DOM 導航
XML DOM - 導航節點
可透過使用節點間的關係對節點進行導航。
導覽 DOM 節點
透過節點間的關係存取節點樹中的節點,通常稱為導覽節點("navigating nodes")。
在XML DOM 中,節點的關係被定義為節點的屬性:
#parentNode
- ##childNodes
- #firstChild
- lastChild
- nextSibling
- previousSibling
books.xml 中節點樹的一個部分,並說明了節點之間的關係:
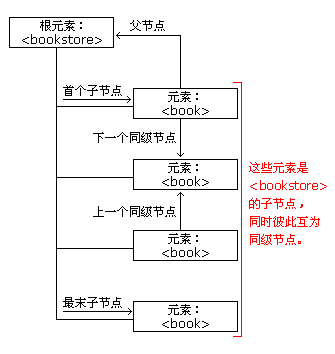
DOM - 父節點所有的節點都只有一個父節點。下面的程式碼導覽到<book> 的父節點:
實例#
運行實例»##點擊"執行實例" 按鈕查看線上實例實例解釋:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="loadxmldoc.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("books.xml");
x=xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0];
document.write(x.parentNode.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>運行實例»##點擊"執行實例" 按鈕查看線上實例實例解釋:
- #使用loadXMLDoc() 把"books.xml" 載入xmlDoc 中
- 取得第一個<book> 元素
- #輸出"x" 的父節點的節點名稱
Firefox 以及其他一些瀏覽器,把空的空白或換行當作文字節點,而Internet Explorer 不會這麼做。
這會在使用以下屬性:firstChild、lastChild、nextSibling、previousSibling 時產生一個問題。
為了避免導航到空的文字節點(元素節點之間的空格和換行符),我們使用一個函數來檢查節點類型:
function get_nextSibling(n){
nodey=n.nextSibling;
while (y.nodeType!=1)
{
y=y.nextSibling;
}
return y;
}
上面的函數可讓您使用 get_nextSibling(while (y.nodeType!=1)
{
y=y.nextSibling;
}
return y;
}
)來取代 node.nextSibling 屬性。 程式碼解釋:
元素節點的類型是 1。如果同級節點不是元素節點,就移動到下一個節點,直到找到元素節點。透過這個辦法,在 Internet Explorer 和 Firefox 中,都可以得到相同的結果。
取得第一個子元素下面的程式碼顯示第一個<book> 的第一個元素:
##實例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="loadxmldoc.js">
</script>
<script>
//check if the first node is an element node
function get_firstChild(n)
{
y=n.firstChild;
while (y.nodeType!=1)
{
y=y.nextSibling;
}
return y;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("books.xml");
x=get_firstChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0]);
document.write(x.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>運行實例»
點擊"運行實例" 按鈕查看線上實例#
實例解釋:
使用loadXMLDoc() 把"books.xml" 載入xmlDoc
在第一個< book> 元素上使用get_firstChild 函數,來取得第一個子節點(屬於元素節點)
輸出第一個子節點(屬於元素節點)的節點名稱
 更多實例
更多實例
#lastChild()
本範例使用lastChild() 方法和一個自訂函數來取得節點的最後一個子節點
實例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="loadxmldoc.js">
</script>
<script>
//check if the first node is an element node
function get_lastChild(n)
{
y=n.lastChild;
while (y.nodeType!=1)
{
y=y.previousSibling;
}
return y;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("books.xml");
x=get_lastChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0]);
document.write(x.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>運行實例»
點擊"運行實例" 按鈕檢視線上實例
nextSibling()
本例使用nextSibling() 方法和一個自訂函數來取得節點的下一個同級節點
實例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="loadxmldoc.js">
</script>
<script>
//check if the first node is an element node
function get_nextSibling(n)
{
y=n.nextSibling;
while (y.nodeType!=1)
{
y=y.nextSibling;
}
return y;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("books.xml");
x=get_nextSibling(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("title")[0]);
document.write(x.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>運行實例»
點擊"運行實例" 按鈕查看線上實例
previousSibling()
本範例使用previousSibling() 方法和一個自訂函數來取得節點的上一個同級節點
#實例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="loadxmldoc.js">
</script>
<script>
//check if the first node is an element node
function get_previousSibling(n)
{
y=n.previousSibling;
while (y.nodeType!=1)
{
y=y.previousSibling;
}
return y;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
xmlDoc=loadXMLDoc("books.xml");
x=get_previousSibling(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("price")[0]);
document.write(x.nodeName);
</script>
</body>
</html>執行實例»
點擊"運行實例" 按鈕查看線上實例








