Python虛擬機器中複數的實作原理是什麼
- 王林轉載
- 2023-05-13 10:40:211515瀏覽
複數資料結構
在cpython 當中對於複數的資料結構實作如下所示:
typedef struct {
double real;
double imag;
} Py_complex;
#define PyObject_HEAD PyObject ob_base;
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
Py_complex cval;
} PyComplexObject;
typedef struct _object {
_PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA
Py_ssize_t ob_refcnt;
struct _typeobject *ob_type;
} PyObject;上面的資料結構圖示如下:
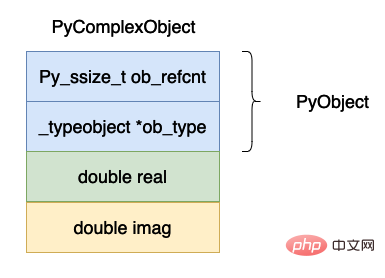
複數的資料在整個cpython 虛擬機當中來說應該算是比較簡單的了,除了一個PyObject 頭部之外就是實部和虛部了。
ob_refcnt,表示物件的參考記數的個數,這個對於垃圾回收很有用處,後面我們分析虛擬機器中垃圾回收部分在深入分析。
ob_type,表示這個物件的資料型別是什麼,在python 當中有時候需要對資料的資料型別進行判斷例如isinstance, type 這兩個關鍵字就會使用到這個字段。
real,表示複數的實部。
imag,表示複數的虛部。
複數的操作
複數加法
#下面是 cpython 當中對於複數加法的實現,為了簡潔刪除了部分無用程式碼。
static PyObject *
complex_add(PyObject *v, PyObject *w)
{
Py_complex result;
Py_complex a, b;
TO_COMPLEX(v, a); // TO_COMPLEX 这个宏的作用就是将一个 PyComplexObject 中的 Py_complex 对象存储到 a 当中
TO_COMPLEX(w, b);
result = _Py_c_sum(a, b); // 这个函数的具体实现在下方
return PyComplex_FromCComplex(result); // 这个函数的具体实现在下方
}
// 真正实现复数加法的函数
Py_complex
_Py_c_sum(Py_complex a, Py_complex b)
{
Py_complex r;
r.real = a.real + b.real;
r.imag = a.imag + b.imag;
return r;
}
PyObject *
PyComplex_FromCComplex(Py_complex cval)
{
PyComplexObject *op;
/* Inline PyObject_New */
// 申请内存空间
op = (PyComplexObject *) PyObject_MALLOC(sizeof(PyComplexObject));
if (op == NULL)
return PyErr_NoMemory();
// 将这个对象的引用计数设置成 1
(void)PyObject_INIT(op, &PyComplex_Type);
// 将复数结构体保存下来
op->cval = cval;
return (PyObject *) op;
}上面程式碼的整體過程比較簡單:
先從 PyComplexObject 提取真正的複數部分。
將提取到的兩個複數進行相加運算。
根據所得到的結果在建立一個 PyComplexObject 對象,並且將這個物件傳回。
複數取反
複數取反操作就是將實部和虛部取相反數就可以了,這個操作也比較簡單。
static PyObject *
complex_neg(PyComplexObject *v)
{
Py_complex neg;
neg.real = -v->cval.real;
neg.imag = -v->cval.imag;
return PyComplex_FromCComplex(neg);
}
PyObject *
PyComplex_FromCComplex(Py_complex cval)
{
PyComplexObject *op;
/* Inline PyObject_New */
