Java日常開發的21個坑,你踩過幾個?
- Java后端技术全栈轉載
- 2023-08-24 15:47:22794瀏覽
#前言
#最近看了極客時間的《Java業務開發常見錯誤100例》,再結合平時踩的一些代碼坑,寫寫總結,希望對大家有幫助,感謝閱讀~
1. 六類典型空指標問題
#包裝類型的空指標問題 級聯呼叫的空指標問題 #Equals方法左邊的空指標問題 -
ConcurrentHashMap 這樣的容器不支援Key 和Value 為null。 集合,陣列直接取得元素 物件直接取得屬性
1.1包裝類型的空指標問題
public class NullPointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(testInteger(null));
}
private static Integer testInteger(Integer i) {
return i + 1; //包装类型,传参可能为null,直接计算,则会导致空指针问题
}
}1.2級聯呼叫的空指標問題
public class NullPointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//fruitService.getAppleService() 可能为空,会导致空指针问题
fruitService.getAppleService().getWeight().equals("OK");
}
}#1.3 Equals方法左邊的空指標問題
#public class NullPointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = null;
if (s.equals("666")) { //s可能为空,会导致空指针问题
System.out.println("公众号:捡田螺的小男孩,666");
}
}
}1.4 ConcurrentHashMap 這樣的容器不支援Key,Value 是null。
public class NullPointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
String key = null;
String value = null;
map.put(key, value);
}
}1.5 集合,数组直接获取元素
public class NullPointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] array=null;
List list = null;
System.out.println(array[0]); //空指针异常
System.out.println(list.get(0)); //空指针一场
}
}1.6 对象直接获取属性
public class NullPointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user=null;
System.out.println(user.getAge()); //空指针异常
}
}2. 日期YYYY格式设置的坑
日常开发,经常需要对日期格式化,但是呢,年份设置为YYYY大写的时候,是有坑的哦。
反例:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(2019, Calendar.DECEMBER, 31);
Date testDate = calendar.getTime();
SimpleDateFormat dtf = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-dd");
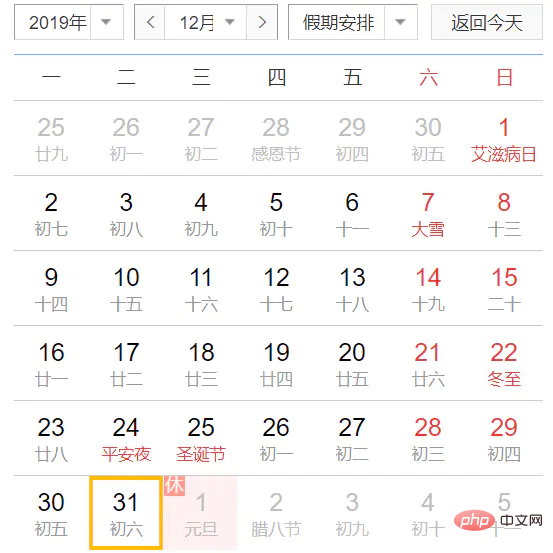
System.out.println("2019-12-31 转 YYYY-MM-dd 格式后 " + dtf.format(testDate));运行结果:
2019-12-31 转 YYYY-MM-dd 格式后 2020-12-31
「解析:」
为什么明明是2019年12月31号,就转了一下格式,就变成了2020年12月31号了?因为YYYY是基于周来计算年的,它指向当天所在周属于的年份,一周从周日开始算起,周六结束,只要本周跨年,那么这一周就算下一年的了。正确姿势是使用yyyy格式。
正例:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(2019, Calendar.DECEMBER, 31);
Date testDate = calendar.getTime();
SimpleDateFormat dtf = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-dd");
