抛弃视觉编码器,这个「原生版」多模态大模型也能媲美主流方法
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB原创
- 2024-07-18 19:21:11414浏览

The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com
Yizuo Diao Haiwen is a doctoral student at Dalian University of Technology, and his supervisor is Professor Lu Huchuan. Currently interning at Beijing Zhiyuan Artificial Intelligence Research Institute, the instructor is Dr. Wang Xinlong. His research interests are vision and language, efficient transfer of large models, multi-modal large models, etc. Co-first author Cui Yufeng graduated from Beihang University and is an algorithm researcher at the Vision Center of Beijing Zhiyuan Artificial Intelligence Research Institute. His research interests are multimodal models, generative models, and computer vision, and his main work is in the Emu series.
Recently, research on multi-modal large models has been in full swing, and the industry has invested more and more in this. Hot models have been launched abroad, such as GPT-4o (OpenAI), Gemini (Google), Phi-3V (Microsoft), Claude-3V (Anthropic), and Grok-1.5V (xAI). At the same time, domestic GLM-4V (Wisdom Spectrum AI), Step-1.5V (Step Star), Emu2 (Beijing Zhiyuan), Intern-VL (Shanghai AI Laboratory), Qwen-VL (Alibaba), etc. Models bloom.
The current visual language model (VLM) usually relies on the visual encoder (Vision Encoder, VE) to extract visual features, and then combines the user instructions with the large language model (LLM) for processing and answering. The main challenge lies in the visual encoder and Training separation for large language models. This separation causes visual encoders to introduce visual induction bias issues when interfacing with large language models, such as limited image resolution and aspect ratio, and strong visual semantic priors. As the capacity of visual encoders continues to expand, the deployment efficiency of multi-modal large models in processing visual signals is also greatly limited. In addition, how to find the optimal capacity configuration of visual encoders and large language models has become increasingly complex and challenging.
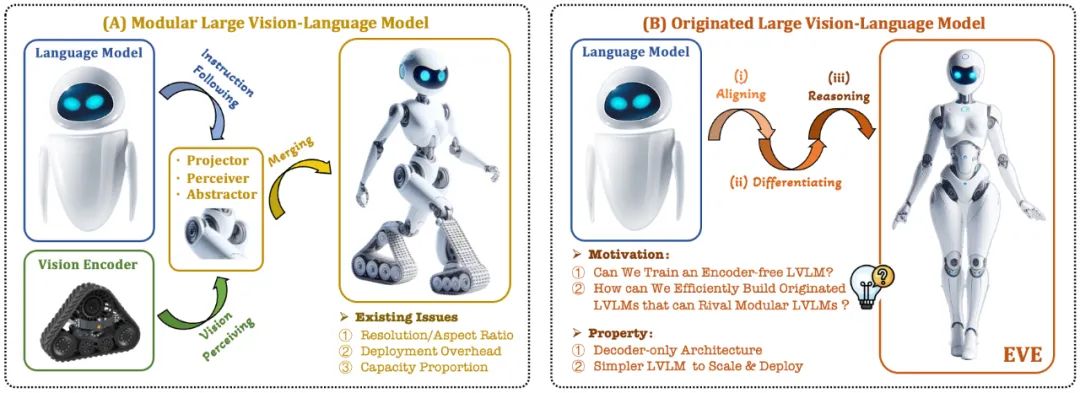
In this context, some more cutting-edge ideas quickly emerged:
Can we remove the visual encoder, that is, directly build a native multi-modal large model without a visual encoder?
How to efficiently and smoothly evolve a large language model into a native multi-modal large model without visual encoder?
How to bridge the performance gap between encoder-less native multi-modal frameworks and mainstream encoder-based multi-modal paradigms?
Adept AI released the Fuyu series model at the end of 2023 and made some related attempts, but did not disclose any training strategies, data resources and equipment information. At the same time, there is a significant performance gap between the Fuyu model and mainstream algorithms in public visual text evaluation indicators. During the same period, some pilot experiments we conducted showed that even if the scale of pre-training data is increased on a large scale, the native multi-modal large model without encoder still faces thorny problems such as slow convergence speed and poor performance.
In response to these challenges, the vision team of Zhiyuan Research Institute, together with Dalian University of Technology, Peking University and other domestic universities, launched a new generation of coder-free visual language model EVE. Through refined training strategies and additional visual supervision, EVE integrates visual-linguistic representation, alignment, and inference into a unified pure decoder architecture. Using publicly available data, EVE performs well on multiple visual-linguistic benchmarks, competing with mainstream encoder-based multimodal methods of similar capacity and significantly outperforming fellow Fuyu-8B. EVE is proposed to provide a transparent and efficient path for the development of native multi-modal architectures for pure decoders.


