Linux指令lsscsi詳解
- 王林轉載
- 2024-02-11 14:12:031349瀏覽
要了解lsscsi指令,首先我們需要了解什麼是SCSI以及常見的硬碟介面和常用的硬碟參數。
一、什麼是SCSI?
#SCSI(Small Computer System Interface)是一種完整的資料傳輸協議,它主要用於在主機和儲存裝置之間傳輸命令、狀態和區塊資料。在各種儲存技術中,SCSI技術是最重要的支柱。
SCSI協定位於作業系統和外部資源之間,它具有一系列功能元件。作業系統對外部設備(如磁碟、磁帶、光碟、印表機等)的I/O操作都可以透過SCSI協定來實現。通常情況下,SCSI協定會嵌入到裝置驅動程式或主機適配器的板載邏輯中。
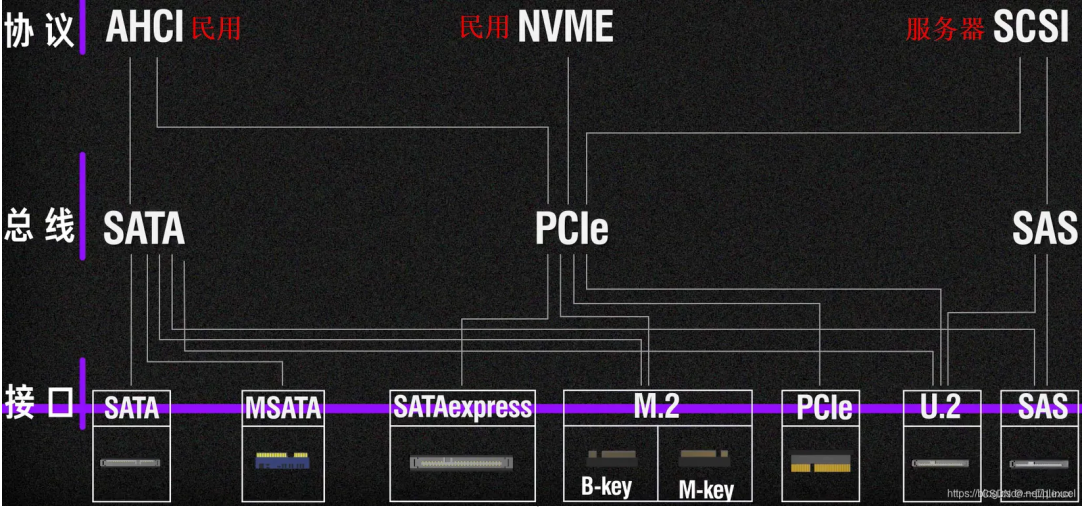
二、常見硬碟介面
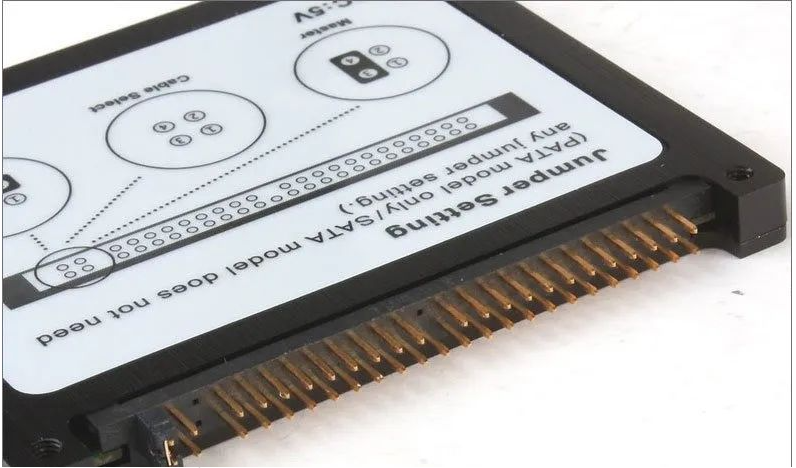
#1. IDE介面的硬碟
其英文名稱:Integrated Drive Electronics,常見的2.5吋IDE硬碟介面它的本意是指把「硬碟控制器」與「磁碟機」整合在一起的硬碟。
IDE代表著硬碟的一種類型,但在實際的應用中,人們也習慣用IDE來稱呼最早出現IDE類型硬碟ATA-1,這種類型的介面隨著介面技術的發展已經被淘汰了,而其後發展分支出更多類型的硬碟接口,例如ATA、Ultra ATA、DMA、Ultra DMA等介面都屬於IDE硬碟。
其特點為:價格低廉,相容性強,性價比高,資料傳輸慢,不支援熱插拔等等。

2. SCSI介面硬碟
#SCSI並不是專為硬碟設計的接口,是一種廣泛應用於小型機上的高速資料傳輸技術。
SCSI介面具有應用範圍廣、多任務、頻寬大、CPU佔用率低,以及熱插拔等優點,但較高的價格使得它很難如IDE硬碟般普及,因此SCSI硬碟主要應用於中、高階伺服器和高檔工作站中。
其特點為:傳輸速率高、讀寫性能好、可連接多個設備、可支援熱插拔,但是價格相對來說比較貴。

3. SATA介面類型
其英文名稱為:Serial Advanced Technology Attachment。使用SATA(Serial ATA)口的硬碟又叫串列式硬碟,是未來PC機硬碟的趨勢。
Serial ATA採用串列連接方式,串列ATA匯流排使用嵌入式時脈訊號,具備了更強的糾錯能力,與以往相比其最大的差異在於能對傳輸指令(不只是資料)進行檢查,如果發現錯誤會自動矯正,這在很大程度上提高了資料傳輸的可靠性。
串行介面還具有結構簡單、支援熱插拔的優點。
三、 lsscsi指令
lsscsi列出scsi/sata設備訊息,例如硬碟驅動器,光碟機。
1. lsscsi 指令安裝
-bash: lsscsi command not found #Debian apt-get install lsscsi #Ubuntu apt-get install lsscsi #Alpine apk add lsscsi #Arch Linux pacman -S lsscsi #Kali Linux apt-get install lsscsi #CentOS yum install lsscsi #Fedora dnf install lsscsi #Raspbian apt-get install lsscsi #Docker docker run cmd.cat/lsscsi lsscsi
2. lsscsi指令英文手冊
詳細命令說明位址
https://sg.danny.cz/scsi/lsscsi.html

2. 指令格式
lsscsi 指令語法:
lsscsi [选项] [H:C:T:L]
lsscsi 指令選項:
| 選項 | #意義 |
|---|---|
| -g | 顯示SCSI通用設備檔案名稱 |
| -k | 顯示核心名稱而不是裝置節點名稱 |
| -d | 顯示設備節點的主要號碼和次要號碼 |
| -H | 列出目前連接到系統的SCSI主機而不是SCSI設備 |
| -l | 顯示每一個SCSI設備(主機)的附加資訊 |
| -c | 相對於執行 cat /proc/scsi/scsi 指令的輸出 |
| -p | 顯示額外的資料完整性(保護)的資訊 |
| -t | 顯示傳輸訊息 |
| -L | 以「屬性名稱=值」的方式顯示附加資訊 |
| -v | 當資訊找到時輸出目錄名稱 |
| -y | 假設sysfs掛載在指定路徑而不是預設的 “/sys” |
| -s | 顯示容量大小。 |
| -c | 用全名顯示預設的資訊。 |
| -d | 顯示設備主,次設備號。 |
| -g | 顯示對應的sg裝置名稱。 |
| -H | 顯示主機控制器列表,-Hl,-Hlv。 |
| -l | 顯示相關屬性,-ll,-lll=-L。 |
| -v | 顯示設備屬性所在目錄。 |
| -x | 以16進位顯示lun號。 |
