最近在使用Testlink时,发现导入的用例是xml格式,且没有合适的工具转成excel格式,xml使用excel打开显示的东西也太多,网上也有相关工具转成csv格式的,结果也不合人意。
那求人不如尔己,自己写一个吧
需要用到的模块有:xml.dom.minidom(python自带)、xlwt
使用版本:
python:2.7.5
xlwt:1.0.0
一、先分析Testlink XML格式:
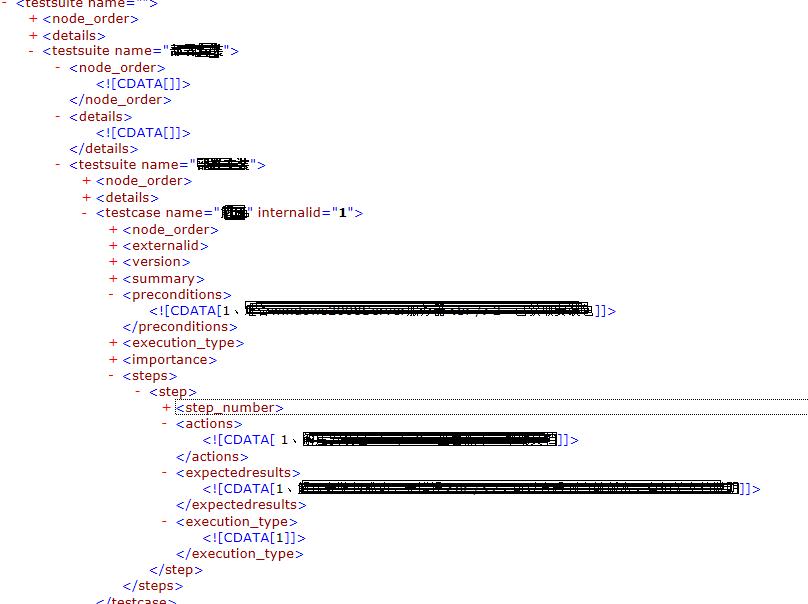
这是一个有两级testusuit的典型的testlink用例结构,我们只需要取testsuite name,testcase name,preconditions,actions,expectedresults
二、程序如下:
#coding:utf-8
'''
Created on 2015-8-20
@author: Administrator
'''
'''
'''
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
import xml.dom.minidom as xx
import os,xlwt,datetime
workbook=xlwt.Workbook(encoding="utf-8")
#
booksheet=workbook.add_sheet(u'sheet_1')
booksheet.col(0).width= 5120
booksheet.col(1).width= 5120
booksheet.col(2).width= 5120
booksheet.col(3).width= 5120
booksheet.col(4).width= 5120
booksheet.col(5).width= 5120
dom=xx.parse(r'D:\\Python27\test.xml')
root = dom.documentElement
row=1
col=1
borders=xlwt.Borders()
borders.left=1
borders.right=1
borders.top=1
borders.bottom=1
style = xlwt.easyxf('align: wrap on,vert centre, horiz center') #自动换行、水平居中、垂直居中
#设置标题的格式,字体方宋、加粗、背景色:菊黄
#测试项的标题
title=xlwt.easyxf(u'font:name 仿宋,height 240 ,colour_index black, bold on, italic off; align: wrap on, vert centre, horiz center;pattern: pattern solid, fore_colour light_orange;')
item='测试项'
Subitem='测试分项'
CaseTitle='测试用例标题'
Condition='预置条件'
actions='操作步骤'
Result='预期结果'
booksheet.write(0,0,item,title)
booksheet.write(0,1,Subitem,title)
booksheet.write(0,2,CaseTitle,title)
booksheet.write(0,3,Condition,title)
booksheet.write(0,4,actions,title)
booksheet.write(0,5,Result,title)
#冻结首行
booksheet.panes_frozen=True
booksheet.horz_split_pos= 1
#一级目录
for i in root.childNodes:
testsuite=i.getAttribute('name').strip()
#print testsuite
#print testsuite
'''
写测试项
'''
print "row is :",row
booksheet.write(row,col,testsuite,style)
#二级目录
for dd in i.childNodes:
print " %s" % dd.getAttribute('name')
testsuite2=dd.getAttribute('name')
if not dd.getElementsByTagName('testcase'):
print "Testcase is %s" % testsuite2
row=row+1
booksheet.write(row,2,testsuite2,style) #写测试分项
row=row+1
booksheet.write(row,1,testsuite2,style)
itemlist=dd.getElementsByTagName('testcase')
for subb in itemlist:
#print " %s" % subb.getAttribute('name')
testcase=subb.getAttribute('name')
row=row+1
booksheet.write(row,2,testcase,style)
ilist=subb.getElementsByTagName('preconditions')
for ii in ilist:
preconditions=ii.firstChild.data.replace("<br />"," ")
col=col+1
booksheet.write(row,3,preconditions,style)
steplist=subb.getElementsByTagName('actions')
#print steplist
for step in steplist:
actions=step.firstChild.data.replace("<br />"," ")
col=col+1
booksheet.write(row,4,actions,style)
#print "测试步骤:",steplist[0].firstChild.data.replace("<br />"," ")
expectlist=subb.getElementsByTagName('expectedresults')
for expect in expectlist:
result=expect.childNodes[0].nodeValue.replace("<br />","" )
booksheet.write(row,5,result,style)
row=row+1
workbook.save('demo.xls')
写入excel的效果如下:

