我們來以應用程式啟動事件:ApplicationStartingEvent為例來進行說明:
以啟動類別的SpringApplication.run方法為入口,跟進SpringApplication的兩個同名方法後,我們會看到主要的run方法,方法比較長,在這裡只貼出與監聽器密切相關的關鍵的部分:
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting();
我們跟進這個starting方法,方法的內容如下:
void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}這裡的listeners已經在getRunListeners方法中完成了加載,加載原理類似於系統初始化器,關於系統初始化器的加載可以參考SpringBoot深入淺出分析初始化器
starting方法邏輯很簡單,就是調用SpringApplicationRunListener的starting方法。下面繼續分析這個starting方法:
我們進入了EventPublishingRunListener類別(SpringApplicationRunListener 的實作類別)的starting方法:
@Override
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}這裡就使用了廣播器,來廣播新的ApplicationStartingEvent事件。
我們跟進這個multicastEvent方法:
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}繼續看同名的方法multicastEvent:
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}這裡的ResolvableType 是對event做了包裝,我們不去關注;由於我們沒有創建線程池,所以executor是空的。我們重點關注兩個部分:
取得所有監聽此事件的應用程式監聽器
2、invokeListener --> 啟動監聽器;
getApplicationListeners (AbstractApplicationEventMulticasterster類別中)方法,程式碼如下:
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Object source = event.getSource();
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// Quick check for existing entry on ConcurrentHashMap...
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
// Fully synchronized building and caching of a ListenerRetriever
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
}
}
else {
// No ListenerRetriever caching -> no synchronization necessary
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
}
}入參中的event是ApplicationStartingEvent,sourceType是org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication類別。我把ListenerRetriever類型看成一個儲存監聽器的容器。