Paper address: https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.11832
Project code: https://github.com/baaivision/EVE
Model address: https ://huggingface.co/BAAI/EVE-7B-HD-v1.0
1. Technical Highlights
原生视觉语言模型:打破了主流的多模态模型的固定范式,去除视觉编码器,可处理任意图像长宽比。在多个视觉语言基准测试中显着优于同类型的 Fuyu-8B 模型,并接近主流的基于视觉编码器的视觉语言架构。
数据和训练代价少: EVE 模型的预训练仅筛选了来自OpenImages、SAM 和LAION 的公开数据,并利用了66.5 万条LLaVA 指令数据和额外的120 万条视觉对话数据,分别构建了常规版本和高分辨版本的EVE-7B。训练在两个 8-A100 (40G) 节点上约需 9 天完成,或者在四个 8-A100 节点上约需 5 天完成。
透明和高效的探索: EVE 尝试探索一条高效、透明且实用的路径通往原生视觉语言模型,为开发新一代纯解码器的视觉语言模型架构提供全新的思路和宝贵的经验,为未来多模态模型的发展开辟新的探索方向。
2. 模型结构
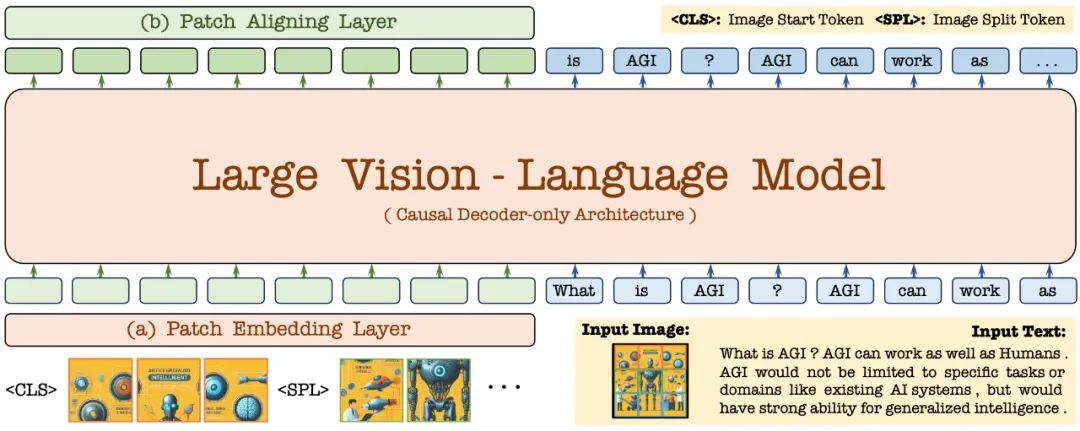
首先,通过 Vicuna-7B 语言模型进行初始化,使其具备丰富的语言知识和强大的指令跟随能力。在此基础上,去除深度视觉编码器,构建轻量级视觉编码层,高效无损地编码图像输入,并将其与用户语言命令输入到统一的解码器中。此外,通过视觉对齐层与通用的视觉编码器进行特征对齐,强化细粒度的视觉信息编码和表征。
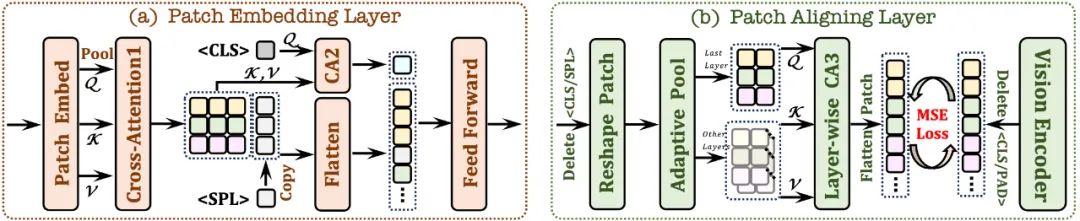
2.1 Patch Embedding Layer
首先使用单层卷积层来获取图像的2D 特征图,然后通过平均池化层进行下采样;
使用交叉注意力模块(CA1)在限定感受野中交互,增强每个 patch 的局部特征;
使用 token 并结合交叉注意力模块(CA2),为后续每个patch 特征提供全局信息;
