LayoutInflater(佈局服務)
本節引言:
本節繼續帶來的是Android系統服務中的LayoutInflater(佈局服務),說到佈局,大家第一時間 可能會想起的是寫完一個佈局的xml,然後呼叫Activity的setContentView()載入佈局,然後把他顯示 到螢幕上是吧~其實這個底層走的還是這個LayoutInflater,用的Android內建的Pull解析器來解析 佈局。一般在Android動態載入佈局或新增控制用得較多,本節我們就來學習下他在實際開發中 的一些用法~
官方API文檔:LayoutInflater
1.LayoutInflater的相關介紹
1)Layout是什麼鬼?
答:一個用來載入佈局的系統服務,就是實例化與Layout XML檔案對應的View對象,不能直接使用, 需要透過getLayoutInflater( )方法或getSystemService( )方法來取得與目前Context綁定的 LayoutInflater實例!
2)LayoutInflater的用法
①取得LayoutInflater實例的三種方法:
LayoutInflater inflater1 = LayoutInflater.from(this); LayoutInflater inflater2 = getLayoutInflater(); LayoutInflater inflater3 = (LayoutInflater) getSystemService(LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
PS:後面兩個其實底層走的都是第一種方法~
##②載入佈局的方法:
public Viewinflate (int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) 此方法的三個參數依序為:
①要載入的佈局對應的資源id#②為該佈局的外部再嵌套一層父佈局,如果不需要的話,寫null就可以了!③是否為載入的佈局檔案的最外層套一層root佈局,不設定該參數的話, 如果root不為null的話,則預設為true 如果root為null的話,attachToRoot就沒有作用了! root不為null,attachToRoot為true的話,會在載入的佈局檔案最外層嵌套一層root佈局; 為false的話,則root失去作用! 簡單理解就是:是否為載入的佈局添加一個root的外層容器~!
#③透過LayoutInflater.LayoutParams來設定相關的屬性:
例如RelativeLayout還可以透過addRule方法加入規則,就是設定位置:是參考父容器呢? 還是參考子控制項?又或者設定margin等等,這個由你決定~
2.純Java程式碼載入版面配置
我們早已習慣了使用XML產生我們需要的佈局,但是在一些特定的情況下,我們 需要使用Java程式碼往我們的佈局中動態的新增元件或佈局! 但不建議大家完全使用Java程式碼來寫Android頁面佈局,首先一點就是程式碼會多, 一多久容易亂,而且不利於業務的分離,我們還是建議使用xml來完成佈局,然後透過 Java程式碼對裡面的元件進行修改,當然有些時候可能需要使用Java動態的來新增元件!
純Java程式碼載入佈局的流程:
#——Step 1:
①建立容器:LinearLayout ly = new LinearLayout(this);
②建立元件:Button btnOne = new Button(this);
— —Step 2:
可以為容器或元件設定相關屬性: 例如:LinearLayout,我們可以設定元件的排列方向:ly.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);而元件也可以:例如Button:btnOne.setText("按鈕1");關於設定屬性的方法可參考Android 的API,通常xml設定的屬性只需在前面新增:set即可,例如setPadding(左,上,右,下) ;
——Step 3:
將元件或容器加入容器中,這個時候我們可能需要設定下元件的新增位置,或設定他的大小: 我們需要用到一個類別:LayoutParams,我們可以把它看成佈局容器的資訊包!封裝位置與大小 等資訊的一個類別!先示範下設定大小的方法:(前面的LinearLayout可以根據不同容器進行更改)
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp1 = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams( LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
很簡單,接著就到這個設定位置了,設定位置的話,通常我們考慮的只是RelativeLayout! 這時候用到LayoutParams的addRule( )方法!可以加入多個addRule( )喔! 設定元件在父容器中的位置,
例如設定元件的對其方式:
RelativeLayout rly = new RelativeLayout(this); RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp2 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams( LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); lp2.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_PARENT_BOTTOM); Button btnOne = new Button(this); rly.addView(btnOne, lp2);
參考其他元件的對其方式: (有個缺點,就是要為參考元件手動設定一個id,是手動!!!!) 例如:設定btnOne居中後,讓BtnTwo位於btnOne的下方以及父容器的右邊!