| -p | 輸出DIF,DIX 保護類型。 |
| -P | 輸出有效的保護模式資訊。 |
| -i | 顯示udev相關的屬性 |
| -w | 顯示WWN |
| -t | 顯示對應傳輸訊息(ATA,FC,SBP,ISCSI,SPI,SAS,SATA,USB),-Ht,-tl.(包括sas位址) |
3. 结果含义

四、命令举例
lsscsi 列出所有 SCSI 设备:
peng@ubuntu:~$ lsscsi [3:0:0:0] cd/dvd NECVMWar VMware SATA CD01 1.00 /dev/sr0 [32:0:0:0] disk VMware, VMware Virtual S 1.0 /dev/sda
lsscsi -L列出所有具有详细属性的 SCSI 设备:
peng@ubuntu:~$ lsscsi -L [3:0:0:0] cd/dvd NECVMWar VMware SATA CD01 1.00 /dev/sr0 device_blocked=0 iocounterbits=32 iodone_cnt=0x229 ioerr_cnt=0x4 iorequest_cnt=0x23a queue_depth=1 queue_type=none scsi_level=6 state=running timeout=30 type=5 [32:0:0:0] disk VMware, VMware Virtual S 1.0 /dev/sda device_blocked=0 iocounterbits=32 iodone_cnt=0x37370 ioerr_cnt=0x3 iorequest_cnt=0x37370 queue_depth=32 queue_type=simple scsi_level=3 state=running timeout=180 type=0
lsscsi -s列出所有具有人类可读磁盘容量的 SCSI 设备:
peng@ubuntu:~$ lsscsi -s [3:0:0:0] cd/dvd NECVMWar VMware SATA CD01 1.00 /dev/sr0 - [32:0:0:0] disk VMware, VMware Virtual S 1.0 /dev/sda 536GB
五、其他
1. Linux下scsi相关文件节点
/proc/scsi/
peng@ubuntu:~$ cd /proc/scsi/ peng@ubuntu:/proc/scsi$ ls device_info mptspi scsi sg peng@ubuntu:/proc/scsi$ cat scsi Attached devices: Host: scsi32 Channel: 00 Id: 00 Lun: 00 Vendor: VMware, Model: VMware Virtual S Rev: 1.0 Type: Direct-Access ANSI SCSI revision: 02 Host: scsi3 Channel: 00 Id: 00 Lun: 00 Vendor: NECVMWar Model: VMware SATA CD01 Rev: 1.00 Type: CD-ROM ANSI SCSI revision: 05
/sys/class/scsi_host
peng@ubuntu:/sys/class/scsi_host$ ls host0 host12 host16 host2 host23 host27 host30 host5 host9 host1 host13 host17 host20 host24 host28 host31 host6 host10 host14 host18 host21 host25 host29 host32 host7 host11 host15 host19 host22 host26 host3 host4 host8
/sys/class/scsi_device
peng@ubuntu:/sys/class/scsi_device$ ls 3:0:0:0 32:0:0:0
/sys/class/scsi_disk
peng@ubuntu:/sys/class/scsi_disk$ ls 32:0:0:0
/sys/class/scsi_generic
peng@ubuntu:/sys/class/scsi_generic$ ls sg0 sg1
/sys/bus/scsi