可以看出,程式先在快取裡面尋找ListenerRetriever類型的retriever,如果沒有找到,加鎖再從快取裡面找一次。這裡我們快取裡是沒有內容的,所以都不會回來。
然後使用retrieveApplicationListeners方法,對監聽器進行遍歷。 retrieveApplicationListeners方法比較長,我們將重點放在下supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)方法,該方法用來判斷是否此監聽器關注該事件,過程主要包括,判斷此類型是否為GenericApplicationListener類型,如果不是,則建構一個代理,代理的目的是,透過泛型解析,最終獲得監聽器所感興趣的事件。
如果經過判斷,監聽器對該事件是感興趣的,則此監聽器會被加入監聽器清單中。
protected boolean supportsEvent(
ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ?
(GenericApplicationListener) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener));
return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType));
}當某個事件所有的監聽器被收集完畢後,multicastEvent(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster類別)方法就會對事件進行傳播。也就是呼叫監聽器的通用觸發介面方法:listener.onApplicationEvent(event);這樣,就完成了這個事件的傳播。
以上是SpringBoot監聽器模式怎麼實現的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
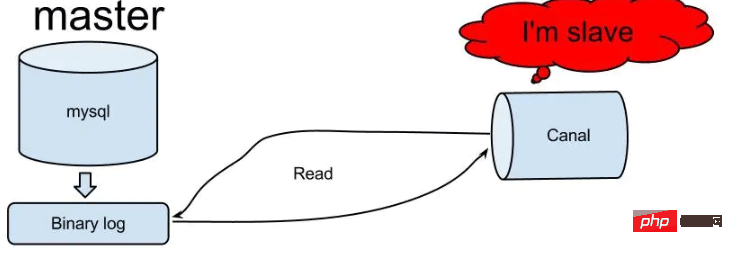 怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PMCanal工作原理Canal模拟MySQLslave的交互协议,伪装自己为MySQLslave,向MySQLmaster发送dump协议MySQLmaster收到dump请求,开始推送binarylog给slave(也就是Canal)Canal解析binarylog对象(原始为byte流)MySQL打开binlog模式在MySQL配置文件my.cnf设置如下信息:[mysqld]#打开binloglog-bin=mysql-bin#选择ROW(行)模式binlog-format=ROW#配置My
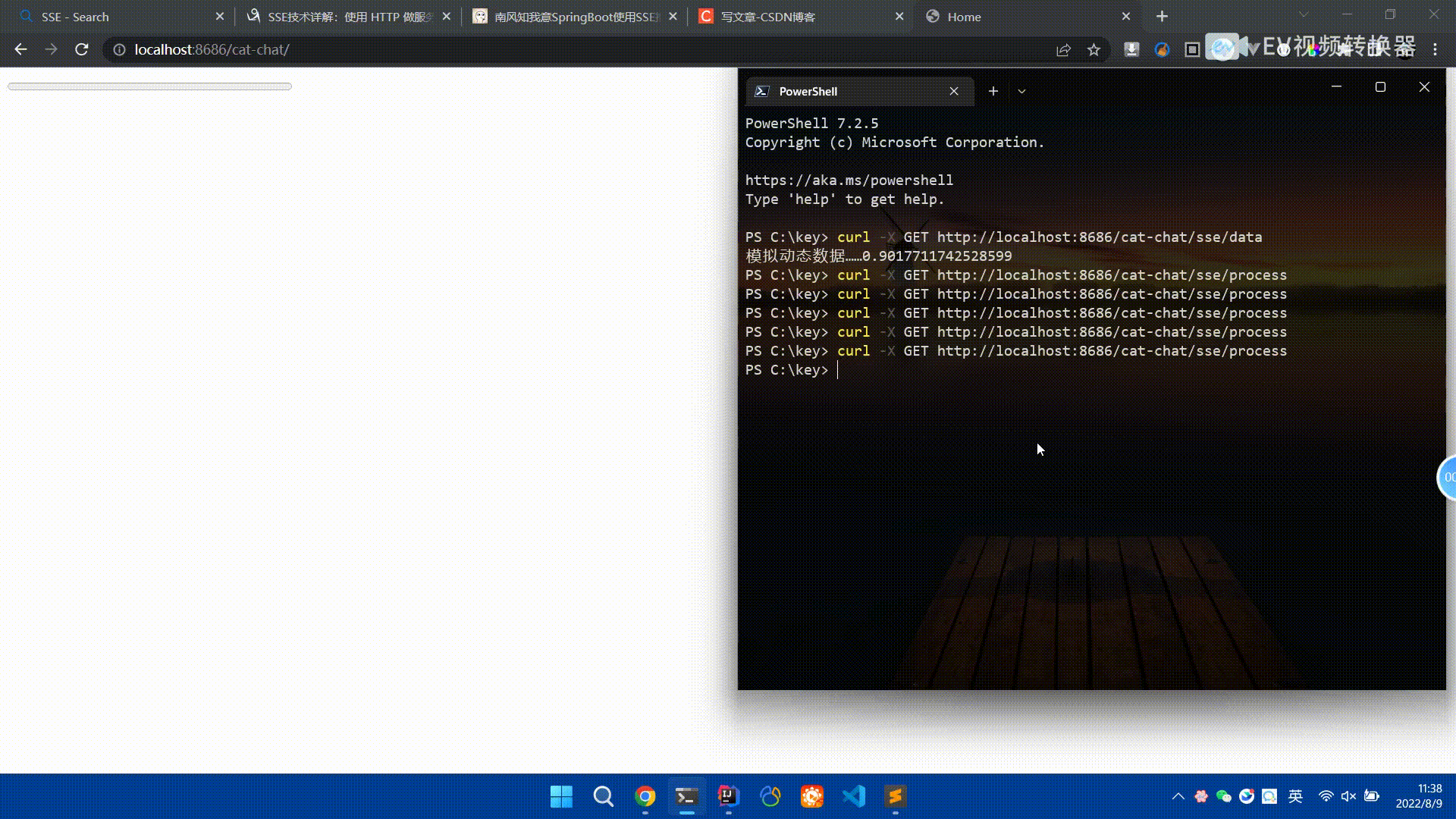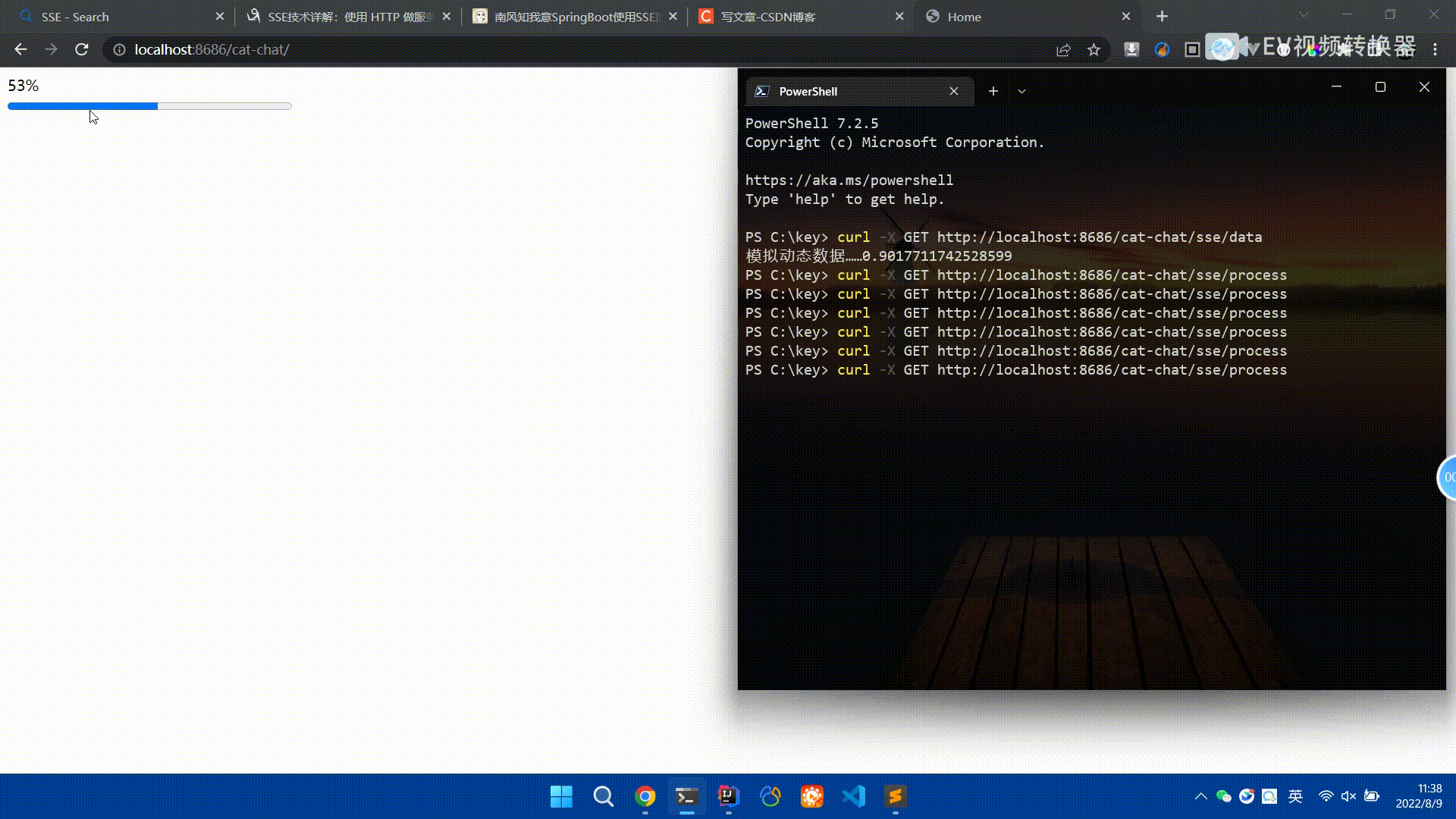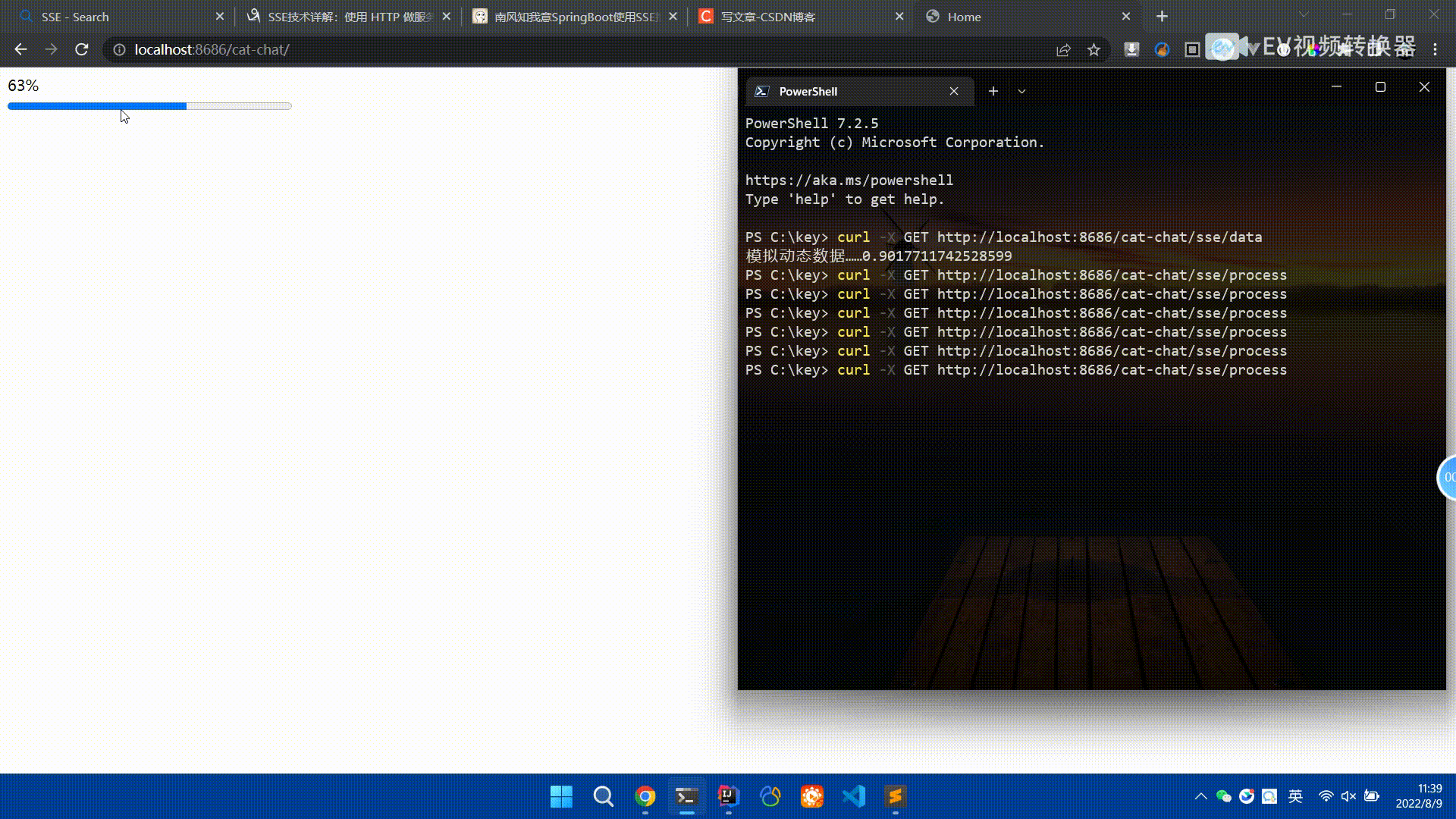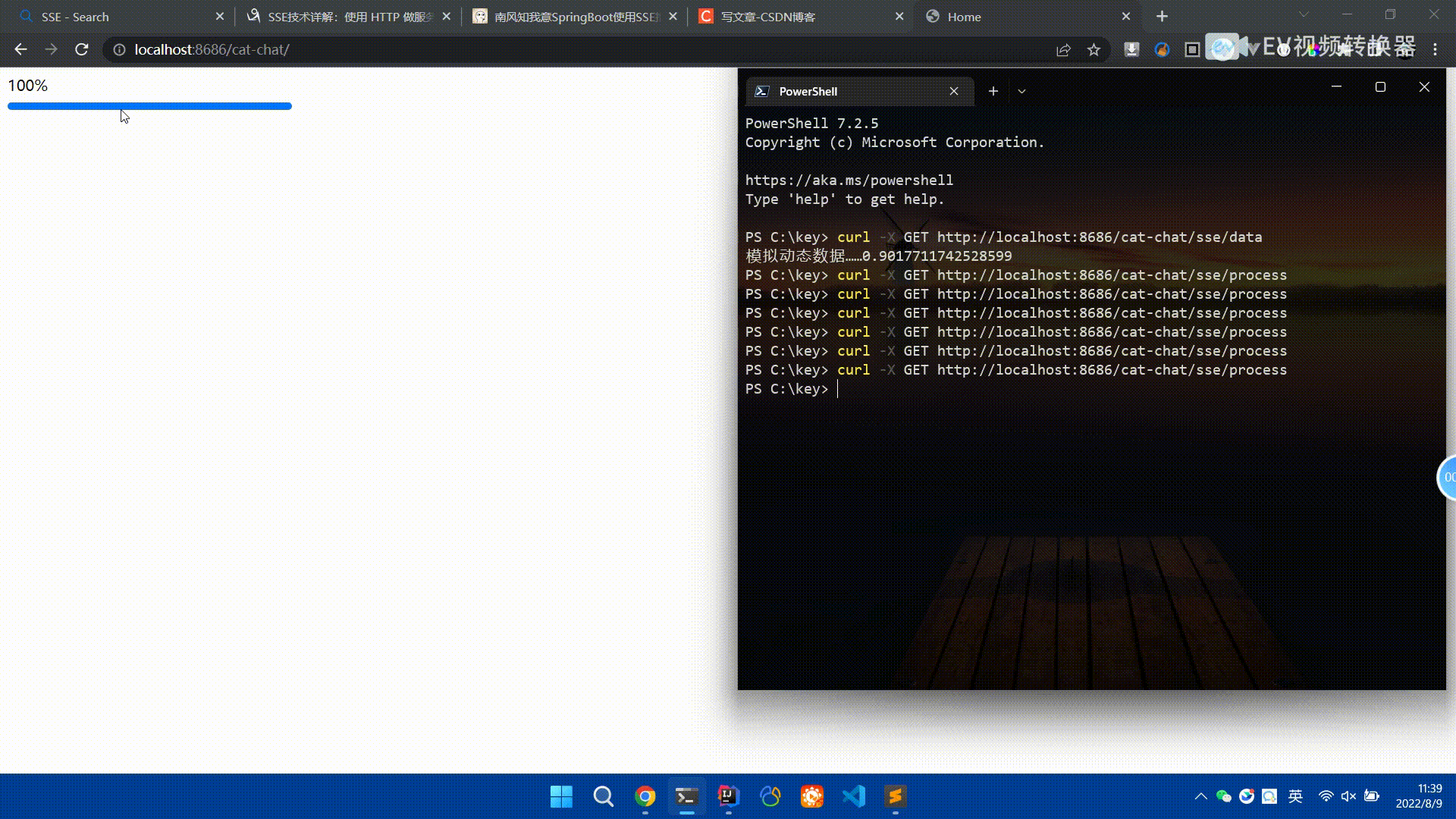 Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM前言SSE简单的来说就是服务器主动向前端推送数据的一种技术,它是单向的,也就是说前端是不能向服务器发送数据的。SSE适用于消息推送,监控等只需要服务器推送数据的场景中,下面是使用SpringBoot来实现一个简单的模拟向前端推动进度数据,前端页面接受后展示进度条。服务端在SpringBoot中使用时需要注意,最好使用SpringWeb提供的SseEmitter这个类来进行操作,我在刚开始时使用网上说的将Content-Type设置为text-stream这种方式发现每次前端每次都会重新创建接。最