System.out.println("2019-12-31 转 YYYY-MM-dd 格式后 " + dtf.format(testDate));3.金额数值计算精度的坑
看下这个浮点数计算的例子吧:
public class DoubleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(0.1+0.2);
System.out.println(1.0-0.8);
System.out.println(4.015*100);
System.out.println(123.3/100);
double amount1 = 3.15;
double amount2 = 2.10;
if (amount1 - amount2 == 1.05){
System.out.println("OK");
}
}
}运行结果:
0.30000000000000004 0.19999999999999996 401.49999999999994 1.2329999999999999
可以发现,结算结果跟我们预期不一致,其实是因为计算机是以二进制存储数值的,对于浮点数也是。对于计算机而言,0.1无法精确表达,这就是为什么浮点数会导致精确度缺失的。因此,「金额计算,一般都是用BigDecimal 类型」
对于以上例子,我们改为BigDecimal,再看看运行效果:
System.out.println(new BigDecimal(0.1).add(new BigDecimal(0.2))); System.out.println(new BigDecimal(1.0).subtract(new BigDecimal(0.8))); System.out.println(new BigDecimal(4.015).multiply(new BigDecimal(100))); System.out.println(new BigDecimal(123.3).divide(new BigDecimal(100)));
运行结果:
0.3000000000000000166533453693773481063544750213623046875 0.1999999999999999555910790149937383830547332763671875 401.49999999999996802557689079549163579940795898437500 1.232999999999999971578290569595992565155029296875
发现结果还是不对,「其实」,使用 BigDecimal 表示和计算浮点数,必须使用「字符串的构造方法」来初始化 BigDecimal,正例如下:
public class DoubleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new BigDecimal("0.1").add(new BigDecimal("0.2")));
System.out.println(new BigDecimal("1.0").subtract(new BigDecimal("0.8")));
System.out.println(new BigDecimal("4.015").multiply(new BigDecimal("100")));
System.out.println(new BigDecimal("123.3").divide(new BigDecimal("100")));
}
}在进行金额计算,使用BigDecimal的时候,我们还需要「注意BigDecimal的几位小数点,还有它的八种舍入模式哈」。
4. FileReader默认编码导致乱码问题
看下这个例子:
public class FileReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Files.deleteIfExists(Paths.get("jay.txt"));
Files.write(Paths.get("jay.txt"), "你好,捡田螺的小男孩".getBytes(Charset.forName("GBK")));
System.out.println("系统默认编码:"+Charset.defaultCharset());
char[] chars = new char[10];
String content = "";
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("jay.txt")) {
int count;
while ((count = fileReader.read(chars)) != -1) {
content += new String(chars, 0, count);
}
}
System.out.println(content);
}
}运行结果:
系统默认编码:UTF-8 ���,�����ݵ�С�к�
从运行结果,可以知道,系统默认编码是utf8,demo中读取出来,出现乱码了。为什么呢?