在每个patch 特征行的末尾插入了一个可学习的 token,帮助网络理解图像的二维空间结构。
2.2 Patch Aligning Layer
记录有效patch 的二维形状;丢弃/
tokens,并利用自适应池化层还原到原始的二维形状; 通过层级交叉注意力模块(CA3),整合多层网络视觉特征,从而实现与视觉编码器输出的细粒度对齐。
3. 训练策略
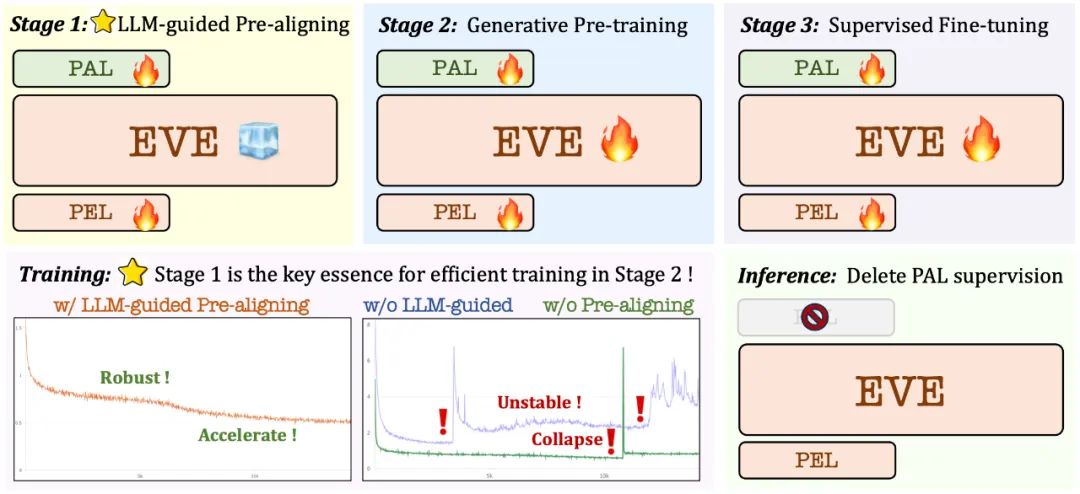
大语言模型引导的预训练阶段:建立视觉和语言之间的初步联系,为后续稳定高效的大规模预训练打下基础;
生成式预训练阶段:进一步提高模型对视觉- 语言内容的理解能力,实现纯语言模型到多模态模型的丝滑转变;
监督式的微调阶段:进一步规范模型遵循语言指令和学习对话模式的能力,满足各种视觉语言基准测试的要求。
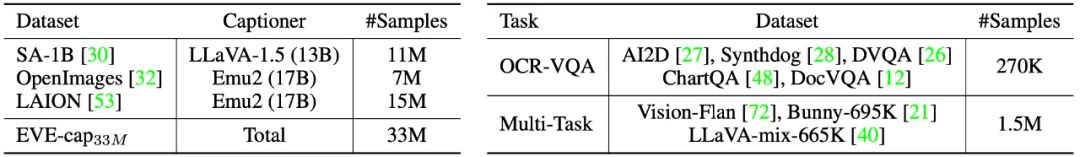
在预训练阶段,筛选了来自 SA-1B、OpenImages 和 LAION 等 3300 万公开数据,仅保留分辨率高于 448×448 的图像样本。特别地,针对LAION 图像冗余度高的问题,通过在EVA-CLIP 提取的图像特征上应用K-means 聚类,生成50,000 个聚类,并从中挑选出最接近每个聚类中心的300 张图像,最终选出1500 万张LAION 图像样本。随后,利用 Emu2 (17B)和 LLaVA-1.5 (13B)重新生成高质量图像描述。
在监督微调阶段,使用LLaVA-mix-665K 微调数据集来训练得到标准版的EVE-7B,并整合AI2D、Synthdog、DVQA、ChartQA、DocVQA、Vision-Flan 和Bunny-695K 等混合数据集来训练得到高分辨率版本的EVE-7B。
4. 定量分析
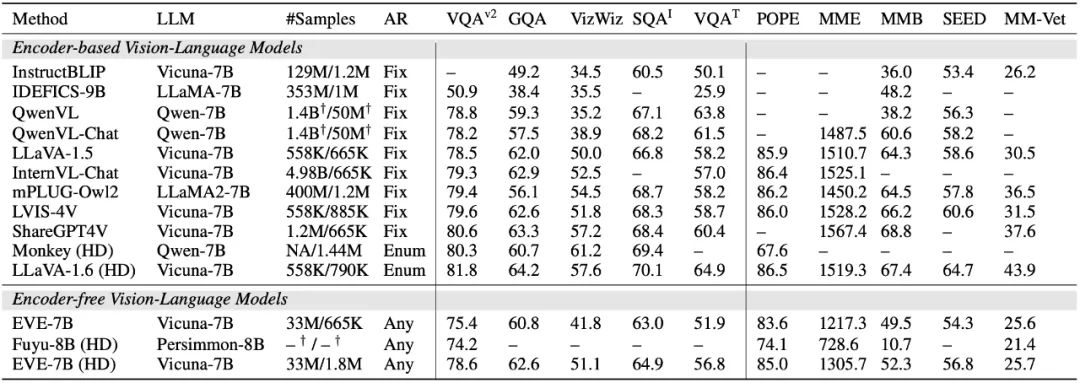
EVE 模型在多个视觉语言基准测试中明显优于同类型的 Fuyu-8B 模型,并且与多种主流的基于编码器的视觉语言模型表现相当。然而,由于使用大量视觉语言数据训练,其在准确响应特定指令方面存在挑战,在部分基准测试中表现有待提高。令人兴奋的是,通过高效的训练策略,可以实现无编码器的 EVE 与带编码器基础的视觉语言模型取得相当的性能,从根本上解决主流模型在输入尺寸灵活性、部署效率和模态容量匹配方面的问题。