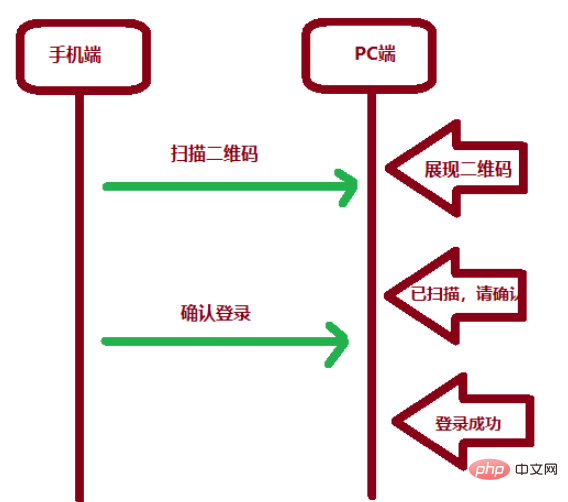 SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM一、手机扫二维码登录的原理二维码扫码登录是一种基于OAuth3.0协议的授权登录方式。在这种方式下,应用程序不需要获取用户的用户名和密码,只需要获取用户的授权即可。二维码扫码登录主要有以下几个步骤:应用程序生成一个二维码,并将该二维码展示给用户。用户使用扫码工具扫描该二维码,并在授权页面中授权。用户授权后,应用程序会获取一个授权码。应用程序使用该授权码向授权服务器请求访问令牌。授权服务器返回一个访问令牌给应用程序。应用程序使用该访问令牌访问资源服务器。通过以上步骤,二维码扫码登录可以实现用户的快
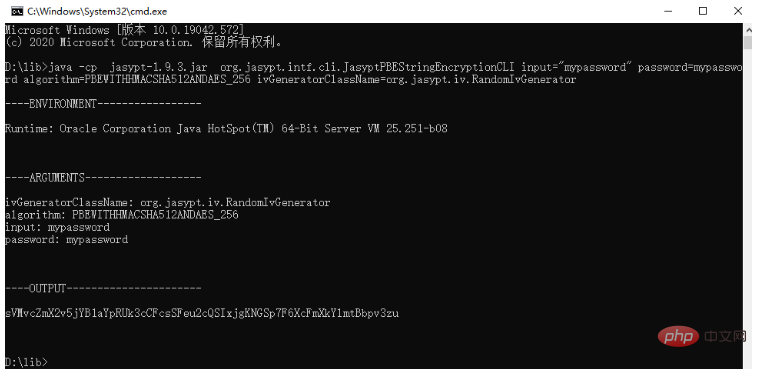 spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM我们使用jasypt最新版本对敏感信息进行加解密。1.在项目pom文件中加入如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter3.0.32.创建加解密公用类:packagecom.myproject.common.utils;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.PooledPBEStringEncryptor;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.SimpleStrin
