本文实例讲述了python开发之tkinter实现图形随鼠标移动的方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
做这个东西的时候,灵感源自于一个js效果:
两个眼睛随鼠标移动而移动
运行效果:
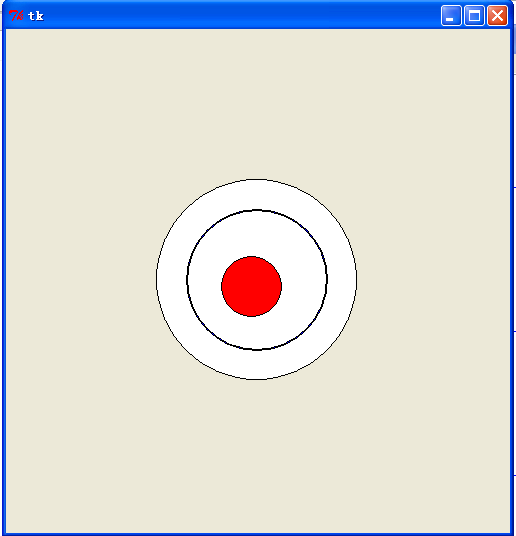
代码部分:
from tkinter import *
#1.获取到小圆当前的圆心坐标(x1, y1)
#2.获取到小圆移动的圆心坐标(x2, y2)
#3.把小圆从坐标(x1, y1)移动到坐标(x2, y2)
__author__ = {'name' : 'Hongten',
'mail' : 'hongtenzone@foxmail.com',
'blog' : 'http://blog.csdn.net/',
'QQ': '648719819',
'created' : '2013-09-20'}
class Eay(Frame):
def createWidgets(self):
## The playing field
self.draw = Canvas(self, width=500, height=500)
#鼠标位置
self.mouse_x = 450
self.mouse_y = 250
#圆心坐标(x,y)
self.oval_zero_x = 250
self.oval_zero_y = 250
#外面大圆半径
self.oval_r = 100
#里面小圆半径
self.oval_R = 30
self.oval_r1 = self.oval_r - self.oval_R + 0.5
self.oval_r2 = self.oval_r - self.oval_R - 0.5
#小圆
self.letter_ball_x1 = 250
self.letter_ball_y1 = 250
# The ball 外面大圆
self.ball = self.draw.create_oval((self.oval_zero_x - self.oval_r),
(self.oval_zero_y - self.oval_r),
(self.oval_zero_x + self.oval_r),
(self.oval_zero_y + self.oval_r),
fill="white")
self.ball = self.draw.create_oval((self.oval_zero_x - self.oval_r1),
(self.oval_zero_y - self.oval_r1),
(self.oval_zero_x + self.oval_r1),
(self.oval_zero_y + self.oval_r1),
fill="blue")
self.ball = self.draw.create_oval((self.oval_zero_x - self.oval_r2),
(self.oval_zero_y - self.oval_r2),
(self.oval_zero_x + self.oval_r2),
(self.oval_zero_y + self.oval_r2),
fill="white")
#里面小圆
self.ball_over = self.draw.create_oval((self.oval_zero_x - self.oval_R),
(self.oval_zero_y - self.oval_R),
(self.oval_zero_x + self.oval_R),
(self.oval_zero_y + self.oval_R),
fill="red")
self.draw.pack(side=LEFT)
def mouseMove(self, event):
self.mouse_x = event.x
self.mouse_y = event.y
if SHOW_LOG:
print('#' * 50)
print('鼠标的坐标为:({}, {})'.format(self.mouse_x, self.mouse_y))
print('小圆当前坐标为:({}, {})'.format(self.letter_ball_x1, self.letter_ball_y1))
'''获取到小圆移动的圆心坐标(x2, y2)'''
ax_x = abs(self.mouse_x - self.oval_zero_x)
ax_y = abs(self.mouse_y - self.oval_zero_y)
if SHOW_LOG:
print('坐标A(oval_zero_x, oval_zero_y)到坐标X(mouse_x, mouse_y)的距离为AX')
print('AX中ax_x = {}, ax_y = {}'.format(ax_x, ax_y))
ax_len = ((ax_x ** 2) + (ax_y ** 2))**0.5
if SHOW_LOG:
print('AX的长度为:{}'.format(ax_len))
#如果鼠标坐标在(ax_len > |r-R|)
if ax_len > abs(self.oval_r - self.oval_R):
ac_len = abs(self.oval_r - self.oval_R)
if SHOW_LOG:
print('AC的产度为:{}'.format(ac_len))
if int(self.mouse_x - self.oval_zero_x) != 0:
if int(self.mouse_y - self.oval_zero_y) != 0:
#求直线斜率 y = kx + b
k = (self.mouse_y - self.oval_zero_y)/(self.mouse_x - self.oval_zero_x)
if SHOW_LOG:
print('鼠标到大圆圆心的直线的斜率为:{}'.format(k))
b = self.mouse_y - (k * self.mouse_x)
###################################################
#小圆移动后的坐标
#这里有三个条件:
# 1.小圆的圆心坐标(x1, y1)在直线AC上(y = kx + b)
# 2.(r-R)^2 = x1^2 + y1^2 由1,2可以得到 => (r-R)^2 = x1^2 + 2*x1*k*b + b^2 => x1有两个值,通过3判断x1的符号,从而求出y1
# 3.if self.mousex_x > 0:
# x1 > 0
#这是一个二元二次方程,方程的解有两组,不过通过鼠标的位置self.mouse_x(self.mouse_y)可以判断圆心坐标x1(y1)
letter_ball_x2 = ((ac_len * (abs(self.mouse_x - self.oval_zero_x)))/ax_len) + self.letter_ball_x1
letter_ball_y2 = (letter_ball_x2 * k) + b
if SHOW_LOG:
print('小圆当前坐标为:({}, {})'.format(self.letter_ball_x1, self.letter_ball_y1))
print('小圆移动后坐标为:({}, {})'.format(letter_ball_x2, letter_ball_y2))
#把小圆从坐标(x1, y1)移动到坐标(x2, y2)
self.moved_x2 = letter_ball_x2 - self.letter_ball_x1
self.moved_y2 = letter_ball_y2 - self.letter_ball_y1
if SHOW_LOG:
print('需要移动的距离是:({}, {})'.format(int(self.moved_x2), int(self.moved_y2)))
self.draw.move(self.ball_over, int(self.moved_x2), int(self.moved_y2))
self.letter_ball_x1 = letter_ball_x2
self.letter_ball_y1 = letter_ball_y2
else:
print('鼠标在X轴上')
else:
print('鼠标在Y轴上')
else:
if SHOW_LOG:
print('小圆的移动后的坐标就是鼠标坐标')
#小圆移动后的坐标
letter_ball_x2 = self.mouse_x
letter_ball_y2 = self.mouse_y
if SHOW_LOG:
print('小圆移动后坐标为:({}, {})'.format(letter_ball_x2, letter_ball_y2))
