本文内容遵从CC版权协议, 可以随意转载, 但必须以超链接形式标明文章原始出处和作者信息及版权声明网址: http://www.penglixun.com/tech/database/plug-in-for-performance-and-scalability.html 原文地址:http://blogs.innodb.com/wp/2009/03/plug-in-for-
本文内容遵从CC版权协议, 可以随意转载, 但必须以超链接形式标明文章原始出处和作者信息及版权声明网址: http://www.penglixun.com/tech/database/plug-in-for-performance-and-scalability.html
原文地址:http://blogs.innodb.com/wp/2009/03/plug-in-for-performance-and-scalability/
Why should you care about the latest “early adopter” release of the InnoDB Plugin, version 1.0.3? ? One word:?performance! The release introduces these features:
为什么你应该关注最近的InnoDB Plugin 1.0.3版?一个词:性能!这个版本包括了这些特性
- Enhanced concurrency & scalability: the “Google SMP patch” using atomic instructions for mutexing
- 增强的并发可可伸缩性:”Google 多处理机 补丁” 为Mutext锁操作使用原子操作
- More efficient memory allocation: ability to use more scalable platform memory allocator
- 更有效的内存分配:可以使用更多的可扩展内存 分配器(例如tcmalloc)
- Improved out-of-the-box scalability: unlimited concurrent thread execution by default
- 改进的即装即用扩展性:默认无限制的线程并发
- Dynamic tuning: at run-time, enable or disable insert buffering and adaptive hash indexing
- 动态优化调整:在运行时,打开或者关闭插入缓 存和自适应哈希索引
These new performance features can yield?up to twice the throughput or more, depending on your workload, platform and other tuning considerations. In another post, we explore some details about these changes, but first, what do these enhancements mean for performance and scalability?
这些新的性能特新可以提升多大两倍甚至更多的的吞吐量,这依赖于你的负载,平台和其他调整事项。在另一篇文章中,我们会探 讨这些改变的一些细节,但首先,我们现探讨这些性能和可扩展性的增强是什么意思,包括哪些内容
In brief, we’ve tested three different workloads (joins, DBT2 OLTP and a modified sysbench) using a memory-resident database. In all cases, the InnoDB Plugin scales significantly better than the built-in InnoDB in MySQL 5.1. And in some cases, the absolute level of performance is dramatically higher too! The charts below illustrate the kinds of performance gains we’ve measured with release 1.0.3 of the InnoDB Plugin. Your mileage may vary, of course. See the?InnoDB website for all the details on these tests.
总之,我们已经使用内存驻留数据库(所有数据都载入在内存中)测试了三种不同的工作负载(关联,DBT2 OLTP和修改过的sysbench)。在所有的情况下,InnoDB Plugin的伸缩性明显优于MySQL 5.1内置的InnoDB。在一些场景中,性能提升的水平高的惊人。下面的图说明了InnoDB Plugin 1.0.3的性能提升。你的测试结果可能不同,当然可以在InnoDB网站看到所有测试的细节。
This release of the InnoDB Plugin incorporates a?patch made by Ben Handy and Mark Callaghan at Google to improve multi-core scalability by using more efficient synchronization methods (mutexing and rw-locks) to reduce cpu utilization and contention. We’re grateful for this contribution, and you will be too!
这个InnoDB Plugin版本包含了Google的Ben Handy和Mark Callaghan的补丁来提升多处理机扩展性,包括使用了更有效的同步机制(Mutexing和RW-Locks)来减少CPU利用和竞争。我们非常感 谢这个补丁的贡献,相信你也是。
Now to our test results …
现在来看我们的测试结果…
连接:下图显示了执行连接时的性能提升,比较了 MySQL 中的内置 InnoDB(蓝色)与 InnoDB 插件 1.0.3(红色)。
关联:下图展示了执行Join操作时的性能提升,内置InnoDB(蓝)和InnoDB Plugin 1.0.3(红)的比较。

从上图中的蓝色条可以看出,使用内置InnoDB的MySQL 5.1,系统可以执行的Join总数随着并发用户数的增加而下降。相比之下,InnoDB Plugin 即使只有一个用户,性能也会略有提高,并且随着用户数量的增加而保持性能。这种性能提升很大程度上归功于 InnoDB 插件中使用原子进行互斥。
正如你在上面蓝柱上看到的速度,MySQL 5.1的内置InnoDB,随着并发数的增加系统的执行速度反而恢复了。与此相反,InnoDB Plugin随着并发数的提升处理甚至达到了提高,并且随着用户的增长保持这种性能。这种性能很大程度上是因为对互斥使用了原子操作。
事务处理 (DBT2): 下图展示了使用 OLTP 读/写 DBT2 基准测试的可扩展性改进,再次比较了 MySQL 中内置 InnoDB 的性能与? InnoDB 插件 1.0.3.
事务处理(DBT2):下入展示了用DBT2测试OLTP读写性能的提升,再次比较了内置InnoDB和InnoDB Plugin 1.0.3的性能。