❝FileReader 是以当「前机器的默认字符集」来读取文件的,如果希望指定字符集的话,需要直接使用 InputStreamReader 和 FileInputStream。
❞
正例如下:
public class FileReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Files.deleteIfExists(Paths.get("jay.txt"));
Files.write(Paths.get("jay.txt"), "你好,捡田螺的小男孩".getBytes(Charset.forName("GBK")));
System.out.println("系统默认编码:"+Charset.defaultCharset());
char[] chars = new char[10];
String content = "";
try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("jay.txt");
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream, Charset.forName("GBK"))) {
int count;
while ((count = inputStreamReader.read(chars)) != -1) {
content += new String(chars, 0, count);
}
}
System.out.println(content);
}
}5. Integer缓存的坑
public class IntegerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 127;
Integer b = 127;
System.out.println("a==b:"+ (a == b));
Integer c = 128;
Integer d = 128;
System.out.println("c==d:"+ (c == d));
}
}运行结果:
a==b:true c==d:false
为什么Integer值如果是128就不相等了呢?「编译器会把 Integer a = 127 转换为 Integer.valueOf(127)。」 我们看下源码。
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}可以发现,i在一定范围内,是会返回缓存的。
❝默认情况下呢,这个缓存区间就是[-128, 127],所以我们业务日常开发中,如果涉及Integer值的比较,需要注意这个坑哈。还有呢,设置 JVM 参数加上 -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=1000,是可以调整这个区间参数的,大家可以自己试一下哈
❞
6. static静态变量依赖spring实例化变量,可能导致初始化出错
之前看到过类似的代码。静态变量依赖于spring容器的bean。
private static SmsService smsService = SpringContextUtils.getBean(SmsService.class);
这个静态的smsService有可能获取不到的,因为类加载顺序不是确定的,正确的写法可以这样,如下:
private static SmsService smsService =null;
//使用到的时候采取获取
public static SmsService getSmsService(){
if(smsService==null){
smsService = SpringContextUtils.getBean(SmsService.class);
}
return smsService;
}7. 使用ThreadLocal,线程重用导致信息错乱的坑
使用ThreadLocal缓存信息,有可能出现信息错乱的情况。看下下面这个例子吧。
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> currentUser = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> null);
@GetMapping("wrong")
public Map wrong(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId) {
//设置用户信息之前先查询一次ThreadLocal中的用户信息
String before = Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + currentUser.get();
//设置用户信息到ThreadLocal
currentUser.set(userId);
//设置用户信息之后再查询一次ThreadLocal中的用户信息
String after = Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + currentUser.get();
//汇总输出两次查询结果
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("before", before);
result.put("after", after);
return result;
}按理说,每次获取的before应该都是null,但是呢,程序运行在 Tomcat 中,执行程序的线程是 Tomcat 的工作线程,而 Tomcat 的工作线程是基于线程池的。
❝线程池会重用固定的几个线程,一旦线程重用,那么很可能首次从 ThreadLocal 获取的值是之前其他用户的请求遗留的值。这时,ThreadLocal 中的用户信息就是其他用户的信息。
❞
把tomcat的工作线程设置为1
server.tomcat.max-threads=1
用户1,请求过来,会有以下结果,符合预期:
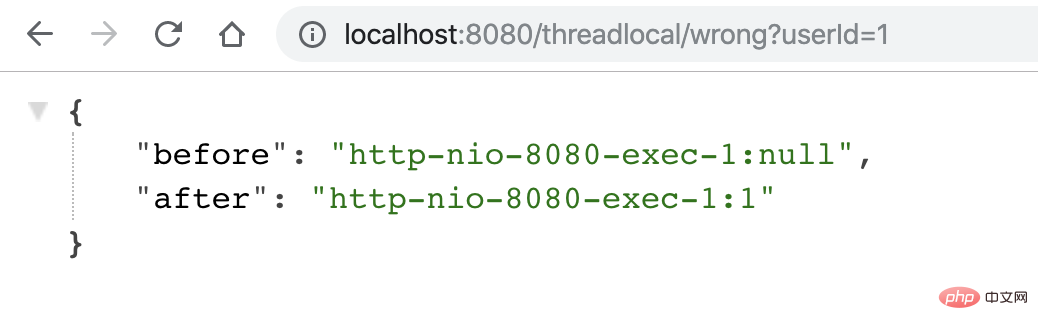
用户2请求过来,会有以下结果,「不符合预期」:
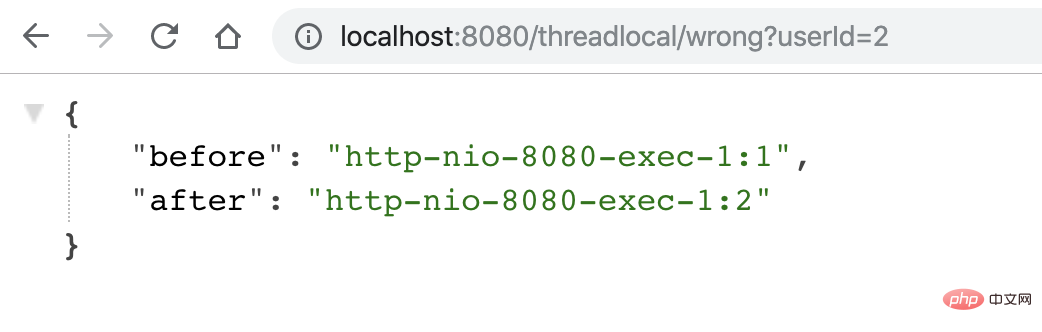
因此,使用类似 ThreadLocal 工具来存放一些数据时,需要特别注意在代码运行完后,显式地去清空设置的数据,正例如下:
@GetMapping("right")
public Map right(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId) {
String before = Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + currentUser.get();
currentUser.set(userId);
try {
String after = Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + currentUser.get();