我们再来看个实例:
需要下载一个module:xlwt,如下是source code
import xml.dom.minidom
import xlwt
import sys
col = 0
row = 0
def handle_xml_report(xml_report, excel):
problems = xml_report.getElementsByTagName("problem")
handle_problems(problems, excel)
def handle_problems(problems, excel):
for problem in problems:
handle_problem(problem, excel)
def handle_problem(problem, excel):
global row
global col
code = problem.getElementsByTagName("code")
file = problem.getElementsByTagName("file")
line = problem.getElementsByTagName("line")
message = problem.getElementsByTagName("message")
for node in code:
excel.write(row, col, node.firstChild.data)
col = col + 1
for node in file:
excel.write(row, col, node.firstChild.data)
col = col + 1
for node in line:
excel.write(row, col, node.firstChild.data)
col = col + 1
for node in message:
excel.write(row, col, node.firstChild.data)
col = col + 1
row = row+1
col = 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
if(len(sys.argv) <= 1):
print ("usage: xml2xls src_file [dst_file]")
exit(0)
#the 1st argument is XML report ; the 2nd is XLS report
if(len(sys.argv) == 2):
xls_report = sys.argv[1][:-3] + 'xls'
#if there are more than 2 arguments, only the 1st & 2nd make sense
else:
xls_report = sys.argv[2]
xmldoc = xml.dom.minidom.parse(sys.argv[1])
wb = xlwt.Workbook()
ws = wb.add_sheet('MOLint')
ws.write(row, col, 'Error Code')
col = col + 1
ws.write(row, col, 'file')
col = col + 1
ws.write(row, col, 'line')
col = col + 1
ws.write(row, col, 'Description')
row = row + 1
col = 0
handle_xml_report(xmldoc, ws)
wb.save(xls_report)
 Python vs. C:了解关键差异Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python vs. C:了解关键差异Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AMPython和C 各有优势,选择应基于项目需求。1)Python适合快速开发和数据处理,因其简洁语法和动态类型。2)C 适用于高性能和系统编程,因其静态类型和手动内存管理。
 Python vs.C:您的项目选择哪种语言?Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Python vs.C:您的项目选择哪种语言?Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM选择Python还是C 取决于项目需求:1)如果需要快速开发、数据处理和原型设计,选择Python;2)如果需要高性能、低延迟和接近硬件的控制,选择C 。
 达到python目标:每天2小时的力量Apr 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
达到python目标:每天2小时的力量Apr 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM通过每天投入2小时的Python学习,可以有效提升编程技能。1.学习新知识:阅读文档或观看教程。2.实践:编写代码和完成练习。3.复习:巩固所学内容。4.项目实践:应用所学于实际项目中。这样的结构化学习计划能帮助你系统掌握Python并实现职业目标。
 最大化2小时:有效的Python学习策略Apr 20, 2025 am 12:20 AM
最大化2小时:有效的Python学习策略Apr 20, 2025 am 12:20 AM在两小时内高效学习Python的方法包括:1.回顾基础知识,确保熟悉Python的安装和基本语法;2.理解Python的核心概念,如变量、列表、函数等;3.通过使用示例掌握基本和高级用法;4.学习常见错误与调试技巧;5.应用性能优化与最佳实践,如使用列表推导式和遵循PEP8风格指南。
 在Python和C之间进行选择:适合您的语言Apr 20, 2025 am 12:20 AM
在Python和C之间进行选择:适合您的语言Apr 20, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython适合初学者和数据科学,C 适用于系统编程和游戏开发。1.Python简洁易用,适用于数据科学和Web开发。2.C 提供高性能和控制力,适用于游戏开发和系统编程。选择应基于项目需求和个人兴趣。
 Python与C:编程语言的比较分析Apr 20, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python与C:编程语言的比较分析Apr 20, 2025 am 12:14 AMPython更适合数据科学和快速开发,C 更适合高性能和系统编程。1.Python语法简洁,易于学习,适用于数据处理和科学计算。2.C 语法复杂,但性能优越,常用于游戏开发和系统编程。
 每天2小时:Python学习的潜力Apr 20, 2025 am 12:14 AM
每天2小时:Python学习的潜力Apr 20, 2025 am 12:14 AM每天投入两小时学习Python是可行的。1.学习新知识:用一小时学习新概念,如列表和字典。2.实践和练习:用一小时进行编程练习,如编写小程序。通过合理规划和坚持不懈,你可以在短时间内掌握Python的核心概念。
 Python与C:学习曲线和易用性Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python与C:学习曲线和易用性Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython更易学且易用,C 则更强大但复杂。1.Python语法简洁,适合初学者,动态类型和自动内存管理使其易用,但可能导致运行时错误。2.C 提供低级控制和高级特性,适合高性能应用,但学习门槛高,需手动管理内存和类型安全。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

VSCode Windows 64位 下载
微软推出的免费、功能强大的一款IDE编辑器

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)





