Greenplum创建表--分布键
Greenplum创建表--分布键
Greenplum是分布式系统,创建表时需要指定分布键(创建表需要CREATEDBA权限),目的在于将数据平均分布到各个segment。选择分布键非常重要,选择错了会导致数据不唯一,更严重的是会造成SQL性能急剧下降。
Greenplum有两种分布策略: 1、hash分布。
Greenplum默认使用hash分布策略。该策略可选一个或者多个列作为分布键(distribution key,简称DK)。分布键做hash算法来确认数据存放到对应的segment上。相同分布键值会hash到相同的segment上。表上最好有唯一键或者主键,这样能保证数据均衡分不到各个segment上。语法,distributed by。 如果没有主键或者唯一键,默认选择第一列作为分布键。增加主键
2、随机(randomly)分布。 数据会被随机分不到segment上,相同记录可能会存放在不同的segment上。随机分布可以保证数据平均,但是Greenplum没有跨节点的唯一键约束数据,所以无法保证数据唯一。基于唯一性和性能考虑,推荐使用hash分布,性能部分会另开一篇文档详细介绍。语法,distributed randomly。
一、hash分布键创建表,未指定分布列、分布类型,默认创建hash分布表,把第一列ID字段作为了分布键。
testDB=# create table t_hash(id int,name varchar(50)) distributed by (id);
CREATE TABLE
testDB=#
testDB=# \d t_hash
Table "public.t_hash"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) |
Distributed by: (id)
添加主键后,主键升级为分布键替代了id列。
testDB=# alter table t_hash addprimary key (name);
NOTICE: updating distribution policy to match new primary key
NOTICE: ALTER TABLE / ADD PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "t_hash_pkey" for table "t_hash"
ALTER TABLE
testDB=# \d t_hash
Table "public.t_hash"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) | not null
Indexes:
"t_hash_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (name)
Distributed by: (name)
验证hash分布表可实现主键或者唯一键值的唯一性
testDB=# insert into t_hash values(1,'szlsd1');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=#
testDB=# insert into t_hash values(2,'szlsd1');
ERROR: duplicate key violates unique constraint "t_hash_pkey"(seg2 gp-s3:40000 pid=3855)
另外,主键列上依然能够创建唯一键
testDB=# create unique index u_id on t_hash(name);
CREATE INDEX
testDB=#
testDB=#
testDB=# \d t_hash
Table "public.t_hash"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) | not null
Indexes:
"t_hash_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (name)
"u_id" UNIQUE, btree (name)
Distributed by: (name)
但是,非主键列无法单独创建唯一索引,想创建的话必须包含多有分布键列
testDB=# create unique index uk_id on t_hash(id);
ERROR: UNIQUE indexmust contain all columns in the distribution keyof relation "t_hash"
testDB=# create unique index uk_id on t_hash(id,name);
CREATE INDEX
testDB=# \d t_hash
Table "public.t_hash"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) | not null
Indexes:
"t_hash_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (name)
"uk_id" UNIQUE, btree (id, name)
Distributed by: (name)
删除主键后,原hash分布键依然不变。
testDB=# alter table t_hash drop constraint t_hash_pkey;
ALTER TABLE
testDB=# \d t_hash
Table "public.t_hash"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) | not null
Distributed by: (name)
当分布键不是主键或者唯一键时,我们来验证分布键的相同值落在一个segment的结论。下面的实验,name列是分布键,我们插入相同的name值,可以看到7条记录都落在了2号segment节点中。
testDB=#insert into t_hash values(1,'szlsd');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=#insert into t_hash values(2,'szlsd');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=#insert into t_hash values(3,'szlsd');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=#insert into t_hash values(4,'szlsd');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=#insert into t_hash values(5,'szlsd');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=#insert into t_hash values(6,'szlsd');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=#
testDB=#
testDB=# select gp_segment_id,count(*) from t_hash group by gp_segment_id;
gp_segment_id | count
---------------+-------
2 |7
(1 row)
二、随机分布键创建随机分布表需加distributed randomly关键字,具体使用哪列作为分布键不得而知。
testDB=# create table t_random(id int ,name varchar(100))distributed randomly;
CREATE TABLE
testDB=#
testDB=#
testDB=# \d t_random