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("before", before);
result.put("after", after);
return result;
} finally {
//在finally代码块中删除ThreadLocal中的数据,确保数据不串
currentUser.remove();
}
}8. 疏忽switch的return和break
这一点严格来说,应该不算坑,但是呢,大家写代码的时候,有些朋友容易疏忽了。直接看例子吧
/*
* 关注公众号:
* 捡田螺的小男孩
*/
public class SwitchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("testSwitch结果是:"+testSwitch("1"));
}
private static String testSwitch(String key) {
switch (key) {
case "1":
System.out.println("1");
case "2":
System.out.println(2);
return "2";
case "3":
System.out.println("3");
default:
System.out.println("返回默认值");
return "4";
}
}
}输出结果:
测试switch 1 2 testSwitch结果是:2
switch 是会「沿着case一直往下匹配的,知道遇到return或者break。」 所以,在写代码的时候留意一下,是不是你要的结果。
9. Arrays.asList的几个坑
9.1 基本类型不能作为 Arrays.asList方法的参数,否则会被当做一个参数。
public class ArrayAsListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1, 2, 3};
List list = Arrays.asList(array);
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}运行结果:
1
Arrays.asList源码如下:
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}9.2 Arrays.asList 返回的 List 不支持增删操作。
public class ArrayAsListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] array = {"1", "2", "3"};
List list = Arrays.asList(array);
list.add("5");
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}运行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException at java.util.AbstractList.add(AbstractList.java:148) at java.util.AbstractList.add(AbstractList.java:108) at object.ArrayAsListTest.main(ArrayAsListTest.java:11)
Arrays.asList 返回的 List 并不是我们期望的 java.util.ArrayList,而是 Arrays 的内部类 ArrayList。内部类的ArrayList没有实现add方法,而是父类的add方法的实现,是会抛出异常的呢。
9.3 使用Arrays.asLis的时候,对原始数组的修改会影响到我们获得的那个List
public class ArrayAsListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = {"1", "2", "3"};
List list = Arrays.asList(arr);
arr[1] = "4";
System.out.println("原始数组"+Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("list数组" + list);
}
}运行结果:
原始数组[1, 4, 3] list数组[1, 4, 3]
从运行结果可以看到,原数组改变,Arrays.asList转化来的list也跟着改变啦,大家使用的时候要注意一下哦,可以用new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(arr))包一下的。
10. ArrayList.toArray() 强转的坑
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(1);
list.add("公众号:捡田螺的小男孩");
String[] array21 = (String[])list.toArray();//类型转换异常
}
}因为返回的是Object类型,Object类型数组强转String数组,会发生ClassCastException。解决方案是,使用toArray()重载方法toArray(T[] a)
String[] array1 = list.toArray(new String[0]);//可以正常运行
11. 异常使用的几个坑
11.1 不要弄丢了你的堆栈异常信息
public void wrong1(){
try {
readFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
//没有把异常e取出来,原始异常信息丢失
throw new RuntimeException("系统忙请稍后再试");
}
}
public void wrong2(){
try {
readFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
//只保留了异常消息,栈没有记录啦
log.error("文件读取错误, {}", e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException("系统忙请稍后再试");
}
}正确的打印方式,应该酱紫
public void right(){
try {
readFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
//把整个IO异常都记录下来,而不是只打印消息
log.error("文件读取错误", e);
throw new RuntimeException("系统忙请稍后再试");
}
}11.2 不要把异常定义为静态变量
public void testStaticExeceptionOne{
try {
exceptionOne();