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
RelativeLayout rly = new RelativeLayout(this);
Button btnOne = new Button(this);
btnOne.setText("按钮1");
Button btnTwo = new Button(this);
btnTwo.setText("按钮2");
// 为按钮1设置一个id值
btnOne.setId(123);
// 设置按钮1的位置,在父容器中居中
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rlp1 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
rlp1.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT);
// 设置按钮2的位置,在按钮1的下方,并且对齐父容器右面
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams rlp2 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
rlp2.addRule(RelativeLayout.BELOW, 123);
rlp2.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_PARENT_RIGHT);
// 将组件添加到外部容器中
rly.addView(btnTwo, rlp2);
rly.addView(btnOne, rlp1);
// 设置当前视图加载的View即rly
setContentView(rly);
}
}——step 4:
呼叫setContentView( )方法載入佈局對象即可! 另外,如果你想移除某個容器中的View,可以呼叫容器.removeView(要移除的元件);
運行截圖:
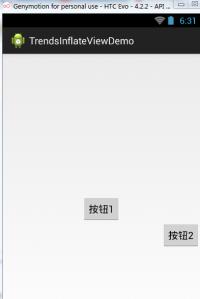
3.Java程式碼動態新增控製或xml佈局
#第二點我們解說了使用純Java程式碼來載入佈局,實際當中用得不多,更多的時候是動態 的新增View控制項以及動態的載入XML佈局!
1)Java程式碼動態增加View
動態新增元件的寫法有兩種,差別在於是否需要先setContentView(R.layout .activity_main); 下面示範下兩種不同寫法加入一個Button的範例:
先寫個佈局檔先:activity_main.xml:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/RelativeLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TextView android:id="@+id/txtTitle" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="我是xml文件加载的布局"/> </RelativeLayout>
第一種不需要setContentView()載入佈局檔先:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Button btnOne = new Button(this);
btnOne.setText("我是动态添加的按钮");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp2 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
lp2.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
RelativeLayout rly = (RelativeLayout) inflater.inflate(
R.layout.activity_main, null)
.findViewById(R.id.RelativeLayout1);
rly.addView(btnOne,lp2);
setContentView(rly);
}
}第二種不需要setContentView()載入佈局檔先:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btnOne = new Button(this);
btnOne.setText("我是动态添加的按钮");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp2 = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
lp2.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT);
RelativeLayout rly = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.RelativeLayout1);
rly.addView(btnOne,lp2);
}
}分析總結:
程式碼很簡單,建立按鈕後,我們又建立了一個LayoutParams對象,用來設定Button的大小, 又透過addRule()方法設定了Button的位置!
第一種方法:透過LayoutInflate的inflate()方法載入了activity_main佈局,獲得了外層容器, 接著addView新增按鈕進容器,最後setContentView();
第二種方法:因為我們已經透過setContetView()方法載入了佈局,此時我們就可以透過 findViewById找到這個外層容器,接著addView,最後setContentView()即可!
#另外,關於這個setContentView( )他設定的視圖節點是整個XML的根節點!