这里,当遇到其他瓶颈或达到系统容量时,InnoDB 插件比内置 InnoDB 可以更好地从 16 个用户扩展到 32 个用户,并在 64 个并发用户下产生约 12% 的吞吐量。这种改进同样主要是由于互斥的变化。
这里,InnoDB Plugin伸缩性在16增加到32线程时表现更好,产生比64线程多大约12%的吞吐量。由于其他性能瓶颈或系统容量达到核心。这个提升仍然主要依赖于Mutexing的改变。
修改的 Sysbench: 此测试使用众所周知的 sysbench 工作负载的一个版本,并根据 Google 的 Mark Callaghan 的建议进行了修改,以包括基于二级索引的查询。
过的sysbench:本次测试使用了著名的sysbench,修改包括基于非主键索引的查询,由Google的Mark Callaghan建议修改。

这次,InnoDB 插件在 8 到 64 个用户的范围内显示出比 MySQL 中内置 InnoDB 更好的可扩展性,在 64 个用户时吞吐量提高了 60%。与前面的示例一样,这种改进很大程度上归功于使用原子进行互斥。
这次,InnoDB Plugin在8~64线程都表现出了明显的内置InnoDB的可伸缩性。在64并发时达到60%的性能提升!像之前的一个例子,这个提升依然主要靠Mutexing的原子性。
使用 tcmalloc 修改的 Sysbench: 此测试使用相同的修改后的 sysbench 工作负载,但显示了内置 InnoDB(使用内部 InnoDB 内存分配器)和 InnoDB 插件在使用更多内存时的差异。可扩展的内存分配器,在本例中是?tcmalloc。
使用 tcmalloc 的修改过的 sysbench:这种测试使用相同的 sysbench 场景,但是中间插入了 InnoDB 或 InnoDB Plugin 使用了 tcmalloc 作为内存分配器。