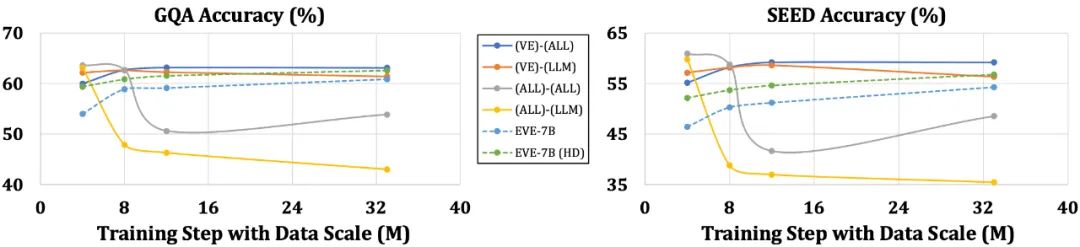
相较于带编码器的模型易受到语言结构简化和丰富知识丢失等问题困扰,EVE 表现出随着数据规模的增加而逐步稳定地提升性能,逐渐逼近基于编码器模型的性能水平。这可能是因为在统一网络中编码和对齐视觉和语言模态更具挑战性,使得无编码器模型相对于带编码器的模型更不容易过拟合。
5. 同行怎么看?
英伟达高级研究员 Ali Hatamizadeh 表示,EVE 令人耳目一新,尝试提出全新的叙事,区别于构建繁杂的评测标准和渐进式的视觉语言模型改进。

谷歌 Deepmind 首席研究员 Armand Joulin 表示,构建纯解码器的视觉语言模型令人兴奋。
苹果机器学习工程师 Prince Canuma 表示,EVE 架构非常有趣,对 MLX VLM 项目集是一个很好的补充。
6.未来展望
作为无编码器的原生视觉语言模型,目前 EVE 取得了令人鼓舞的结果。沿着这条路径,未来还有一些有趣的方向值得探索尝试:
进一步的性能提升:实验发现,仅使用视觉 - 语言数据进行预训练显著地降低了模型的语言能力(SQA 得分从 65.3% 降至 63.0%),但逐步提升了模型的多模态性能。这表明在大语言模型更新时,内部存在语言知识的灾难性遗忘。建议适当融合纯语言的预训练数据,或采用专家混合(MoE)策略来减少视觉与语言模态间干扰。
无编码器架构的畅想:通过恰当策略和高质量数据的训练,无编码器视觉语言模型可以与带编码器的模型相匹敌。那么在相同的模型容量和海量的训练数据下,二者性能如何?我们推定通过扩大模型容量和训练数据量,无编码器架构是能够达到甚至超越基于编码器架构,因为前者几乎无损地输入图像,避开了视觉编码器的先验偏置。
原生多模态的构建: EVE 完整地展现了如何高效稳定地构建原生多模态模型,这为之后整合更多模态(如音频、视频、热成像、深度等)开辟了透明和切实可行的道路。核心思想是在引入大规模统一训练之前,先通过冻结的大语言模型对这些模态进行预对齐,并利用相应的单模态编码器和语言概念对齐进行监督。
以上是抛弃视觉编码器,这个「原生版」多模态大模型也能媲美主流方法的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