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("exception one error", ex);
}
try {
exceptionTwo();
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("exception two error", ex);
}
}
private void exceptionOne() {
//这里有问题
throw Exceptions.ONEORTWO;
}
private void exceptionTwo() {
//这里有问题
throw Exceptions.ONEORTWO;
}exceptionTwo抛出的异常,很可能是 exceptionOne的异常哦。正确使用方法,应该是new 一个出来。
private void exceptionTwo() {
throw new BusinessException("业务异常", 0001);
}11.3 生产环境不要使用e.printStackTrace();
public void wrong(){
try {
readFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
//生产环境别用它
e.printStackTrace();
}
}因为它占用太多内存,造成锁死,并且,日志交错混合,也不易读。正确使用如下:
log.error("异常日志正常打印方式",e);11.4 线程池提交过程中,出现异常怎么办?
public class ThreadExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10).forEach(i -> executorService.submit(()-> {
if (i == 5) {
System.out.println("发生异常啦");
throw new RuntimeException("error");
}
System.out.println("当前执行第几:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() );
}
));
executorService.shutdown();
}
}运行结果:
当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-1 当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-2 当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-3 当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-4 发生异常啦 当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-6 当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-7 当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-8 当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-9 当前执行第几:pool-1-thread-10
可以发现,如果是使用submit方法提交到线程池的异步任务,异常会被吞掉的,所以在日常发现中,如果会有可预见的异常,可以采取这几种方案处理:
1.在任务代码try/catch捕获异常 2.通过Future对象的get方法接收抛出的异常,再处理 3.为工作者线程设置UncaughtExceptionHandler,在uncaughtException方法中处理异常 4.重写ThreadPoolExecutor的afterExecute方法,处理传递的异常引用
11.5 finally重新抛出的异常也要注意啦
public void wrong() {
try {
log.info("try");
//异常丢失
throw new RuntimeException("try");
} finally {
log.info("finally");
throw new RuntimeException("finally");
}
}一个方法是不会出现两个异常的呢,所以finally的异常会把try的「异常覆盖」。正确的使用方式应该是,finally 代码块「负责自己的异常捕获和处理」。
public void right() {
try {
log.info("try");
throw new RuntimeException("try");
} finally {
log.info("finally");
try {
throw new RuntimeException("finally");
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("finally", ex);
}
}
}12.JSON序列化,Long类型被转成Integer类型!
public class JSONTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long idValue = 3000L;
Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>(2);
data.put("id", idValue);
data.put("name", "捡田螺的小男孩");
Assert.assertEquals(idValue, (Long) data.get("id"));
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(data);
// 反序列化时Long被转为了Integer
Map map = JSON.parseObject(jsonString, Map.class);
Object idObj = map.get("id");
System.out.println("反序列化的类型是否为Integer:"+(idObj instanceof Integer));
Assert.assertEquals(idValue, (Long) idObj);
}
}「运行结果:」
Exception in thread "main" 反序列化的类型是否为Integer:true java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.Integer cannot be cast to java.lang.Long at object.JSONTest.main(JSONTest.java:24)
❝「注意啦」,序列化为Json串后,Josn串是没有Long类型呢。而且反序列化回来如果也是Object接收,数字小于Interger最大值的话,给转成Integer啦!