2)Java程式碼動態載入xml佈局
接下來的話,我們換一個,這次載入的是xml檔!動態地加入xml檔! 先寫下主佈局檔案和動態載入的佈局檔案:
activity_main.xml:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/RelativeLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button android:id="@+id/btnLoad" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="动态加载布局"/></RelativeLayout>
inflate.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center" android:orientation="vertical" android:id="@+id/ly_inflate" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="我是Java代码加载的布局" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="我是布局里的一个小按钮" /> </LinearLayout>
接著到我們的MainActivity.java在這裡動態載入xml佈局:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//获得LayoutInflater对象;
final LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
//获得外部容器对象
final RelativeLayout rly = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.RelativeLayout1);
Button btnLoad = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnLoad);
btnLoad.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//加载要添加的布局对象
LinearLayout ly = (LinearLayout) inflater.inflate(
R.layout.inflate, null, false).findViewById(
R.id.ly_inflate);
//设置加载布局的大小与位置
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
lp.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT);
rly.addView(ly,lp);
}
});
}
}運行截圖:
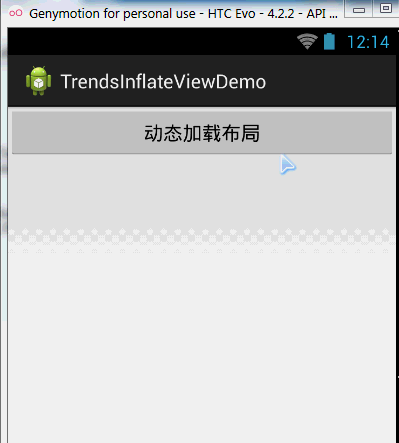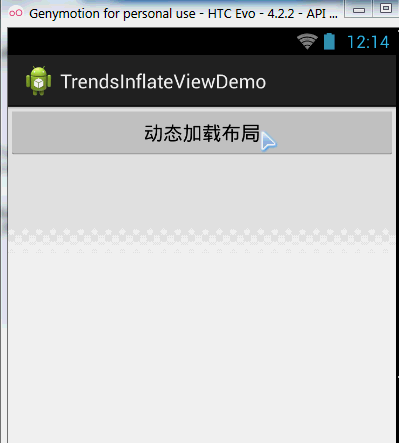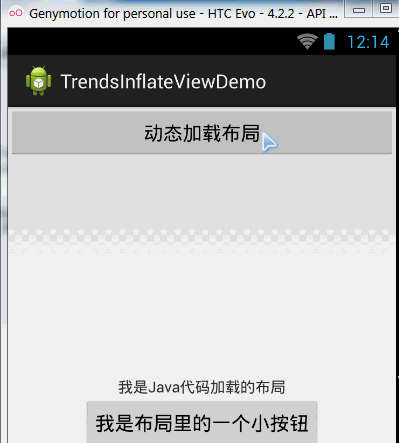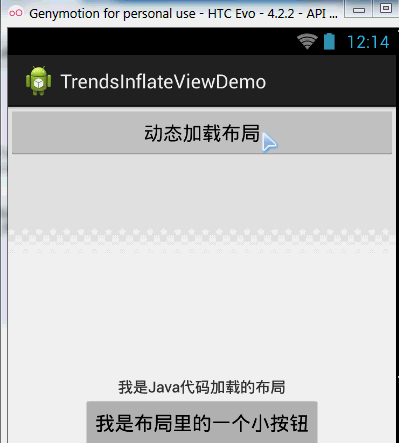
程式碼分析:
①取得容器物件:
final RelativeLayout rly = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.RelativeLayout1);②取得Inflater物件,同時加載被加入的佈局的xml,透過findViewById找到最外層的根節點
final LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this); LinearLayout ly = (LinearLayout) inflater.inflate(R.layout.inflate, null, false) .findViewById(R.id.ly_inflate);③為這個容器設定大小與位置資訊:
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams( LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); lp.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT);④加入外層容器:
rly.addView(ly,lp);
4.LayoutInflater的inflate()方法原始碼
最後提供下LayoutInflater的inflate ()方法的源碼吧,有興趣的可以看看~,其實就是Pull解析而已~
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
mConstructorArgs[0] = mContext;
View result = root;
try {
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
}
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": No start tag found!");
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("merge can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
}
rInflate(parser, root, attrs);
} else {
View temp = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
if (root != null) {
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (!attachToRoot) {
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
rInflate(parser, temp, attrs);
if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
root.addView(temp, params);
}
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
result = temp;
}
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
} catch (IOException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(
parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": " + e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
}
return result;
}
}本節小結:
本節給大家講解了一下Android中的LayoutInflater(佈局服務),以及動態載入View和控件 相關的東西,相信對初學控件的朋友帶來幫助~好的,就說這麼多,謝謝~