Table "public.t_random"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+------------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(100) |
Distributed randomly
验证主键/唯一键的唯一性,可以看到随机分布表不能创建主键和唯一键
testDB=# alter table t_random add primary key (id,name);
ERROR: PRIMARY KEY and DISTRIBUTED RANDOMLY are incompatible
testDB=#
testDB=# create unique index uk_r_id on t_random(id);
ERROR: UNIQUE and DISTRIBUTED RANDOMLY are incompatible
testDB=#
从实验中可以看出无法实现数据的唯一性。并且,数据插入随机分布表,并不是轮询插入,实验中共有3个segment,但是在1号插入3条记录,在2号segment节点插入2条记录后,才在0号segment中插入数据。随机分布表如何实现数据平均分配不得而知。这个实验也验证了随机分布表的相同值分布在不同segment的结论。
testDB=# insert into t_random values(1,'szlsd3');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=# select gp_segment_id,count(*) from t_random group by gp_segment_id;
gp_segment_id | count
---------------+-------
1 | 1
(1 row)
testDB=#
testDB=# insert into t_random values(1,'szlsd3');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=# select gp_segment_id,count(*) from t_random group by gp_segment_id;
gp_segment_id | count
---------------+-------
2 | 1
1 | 1
(2 rows)
testDB=# insert into t_random values(1,'szlsd3');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=# select gp_segment_id,count(*) from t_random group by gp_segment_id;
gp_segment_id | count
---------------+-------
2 | 1
1 | 2
(2 rows)
testDB=# insert into t_random values(1,'szlsd3');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=# select gp_segment_id,count(*) from t_random group by gp_segment_id;
gp_segment_id | count
---------------+-------
2 | 2
1 | 2
(2 rows)
testDB=# insert into t_random values(1,'szlsd3');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=# select gp_segment_id,count(*) from t_random group by gp_segment_id;
gp_segment_id | count
---------------+-------
2 | 2
1 | 3
(2 rows)
testDB=# insert into t_random values(1,'szlsd3');
INSERT 0 1
testDB=# select gp_segment_id,count(*) from t_random group by gp_segment_id;
gp_segment_id | count
---------------+-------
2 |2
1 |3
0 | 1
(3 rows)
三、CTAS继承原表分布键 Greenplum中有两种CTAS语法,无论哪种语法,都默认继承原表的分布键。但是,不会继承表的一些特殊属性,如主键、唯一键、APPENDONLY、COMPRESSTYPE(压缩)等。
testDB=# \d t_hash;
Table "public.t_hash"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) | not null
Indexes:
"t_hash_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (name)
"uk_id" UNIQUE, btree (id, name)
Distributed by: (name)
testDB=#
testDB=#
testDB=# create table t_hash_1 as select * from t_hash;
NOTICE: Table doesn't have 'DISTRIBUTED BY' clause -- Using column(s) named 'name' as the Greenplum Database data distribution key for this table.
HINT: The 'DISTRIBUTED BY' clause determines the distribution of data. Make sure column(s) chosen are the optimal data distribution key to minimize skew.
SELECT 0
testDB=# \d t_hash_1
Table "public.t_hash_1"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) |
Distributed by: (name)
testDB=#
testDB=# create table t_hash_2 (like t_hash);
NOTICE: Table doesn't have 'distributed by' clause, defaulting to distribution columns from LIKE table
CREATE TABLE
testDB=# \d t_hash_2
Table "public.t_hash_2"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) | not null
Distributed by: (name)
如果CTAS创建表改变分布键,加上distributed by即可。
testDB=# create table t_hash_3 as select * from t_hash distributed by (id);
SELECT 0
testDB=#
testDB=# \d t_hash_3
Table "public.t_hash_3"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) |
Distributed by: (id)
testDB=#
testDB=#
testDB=# create table t_hash_4 (like t_hash) distributed by (id);
CREATE TABLE
testDB=#
testDB=# \d t_hash4
Did not find any relation named "t_hash4".