#把小圆从坐标(x1, y1)移动到坐标(x2, y2)
self.moved_x2 = letter_ball_x2 - self.letter_ball_x1
self.moved_y2 = letter_ball_y2 - self.letter_ball_y1
if SHOW_LOG:
print('需要移动的距离是:({}, {})'.format(int(self.moved_x2), int(self.moved_y2)))
self.draw.move(self.ball_over, int(self.moved_x2), int(self.moved_y2))
self.letter_ball_x1 = letter_ball_x2
self.letter_ball_y1 = letter_ball_y2
def move_ball(self, *args):
#当鼠标在窗口中按下左键拖动的时候执行
#Widget.bind(self.draw, "<B1-Motion>", self.mouseMove)
#当鼠标在大圆内移动的时候执行
self.draw.tag_bind(self.ball, "<Any-Enter>", self.mouseMove)
def __init__(self, master=None):
global letter_ball_x2
letter_ball_x2 = 0
global letter_ball_y2
letter_ball_y2 = 0
global SHOW_LOG
SHOW_LOG = True
Frame.__init__(self, master)
Pack.config(self)
self.createWidgets()
self.after(10, self.move_ball)
game = Eay()
game.mainloop()
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
 Python:深入研究汇编和解释May 12, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:深入研究汇编和解释May 12, 2025 am 12:14 AMpythonisehybridmodelofcompilationand interpretation:1)thepythoninterspretercompilesourcececodeintoplatform- interpententbybytecode.2)thepytythonvirtualmachine(pvm)thenexecuteCutestestestesteSteSteSteSteSteSthisByTecode,BelancingEaseofuseWithPerformance。
 Python是一种解释或编译语言,为什么重要?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python是一种解释或编译语言,为什么重要?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AMpythonisbothinterpretedAndCompiled.1)它的compiledTobyTecodeForportabilityAcrosplatforms.2)bytecodeisthenInterpreted,允许fordingfordforderynamictynamictymictymictymictyandrapiddefupment,尽管Ititmaybeslowerthananeflowerthanancompiledcompiledlanguages。
 对于python中的循环时循环与循环:解释了关键差异May 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM
对于python中的循环时循环与循环:解释了关键差异May 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM在您的知识之际,而foroopsareideal insinAdvance中,而WhileLoopSareBetterForsituations则youneedtoloopuntilaconditionismet
 循环时:实用指南May 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
循环时:实用指南May 12, 2025 am 12:07 AMForboopSareSusedwhenthentheneMberofiterationsiskNownInAdvance,而WhileLoopSareSareDestrationsDepportonAcondition.1)ForloopSareIdealForiteratingOverSequencesLikelistSorarrays.2)whileLeleLooleSuitableApeableableableableableableforscenarioscenarioswhereTheLeTheLeTheLeTeLoopContinusunuesuntilaspecificiccificcificCondond
 Python:它是真正的解释吗?揭穿神话May 12, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Python:它是真正的解释吗?揭穿神话May 12, 2025 am 12:05 AMpythonisnotpuroly interpred; itosisehybridablectofbytecodecompilationandruntimeinterpretation.1)PythonCompiLessourceceCeceDintobyTecode,whitsthenexecececected bytybytybythepythepythepythonvirtirtualmachine(pvm).2)
 您可以使用Python中的循环加入列表吗?May 10, 2025 am 12:14 AM
您可以使用Python中的循环加入列表吗?May 10, 2025 am 12:14 AM是的,YouCanconCatenatElistsusingAloopInpyThon.1)使用eparateLoopsForeachListToAppendIteMstoaresultList.2)useanestedlooptoiterateOverMultipliplipliplipliplipliplipliplipliplipliplistforamoreConciseApprace.3)
 condenate列表python:使用,扩展()等May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AM
condenate列表python:使用,扩展()等May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AMThemostefficientmethodsforconcatenatinglistsinPythonare:1)theextend()methodforin-placemodification,2)itertools.chain()formemoryefficiencywithlargedatasets.Theextend()methodmodifiestheoriginallist,makingitmemory-efficientbutrequirescautionifpreserving
 Python循环:示例和最佳实践May 10, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Python循环:示例和最佳实践May 10, 2025 am 12:05 AMpythonboopsincludeforandwhileloops,with forloopsidealforequencessand and whileloopsforcondition repetition.bestpracticesinvolve:1)使用listComprehensionsforshensionsforsimpletranspletransformations,2)obseringEnumerateForIndex-valuepairs,3)optingftingftingfortermornemoremoremoremore


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境