peng@ubuntu:/sys/bus/scsi$ ls devices drivers drivers_autoprobe drivers_probe uevent peng@ubuntu:/sys/bus/scsi/devices$ ls 3:0:0:0 host11 host16 host20 host25 host3 host5 target3:0:0 32:0:0:0 host12 host17 host21 host26 host30 host6 target32:0:0 host0 host13 host18 host22 host27 host31 host7 host1 host14 host19 host23 host28 host32 host8 host10 host15 host2 host24 host29 host4 host9
其中target3:0:0
对应
host:bus:id:lun
2. Linux 开启 SCSI 日志调试功能
- 1.编译选项中需开启 CONFIG_SCSI_LOGGING
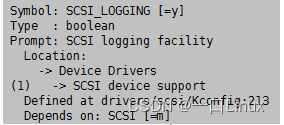
- 2.该编译选项说明
drivers/scsi/Kconfig:213 config SCSI_LOGGING bool "SCSI logging facility" depends on SCSI ---help--- This turns on a logging facility that can be used to debug a number of SCSI related problems. If you say Y here, no logging output will appear by default, but you can enable logging by saying Y to "/proc file system support" and "Sysctl support" below and executing the command echo > /proc/sys/dev/scsi/logging_level where is a four byte value representing the logging type and logging level for each type of logging selected. There are a number of logging types and you can find them in the source at . The logging levels are also described in that file and they determine the verbosity of the logging for each logging type. If you say N here, it may be harder to track down some types of SCSI problems. If you say Y here your kernel will be somewhat larger, but there should be no noticeable performance impact as long as you have logging turned off.
- 3.logging 类型源码文件位置(有说明)
-> drivers\scsi\scsi_logging.h
- 4.使用说明
/* * Note - the initial logging level can be set here to log events at boot time. * After the system is up, you may enable logging via the /proc interface. */ unsigned int scsi_logging_level; #if defined(CONFIG_SCSI_LOGGING) EXPORT_SYMBOL(scsi_logging_level); #endif
scsi_logging_level 被定义成int类型(32bit),该机制使用了30个bit,从低位到高位每3bit为一个logging level从SCSI_LOG_ERROR_SHIFT到SCSI_LOG_IOCTL_SHIFT(SCSI_LOG_XXX_SHIFT为不同level的移位数),每个level使用的bit数都是3,所以 SCSI_LOG_XXX_BITS 均为3
- 5.scsi_logging_level 值可以在 boot 命令行设置也可以开启设备后在 /proc 文件系统中设置:
-1 - Enable scsi events to syslog. // 开启所有scsi log 0 - Disable scsi events to syslog. // 关闭所有scsi log
命令:
echo 0/-1 > /proc/sys/dev/scsi/logging_level
以上是Linux指令lsscsi詳解的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