❞
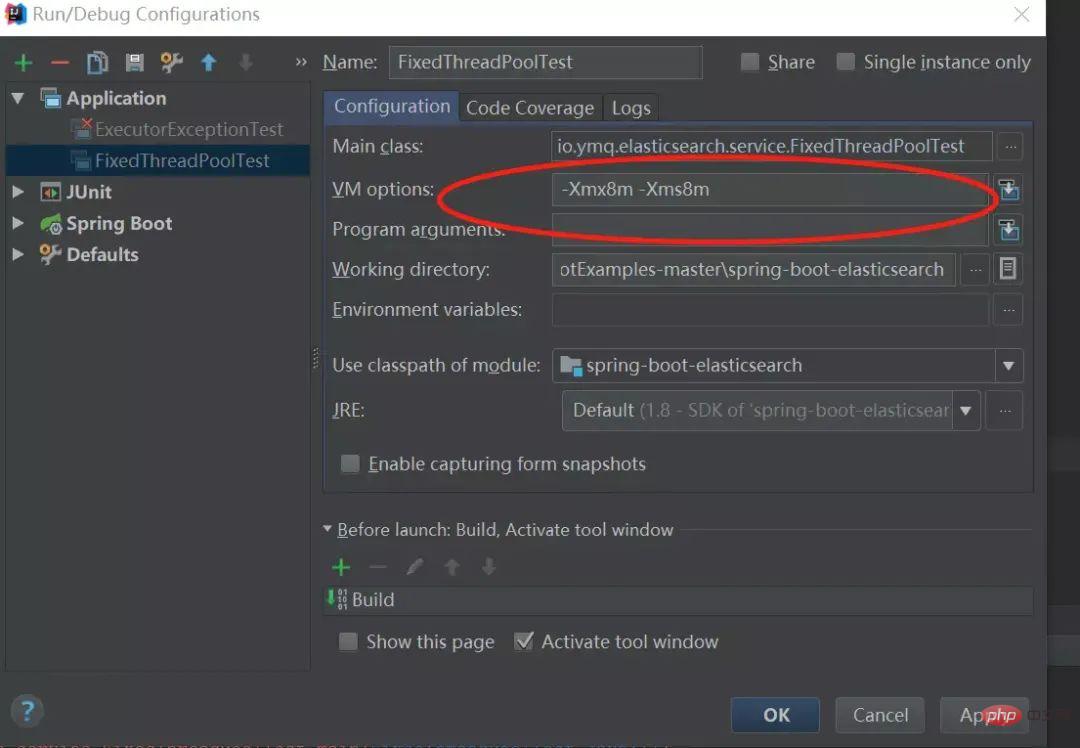
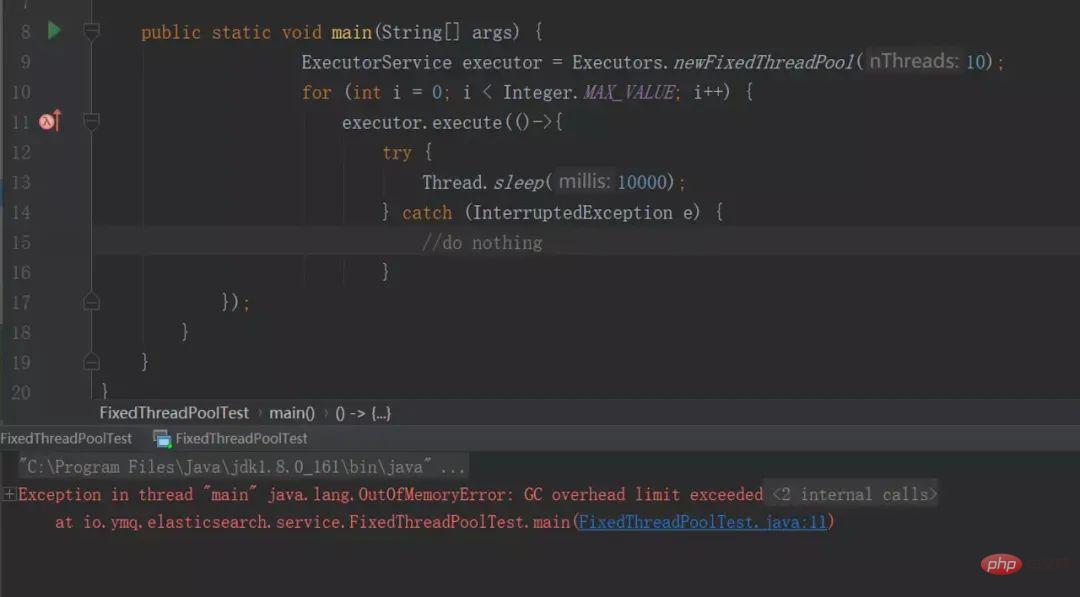
13. 使用Executors声明线程池,newFixedThreadPool的OOM问题
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//do nothing
}
});
}「IDE指定JVM参数:-Xmx8m -Xms8m :」
运行结果:
我们看下源码,其实newFixedThreadPool使用的是无界队列!
