证。它具有安全的身份验证机制,用户可以注册和登录,接收根据分配的角色(例如 USER 或 ADMIN)授予访问权限的 JWT。 SecurityConfig 类配置访问权限,确保每个人都可以访问公共端点,同时将敏感操作仅限于授权用户。 JWTUtil 类处理令牌创建、验证和用户提取。总体而言,此设置增强了安全性,实现了整个应用程序的无缝且强大的访问控制。
该项目采用了一个全面的安全框架,利用 Spring Security 进行用户身份验证和授权。 AuthController 方便用户注册和登录,在身份验证成功后生成 JWT。该应用程序使用 JWTFilter 拦截请求并验证令牌,确保只有经过身份验证的用户才能访问受保护的资源。通过集成基于角色的访问控制,该项目提供了灵活且安全的用户管理系统。这种设计不仅提高了安全性,还通过最大限度地减少重复登录的需要来增强用户体验。总的来说,它为构建可扩展且安全的微服务奠定了坚实的基础。
您可以在我的 GitHub 存储库上探索用户身份验证服务的完整源代码。该项目展示了各种功能,例如用户注册、登录和使用 JWT 进行身份验证的安全访问。请随意查看、贡献或将其用作您自己的项目的参考!
GitHub 存储库:https://github.com/ishrivasayush/user-auth-service
对于那些有兴趣深入研究 JSON Web Tokens (JWT) 的人,我建议访问 jwt.io。该资源提供了有关 JWT 的全面信息,包括其工作原理、结构和实际示例。这是理解基于令牌的身份验证和授权的一个很好的起点,这对于现代 Web 应用程序至关重要。无论您是初学者还是想要刷新知识,jwt.io 都提供了有关安全管理用户会话的宝贵见解。
以上是使用 Spring Security 保护微服务:实施 JWT的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