testDB=# \d t_hash_4
Table "public.t_hash_4"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(50) | not null
Distributed by: (id)
CTAS时,randomly随机分布键要特别注意,一定要加上distributed randomly,不然原表是hash分布键,CTAS新表则是随机分布键。
testDB=# \d t_random
Table "public.t_random"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+------------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(100) |
Distributed randomly
testDB=#
testDB=# \d t_random_1
Table "public.t_random_1"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+------------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(100) |
Distributed by: (id)
testDB=# create table t_random_2 as select * from t_randomdistributed randomly;
SELECT 7
testDB=#
testDB=# \d t_random_2
Table "public.t_random_2"
Column |Type| Modifiers
--------+------------------------+-----------
id| integer|
name| character varying(100) |
Distributed randomly
参考:《Greenplum企业应用实战》《Greenplum4.2.2管理员指南》
转载请注明:
十字螺丝钉
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid/23284114.html
QQ:463725310
E-MAIL:houora#gmail.com(#请自行替换为@
 如何在 iPhone 和 Android 上关闭蓝色警报Feb 29, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
如何在 iPhone 和 Android 上关闭蓝色警报Feb 29, 2024 pm 10:10 PM根据美国司法部的解释,蓝色警报旨在提供关于可能对执法人员构成直接和紧急威胁的个人的重要信息。这种警报的目的是及时通知公众,并让他们了解与这些罪犯相关的潜在危险。通过这种主动的方式,蓝色警报有助于增强社区的安全意识,促使人们采取必要的预防措施以保护自己和周围的人。这种警报系统的建立旨在提高对潜在威胁的警觉性,并加强执法机构与公众之间的沟通,以共尽管这些紧急通知对我们社会至关重要,但有时可能会对日常生活造成干扰,尤其是在午夜或重要活动时收到通知时。为了确保安全,我们建议您保持这些通知功能开启,但如果
 在Android中实现轮询的方法是什么?Sep 21, 2023 pm 08:33 PM
在Android中实现轮询的方法是什么?Sep 21, 2023 pm 08:33 PMAndroid中的轮询是一项关键技术,它允许应用程序定期从服务器或数据源检索和更新信息。通过实施轮询,开发人员可以确保实时数据同步并向用户提供最新的内容。它涉及定期向服务器或数据源发送请求并获取最新信息。Android提供了定时器、线程、后台服务等多种机制来高效地完成轮询。这使开发人员能够设计与远程数据源保持同步的响应式动态应用程序。本文探讨了如何在Android中实现轮询。它涵盖了实现此功能所涉及的关键注意事项和步骤。轮询定期检查更新并从服务器或源检索数据的过程在Android中称为轮询。通过
 如何在Android中实现按下返回键再次退出的功能?Aug 30, 2023 am 08:05 AM