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
...
/**
* Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of
* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}.
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
...
}❝newFixedThreadPool线程池的核心线程数是固定的,它使用了近乎于无界的LinkedBlockingQueue阻塞队列。当核心线程用完后,任务会入队到阻塞队列,如果任务执行的时间比较长,没有释放,会导致越来越多的任务堆积到阻塞队列,最后导致机器的内存使用不停的飙升,造成JVM OOM。
❞
14. 直接大文件或者一次性从数据库读取太多数据到内存,可能导致OOM问题
如果一次性把大文件或者数据库太多数据达到内存,是会导致OOM的。所以,为什么查询DB数据库,一般都建议分批。
读取文件的话,一般问文件不会太大,才使用Files.readAllLines()。为什么呢?因为它是直接把文件都读到内存的,预估下不会OOM才使用这个吧,可以看下它的源码:
public static List<String> readAllLines(Path path, Charset cs) throws IOException {
try (BufferedReader reader = newBufferedReader(path, cs)) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (;;) {
String line = reader.readLine();
if (line == null)
break;
result.add(line);
}
return result;
}
}如果是太大的文件,可以使用Files.line()按需读取,当时读取文件这些,一般是使用完需要「关闭资源流」的哈
15. 先查询,再更新/删除的并发一致性问题
再日常开发中,这种代码实现经常可见:先查询是否有剩余可用的票,再去更新票余量。
if(selectIsAvailable(ticketId){
1、deleteTicketById(ticketId)
2、给现金增加操作
}else{
return “没有可用现金券”
}如果是并发执行,很可能有问题的,应该利用数据库的更新/删除的原子性,正解如下:
if(deleteAvailableTicketById(ticketId) == 1){
1、给现金增加操作
}else{
return “没有可用现金券”
}16. 数据库使用utf-8存储, 插入表情异常的坑
低版本的MySQL支持的utf8编码,最大字符长度为 3 字节,但是呢,存储表情需要4个字节,因此如果用utf8存储表情的话,会报SQLException: Incorrect string value: '\xF0\x9F\x98\x84' for column,所以一般用utf8mb4编码去存储表情。
17. 事务未生效的坑
日常业务开发中,我们经常跟事务打交道,「事务失效」主要有以下几个场景:
底层数据库引擎不支持事务 在非public修饰的方法使用 rollbackFor属性设置错误 本类方法直接调用 异常被try...catch吃了,导致事务失效。
其中,最容易踩的坑就是后面两个,「注解的事务方法给本类方法直接调用」,伪代码如下:
public class TransactionTest{
public void A(){
//插入一条数据
//调用方法B (本地的类调用,事务失效了)
B();
}
@Transactional
public void B(){
//插入数据
}
}如果异常被catch住,「那事务也是会失效呢」~,伪代码如下:
@Transactional
public void method(){
try{
//插入一条数据
insertA();
//更改一条数据
updateB();
}catch(Exception e){