When the new configuration parameter?innodb_use_sys_malloc is set to enable use of the memory allocator tcmalloc, the InnoDB Plugin really shines! Transaction throughput continues to scale, and the actual throughput with 64 users has nearly doubled!
当设置innodb_user_sys_malloc变量为tcmalloc作为内存分配器时,InnoDB Plugin依然是亮点!事务吞吐量继续扩展,在64并发时吞吐量提升接近1倍(相对没有tcmalloc的)。
 从头开始,逐步指导您安装Flask,快速建立个人博客Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
从头开始,逐步指导您安装Flask,快速建立个人博客Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:01 PM从零开始,手把手教你安装Flask和快速搭建个人博客作为一个喜欢写作的人来说,拥有一个个人博客是非常重要的。而Flask作为一个轻量级的PythonWeb框架,可以帮助我们快速搭建一个简洁而功能完善的个人博客。在本文中,我将从零开始,手把手教你如何安装Flask并快速搭建个人博客。第一步:安装Python和pip在开始之前,我们需要先安装Python和pi
 2022年十大开源php博客系统有哪些?【推荐】Jul 27, 2022 pm 05:38 PM
2022年十大开源php博客系统有哪些?【推荐】Jul 27, 2022 pm 05:38 PM博客,又译为网络日志、部落格或部落阁等,是一种通常由个人管理、不定期张贴新的文章的网站。那么怎么搭建博客?PHP博客系统有哪些?哪个博客系统好用?下面PHP中文网就来给大家总结分享十大开源php博客系统,一起来看看吧!
 创建一个简单的博客:使用PHP和SQLiteJun 21, 2023 pm 01:23 PM
创建一个简单的博客:使用PHP和SQLiteJun 21, 2023 pm 01:23 PM随着互联网的发展,博客成为越来越多人分享自己生活、知识和想法的平台。如果你也想创建一个自己的博客,那么本文将介绍如何使用PHP和SQLite来创建一个简单的博客。确定需求在开始创建博客之前,我们需要确定自己想要实现的功能。例如:创建博客文章编辑博客文章删除博客文章显示博客文章列表显示博客文章详情用户认证和权限控制安装PHP和SQLite我们需要安装PHP和S
 mysql innodb是什么Apr 14, 2023 am 10:19 AM
mysql innodb是什么Apr 14, 2023 am 10:19 AMInnoDB是MySQL的数据库引擎之一,现为MySQL的默认存储引擎,为MySQL AB发布binary的标准之一;InnoDB采用双轨制授权,一个是GPL授权,另一个是专有软件授权。InnoDB是事务型数据库的首选引擎,支持事务安全表(ACID);InnoDB支持行级锁,行级锁可以最大程度的支持并发,行级锁是由存储引擎层实现的。
 MySQL如何从二进制内容看InnoDB行格式Jun 03, 2023 am 09:55 AM
MySQL如何从二进制内容看InnoDB行格式Jun 03, 2023 am 09:55 AMInnoDB是一个将表中的数据存储到磁盘上的存储引擎,所以即使关机后重启我们的数据还是存在的。而真正处理数据的过程是发生在内存中的,所以需要把磁盘中的数据加载到内存中,如果是处理写入或修改请求的话,还需要把内存中的内容刷新到磁盘上。而我们知道读写磁盘的速度非常慢,和内存读写差了几个数量级,所以当我们想从表中获取某些记录时,InnoDB存储引擎需要一条一条的把记录从磁盘上读出来么?InnoDB采取的方式是:将数据划分为若干个页,以页作为磁盘和内存之间交互的基本单位,InnoDB中页的大小一般为16
 使用Python Django框架构建博客网站Jun 17, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
使用Python Django框架构建博客网站Jun 17, 2023 pm 03:37 PM随着互联网的普及,博客在信息传播和交流方面扮演着越来越重要的角色。在此背景下,越来越多的人开始构建自己的博客网站。本文将介绍如何使用PythonDjango框架来构建自己的博客网站。一、PythonDjango框架简介PythonDjango是一个免费的开源Web框架,可用于快速开发Web应用程序。该框架为开发人员提供了强大的工具,可帮助他们构建功能丰
 mysql innodb异常怎么处理Apr 17, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
mysql innodb异常怎么处理Apr 17, 2023 pm 09:01 PM一、回退重新装mysql为避免再从其他地方导入这个数据的麻烦,先对当前库的数据库文件做了个备份(/var/lib/mysql/位置)。接下来将Perconaserver5.7包进行了卸载,重新安装原先老的5.1.71的包,启动mysql服务,提示Unknown/unsupportedtabletype:innodb,无法正常启动。11050912:04:27InnoDB:Initializingbufferpool,size=384.0M11050912:04:27InnoDB:Complete
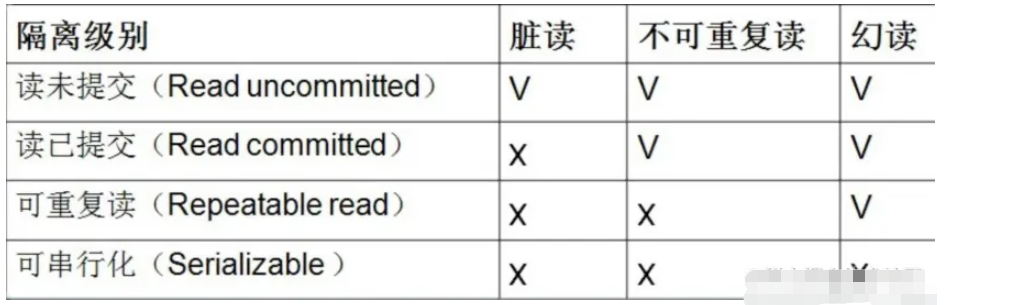 Mysql中的innoDB怎么解决幻读May 27, 2023 pm 03:34 PM
Mysql中的innoDB怎么解决幻读May 27, 2023 pm 03:34 PM1.Mysql的事务隔离级别这四种隔离级别,当存在多个事务并发冲突的时候,可能会出现脏读,不可重复读,幻读的一些问题,而innoDB在可重复读隔离级别模式下解决了幻读的一个问题,2.什么是幻读幻读是指在同一个事务中,前后两次查询相同范围的时候得到的结果不一致如图,第一个事务里面,我们执行一个范围查询,这个时候满足条件的数据只有一条,而在第二个事务里面,它插入一行数据并且进行了提交,接着第一个事务再去查询的时候,得到的结果比第一次查询的结果多出来一条数据,注意第一个事务的第一次和第二次查询,都在同


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能