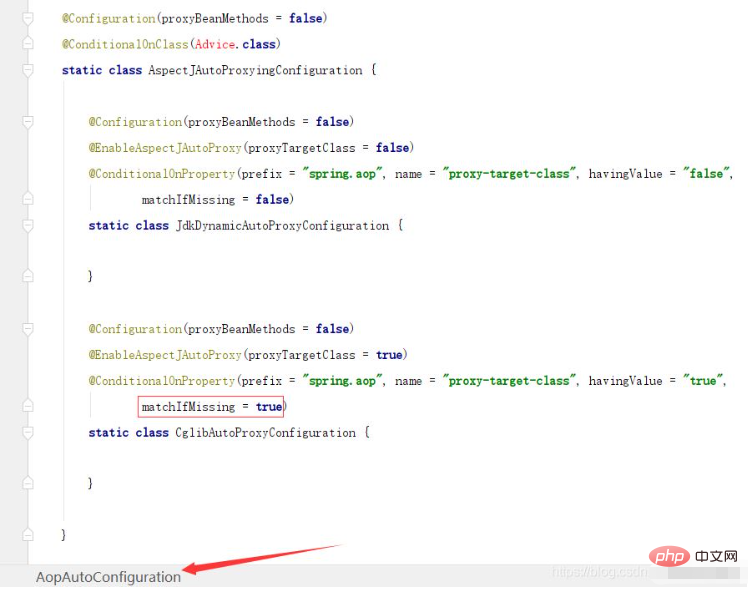 SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM1.springboot2.x及以上版本在SpringBoot2.xAOP中会默认使用Cglib来实现,但是Spring5中默认还是使用jdk动态代理。SpringAOP默认使用JDK动态代理,如果对象没有实现接口,则使用CGLIB代理。当然,也可以强制使用CGLIB代理。在SpringBoot中,通过AopAutoConfiguration来自动装配AOP.2.Springboot1.xSpringboot1.xAOP默认还是使用JDK动态代理的3.SpringBoot2.x为何默认使用Cgl
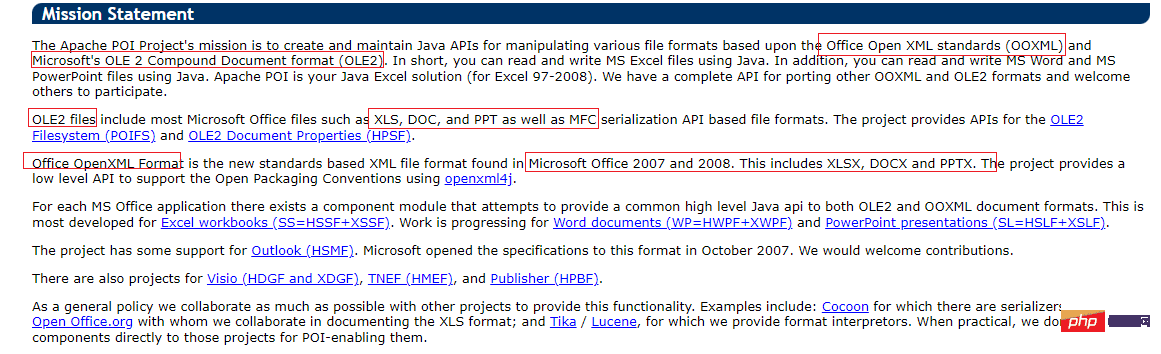 使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM知识准备需要理解ApachePOI遵循的标准(OfficeOpenXML(OOXML)标准和微软的OLE2复合文档格式(OLE2)),这将对应着API的依赖包。什么是POIApachePOI是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的JavaAPI,ApachePOI提供API给Java程序对MicrosoftOffice格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“PoorObfuscationImplementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。ApachePOI是创建和维护操作各种符合Offic
 springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM
springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM1.首先新建一个shiroConfigshiro的配置类,代码如下:@ConfigurationpublicclassSpringShiroConfig{/***@paramrealms这儿使用接口集合是为了实现多验证登录时使用的*@return*/@BeanpublicSecurityManagersecurityManager(Collectionrealms){DefaultWebSecurityManagersManager=newDefaultWebSecurityManager();
 Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM一、定义视频上传请求接口publicAjaxResultvideoUploadFile(MultipartFilefile){try{if(null==file||file.isEmpty()){returnAjaxResult.error("文件为空");}StringossFilePrefix=StringUtils.genUUID();StringfileName=ossFilePrefix+"-"+file.getOriginalFilename(


熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
將Eclipse與SAP NetWeaver應用伺服器整合。

mPDF
mPDF是一個PHP庫,可以從UTF-8編碼的HTML產生PDF檔案。原作者Ian Back編寫mPDF以從他的網站上「即時」輸出PDF文件,並處理不同的語言。與原始腳本如HTML2FPDF相比,它的速度較慢,並且在使用Unicode字體時產生的檔案較大,但支援CSS樣式等,並進行了大量增強。支援幾乎所有語言,包括RTL(阿拉伯語和希伯來語)和CJK(中日韓)。支援嵌套的區塊級元素(如P、DIV),

Atom編輯器mac版下載
最受歡迎的的開源編輯器