logger.error("异常被捕获了,那你的事务就失效咯",e);
}
}18. 当反射遇到方法重载的坑
/**
* 反射demo
* @author 捡田螺的小男孩
*/
public class ReflectionTest {
private void score(int score) {
System.out.println("int grade =" + score);
}
private void score(Integer score) {
System.out.println("Integer grade =" + score);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ReflectionTest reflectionTest = new ReflectionTest();
reflectionTest.score(100);
reflectionTest.score(Integer.valueOf(100));
reflectionTest.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("score", Integer.TYPE).invoke(reflectionTest, Integer.valueOf("60"));
reflectionTest.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("score", Integer.class).invoke(reflectionTest, Integer.valueOf("60"));
}
}运行结果:
int grade =100 Integer grade =100 int grade =60 Integer grade =60
如果「不通过反射」,传入Integer.valueOf(100),走的是Integer重载。但是呢,反射不是根据入参类型确定方法重载的,而是「以反射获取方法时传入的方法名称和参数类型来确定」的
getClass().getDeclaredMethod("score", Integer.class)
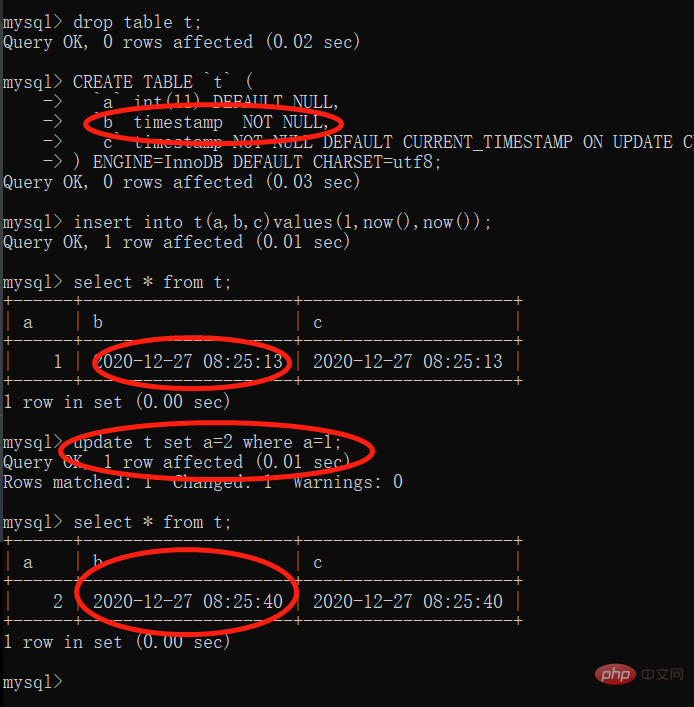
getClass().getDeclaredMethod("score", Integer.TYPE)19. mysql 时间 timestamp的坑
有更新语句的时候,timestamp可能会自动更新为当前时间,看个demo
CREATE TABLE `t` ( `a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `b` timestamp NOT NULL, `c` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
我们可以发现 「c列」 是有CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,所以c列会随着记录更新而「更新为当前时间」。但是b列也会随着有记录更新为而「更新为当前时间」。
可以使用datetime代替它,需要更新为当前时间,就把now()赋值进来,或者修改mysql的这个参数explicit_defaults_for_timestamp。
20. mysql8数据库的时区坑
之前我们对mysql数据库进行升级,新版本为8.0.12。但是升级完之后,发现now()函数,获取到的时间比北京时间晚8小时,原来是因为mysql8默认为美国那边的时间,需要指定下时区
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8& serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
参考与感谢
Java业务开发常见错误100例: https://time.geekbang.org/column/article/220230
以上是Java日常開發的21個坑,你踩過幾個?的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