op = (PyComplexObject *) PyObject_MALLOC(sizeof(PyComplexObject));
if (op == NULL)
return PyErr_NoMemory();
(void)PyObject_INIT(op, &PyComplex_Type);
op->cval = cval;
return (PyObject *) op;
}Repr 函數
我們現在來介紹一個有趣的方法,就是複數類型的repr 函數,這個和類別的__repr__ 函數是作用是一樣的我們看一下複數的輸出是什麼:
>>> data = complex(0, 1) >>> data 1j >>> data = complex(1, 1) >>> data (1+1j) >>> print(data) (1+1j)
複數的repr 對應的C 函數如下所示:
static PyObject *
complex_repr(PyComplexObject *v)
{
int precision = 0;
char format_code = 'r';
PyObject *result = NULL;
/* If these are non-NULL, they'll need to be freed. */
char *pre = NULL;
char *im = NULL;
/* These do not need to be freed. re is either an alias
for pre or a pointer to a constant. lead and tail
are pointers to constants. */
char *re = NULL;
char *lead = "";
char *tail = "";
// 对应实部等于 0 虚部大于 0 的情况
if (v->cval.real == 0. && copysign(1.0, v->cval.real)==1.0) {
/* Real part is +0: just output the imaginary part and do not
include parens. */
re = "";
im = PyOS_double_to_string(v->cval.imag, format_code,
precision, 0, NULL);
if (!im) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
goto done;
}
} else {
/* Format imaginary part with sign, real part without. Include
parens in the result. */
// 将实部浮点数变成字符串
pre = PyOS_double_to_string(v->cval.real, format_code,
precision, 0, NULL);
if (!pre) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
goto done;
}
re = pre;
// 将虚部浮点数变成字符串
im = PyOS_double_to_string(v->cval.imag, format_code,
precision, Py_DTSF_SIGN, NULL);
if (!im) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
goto done;
}
// 用什么括号包围起来
lead = "(";
tail = ")";
}
result = PyUnicode_FromFormat("%s%s%sj%s", lead, re, im, tail);
done:
PyMem_Free(im);
PyMem_Free(pre);
return result;
}我們現在修改原始程式將上面的() 兩個括號變成[],編譯之後執行的結果如下圖所示:
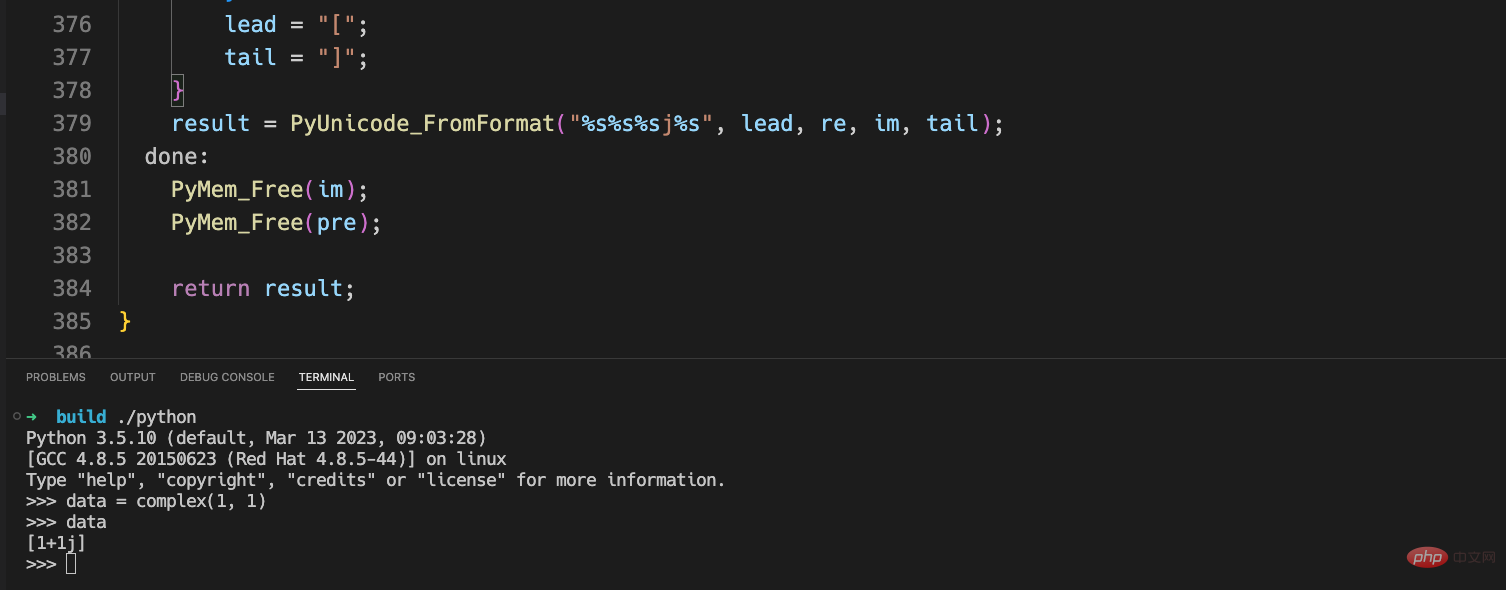
可以看到括號變成了[] 。
以上是Python虛擬機器中複數的實作原理是什麼的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
陳述:
本文轉載於:yisu.com。如有侵權,請聯絡admin@php.cn刪除