如何在Android中实现按下返回键再次退出的功能?Aug 30, 2023 am 08:05 AM为了提升用户体验并防止数据或进度丢失,Android应用程序开发者必须避免意外退出。他们可以通过加入“再次按返回退出”功能来实现这一点,该功能要求用户在特定时间内连续按两次返回按钮才能退出应用程序。这种实现显著提升了用户参与度和满意度,确保他们不会意外丢失任何重要信息Thisguideexaminesthepracticalstepstoadd"PressBackAgaintoExit"capabilityinAndroid.Itpresentsasystematicguid
 Android逆向中smali复杂类实例分析May 12, 2023 pm 04:22 PM
Android逆向中smali复杂类实例分析May 12, 2023 pm 04:22 PM1.java复杂类如果有什么地方不懂,请看:JAVA总纲或者构造方法这里贴代码,很简单没有难度。2.smali代码我们要把java代码转为smali代码,可以参考java转smali我们还是分模块来看。2.1第一个模块——信息模块这个模块就是基本信息,说明了类名等,知道就好对分析帮助不大。2.2第二个模块——构造方法我们来一句一句解析,如果有之前解析重复的地方就不再重复了。但是会提供链接。.methodpublicconstructor(Ljava/lang/String;I)V这一句话分为.m
 如何在2023年将 WhatsApp 从安卓迁移到 iPhone 15?Sep 22, 2023 pm 02:37 PM
如何在2023年将 WhatsApp 从安卓迁移到 iPhone 15?Sep 22, 2023 pm 02:37 PM如何将WhatsApp聊天从Android转移到iPhone?你已经拿到了新的iPhone15,并且你正在从Android跳跃?如果是这种情况,您可能还对将WhatsApp从Android转移到iPhone感到好奇。但是,老实说,这有点棘手,因为Android和iPhone的操作系统不兼容。但不要失去希望。这不是什么不可能完成的任务。让我们在本文中讨论几种将WhatsApp从Android转移到iPhone15的方法。因此,坚持到最后以彻底学习解决方案。如何在不删除数据的情况下将WhatsApp
 同样基于linux为什么安卓效率低Mar 15, 2023 pm 07:16 PM
同样基于linux为什么安卓效率低Mar 15, 2023 pm 07:16 PM原因:1、安卓系统上设置了一个JAVA虚拟机来支持Java应用程序的运行,而这种虚拟机对硬件的消耗是非常大的;2、手机生产厂商对安卓系统的定制与开发,增加了安卓系统的负担,拖慢其运行速度影响其流畅性;3、应用软件太臃肿,同质化严重,在一定程度上拖慢安卓手机的运行速度。
 Android中动态导出dex文件的方法是什么May 30, 2023 pm 04:52 PM
Android中动态导出dex文件的方法是什么May 30, 2023 pm 04:52 PM1.启动ida端口监听1.1启动Android_server服务1.2端口转发1.3软件进入调试模式2.ida下断2.1attach附加进程2.2断三项2.3选择进程2.4打开Modules搜索artPS:小知识Android4.4版本之前系统函数在libdvm.soAndroid5.0之后系统函数在libart.so2.5打开Openmemory()函数在libart.so中搜索Openmemory函数并且跟进去。PS:小知识一般来说,系统dex都会在这个函数中进行加载,但是会出现一个问题,后
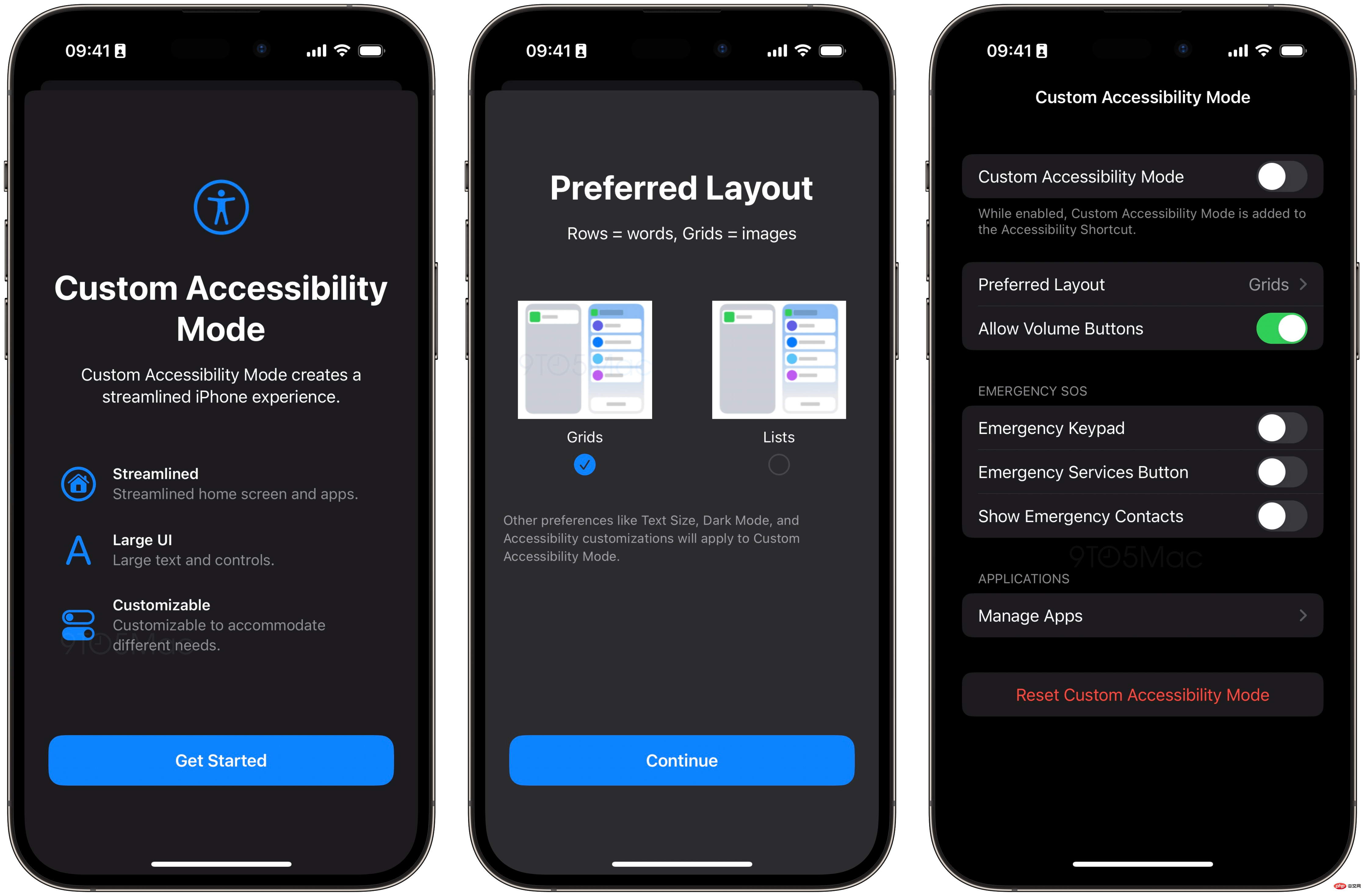 iOS 16.2 引入“自定义辅助功能模式”,为 iPhone 和 iPad 提供简化的体验Apr 13, 2023 am 11:07 AM
iOS 16.2 引入“自定义辅助功能模式”,为 iPhone 和 iPad 提供简化的体验Apr 13, 2023 am 11:07 AM苹果公司周二向开发人员发布了iOS 16.2 beta 2,因为该公司准备在 12 月向公众提供更新。正式地,它添加了新的 Freeform 协作应用程序和对 Home 应用程序的改进。在后台,9to5Mac发现 Apple 一直在开发一种新的“自定义辅助功能模式”,该模式将为 iPhone 和 iPad 提供“流线型”体验。自定义辅助功能模式这种代号为“Clarity”的新模式基本上用更精简的模式取代了 Springboard(这是 iOS 的主要界面)。该功能在当前测试版中仍对用户不可用,将


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中






