案例研究:评估表达式
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB原创
- 2024-07-18 14:10:09723浏览
堆栈可用于计算表达式。栈和队列有很多应用。本节提供了一个使用堆栈来计算表达式的应用程序。您可以输入来自Google的算术表达式来计算该表达式,如下图所示。
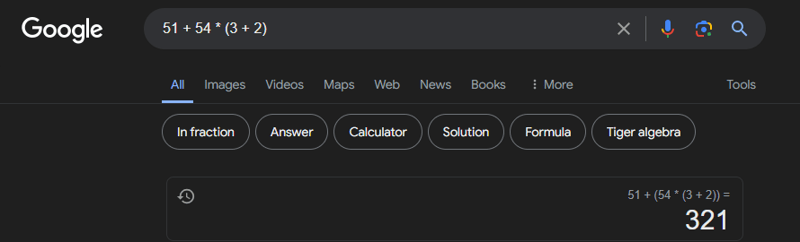
Google 如何评估表达式?本节介绍一个程序,用于计算具有多个运算符和括号的 复合表达式 (例如 (15 + 2) * 34 – 2)。为简单起见,假设操作数为整数,运算符有四种类型:+、-、** 和 */.
这个问题可以使用两个栈来解决,分别命名为operandStack和operatorStack,分别用于存储操作数和运算符。操作数和运算符在处理之前被推入堆栈。当处理 运算符 时,它会从 operatorStack 中弹出,并应用于 operandStack 中的前两个操作数(这两个操作数从 operandStack)。结果值被推回operandStack.
算法分两个阶段进行:第一阶段:扫描表达式
程序从左到右扫描表达式以提取操作数、运算符和括号。
- 如果提取的项是操作数,则将其推送到
- operandStack。 如果提取的项是
- + 或 - 运算符,则处理 operatorStack 顶部的所有运算符,并将提取的运算符压入 运算符栈. 如果提取的项是 ***** 或
- / 运算符,则处理 operatorStack/ 运算符> 并将提取的运算符推送到 operatorStack. 如果提取的项是 (
- 符号,则将其推送到 operatorStack. 如果提取的项是 )
- 符号,则从 operatorStack 顶部开始重复处理运算符,直到在堆栈上看到 ( 符号。 第 2 阶段:清除堆栈
从
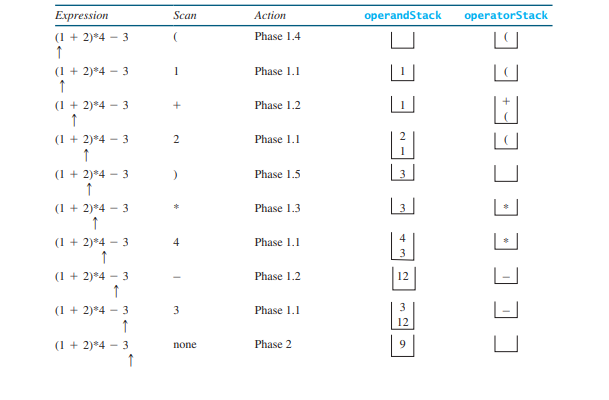
operatorStack顶部开始重复处理操作符,直到operatorStack为空。 下表显示了如何应用该算法来计算表达式
(1 + 2) * 4 - 3.
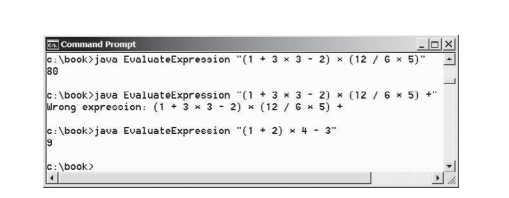
 下面的代码给出了程序,下图显示了一些示例输出。
下面的代码给出了程序,下图显示了一些示例输出。
package demo;
import java.util.Stack;
public class EvaluateExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Check number of arguments passed
if(args.length != 1) {
System.out.println("Usage: java EvaluateExpression \"expression\"");
System.exit(1);
}
try {
System.out.println(evaluateExpression(args[0]));
}
catch(Exception ex) {
System.out.println("Wrong expression: " + args[0]);
}
}
/** Evaluate an expression */
public static int evaluateExpression(String expression) {
// Create operandStack to store operands
Stack<Integer> operandStack = new Stack<>();
// Create operatorStack to store operators
Stack<Character> operatorStack = new Stack<>();
// Insert blanks around (, ), +, -, /, and *
expression = insertBlanks(expression);
// Extract operands and operators
String[] tokens = expression.split(" ");
// Phase 1: Scan tokens
for(String token: tokens) {
if(token.length() == 0) // Blank space
continue; // Back to the while loop to extract the next token
else if(token.charAt(0) == '+' || token.charAt(0) == '-') {
// Process all +, -, *, / in the top of the operator stack
while(!operatorStack.isEmpty() && (operatorStack.peek() == '+' || operatorStack.peek() == '-' || operatorStack.peek() == '*' || operatorStack.peek() == '/')) {
processAnOperator(operandStack, operatorStack);
}
// Push the + or - operator into the operator stack
operatorStack.push(token.charAt(0));
}
else if(token.charAt(0) == '*' || token.charAt(0) == '/') {
// Process all *, / in the top of the operator stack
while(!operatorStack.isEmpty() && (operatorStack.peek() == '*' || operatorStack.peek() == '/')) {
processAnOperator(operandStack, operatorStack);
}
// Push the * or / operator into the operator stack
operatorStack.push(token.charAt(0));
}
else if(token.trim().charAt(0) == '(') {
operatorStack.push('('); // Push '(' to stack
}
else if(token.trim().charAt(0) == ')') {
// Process all the operators in the stack until seeing '('
while(operatorStack.peek() != '(') {
processAnOperator(operandStack, operatorStack);
}
operatorStack.pop(); // Pop the '(' symbol from the stack
}
else {
// Push an operand to the stack
operandStack.push(Integer.valueOf(token));
}
}
// Phase 2: Process all the remaining operators in the stack
while(!operatorStack.isEmpty()) {
processAnOperator(operandStack, operatorStack);
}
// Return the result
return operandStack.pop();
}
/** Process one operator: Take an operator from operatorStack and apply it on the operands in the operandStack */
public static void processAnOperator(Stack<Integer> operandStack, Stack<Character> operatorStack) {
char op = operatorStack.pop();
int op1 = operandStack.pop();
int op2 = operandStack.pop();
if(op == '+')
operandStack.push(op2 + op1);
else if(op == '-')
operandStack.push(op2 - op1);
else if(op == '*')
operandStack.push(op2 * op1);
else if(op == '/')
operandStack.push(op2 / op1);
}
public static String insertBlanks(String s) {
String result = "";
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if(s.charAt(i) == '(' || s.charAt(i) == ')' || s.charAt(i) == '+' || s.charAt(i) == '-' || s.charAt(i) == '*' || s.charAt(i) == '/')
result += " " + s.charAt(i) + " ";
else
result += s.charAt(i);
}
return result;
}
}
GenericStack类或Java API中定义的java.util.Stack类来创建堆栈。此示例使用 java.util.Stack 类。如果将其替换为 GenericStack.,该程序将运行。 程序将表达式作为一个字符串中的命令行参数。
evaluateExpression方法创建两个堆栈,operandStack 和 operatorStack(第 24、27 行),并提取由空格分隔的操作数、运算符和括号 (第 30-33 行)。 insertBlanks 方法用于确保操作数、运算符和括号之间至少有一个空格分隔(第 30 行)。 程序扫描
for 循环中的每个标记(第 36-72 行)。如果标记为空,则跳过它(第 38 行)。如果令牌是操作数,则将其推送到 operandStack(第 70 行)。如果令牌是 + 或 – 运算符(第 39 行),则处理 operatorStack 顶部的所有运算符(如果有)(第 41-43 行) ,并将新扫描的运算符推入堆栈(第 46 行)。如果令牌是 ***** 或 / 运算符(第 48 行),则处理 operatorStack/ 运算符🎜>,如果有的话(第 50-51 行),并将新扫描的运算符推入堆栈(第 55 行)。如果令牌是 ( 符号(第 57 行),则将其推入 operatorStack。如果令牌是 ) 符号(第 60 行),则处理从 operatorStack 直到看到 ) 符号(第 62-64 行),然后从堆栈中弹出 ) 符号。 考虑完所有标记后,程序将处理 operatorStack 中剩余的运算符(第 75-77 行)。 processAnOperator 方法(第 84-96 行)处理一个运算符。该方法从 operatorStack 中弹出运算符(第 85 行),并从 operandStack 中弹出两个操作数(第 86-87 行)。根据运算符,该方法执行操作并将操作结果推送回 operandStack(第 89、91、93、95 行)。
以上是案例研究:评估表达式的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

