JAVA流程控制的方法
- 王林轉載
- 2023-05-02 21:04:15833瀏覽

JAVA輸入輸出
輸入
兩種輸入方法:
方法一:java.util.Scanner
程式碼如下:
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.printf("%n欢迎你:%s", name);
}}產生Scanner對象,輸出“請輸入姓名:”,返回輸入的字串並賦值給name,輸出「%n歡迎您%s」其中%n表示換行%s表示name
#結果: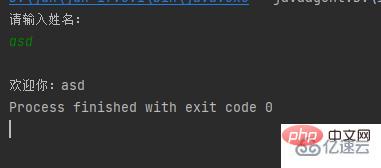
方法二:JOptionPane 輸入內容確定就字串值,只要不是確定都是null
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String w = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("请输入词汇:");
System.out.println(w);
}}結果: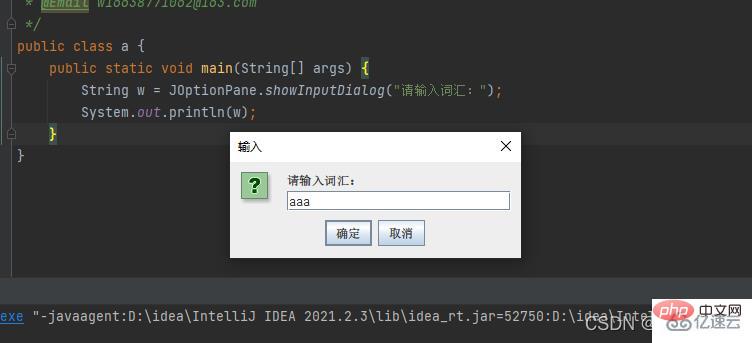
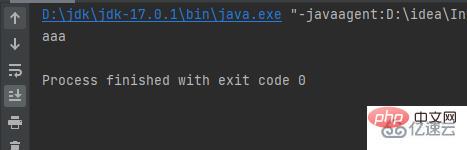
輸出
三種在控制台輸出的方法
方法一:System.out.print();輸出到控制台
方法二:System.out.println();輸出到控制台並換行
方法三:System.out.printf();格式化輸出到控制台
#程式碼示範:
第一種沒有換行直接輸出
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w = 1;
int a = 2;
System.out.print(w);
System.out.print(a);
}}結果: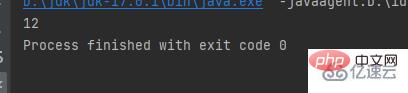
第二個換行輸出
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w = 1;
int a = 2;
System.out.println(w);
System.out.println(a);
}}結果: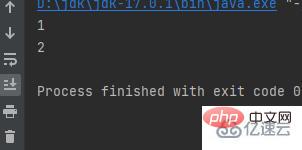
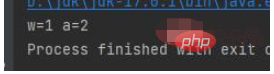
##第三種格式化輸出結果:%d的意思是int型別變量,就是將w的值替換第一個%d,a的值替換第二個%d
#public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int w = 1; int a = 2; System.out.printf("w=%d a=%d", w, a); }}
if() 括號中的條件只要是正確的就回傳true,錯誤的就回傳falseelse是否則的意思
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { if (1>2){ System.out.println("A"); }else { System.out.println("B"); } }}
多次判斷如下:第一次判斷不對就進行下一條判斷,當回傳值為true時執行,否則執行elsepublic class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (1 > 2) {
System.out.println("A");
} else if (1 > 0) {
System.out.println("B");
} else {
System.out.println("C");
}
}}switch case default
switch 多分支開關語句結果:switch(w) 括號中w為判斷參數,case 後面的數字是和w匹配的值。當w的值與case後面的值匹配上就執行當前case中的語句
break 是退出當前判斷,就是直接結束後面不需要再判斷的意思
default 的意思是默認值,當沒有匹配的時候就預設這個public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int w=1; String wk = ""; switch (w) { case 2: wk = "星期一"; break; case 3: wk = "星期二"; break; case 4: wk = "星期三"; break; case 5: wk = "星期四"; break; case 6: wk = "星期五"; break; case 7: wk = "星期六"; break; default: wk = "星期日"; break; } System.out.println(wk); }}

for ( int i = 0; i 5時退出迴圈public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}}結果: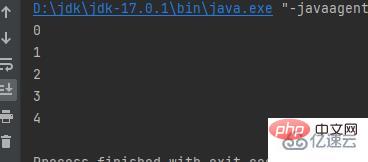
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i : a) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}}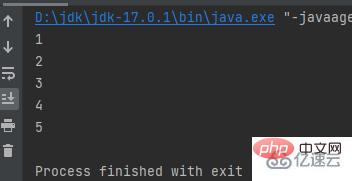 while do while
while do while
while(條件){ }
- 滿足條件執行語句,不滿足退出。
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; while (i < 5) { i++; System.out.println(i); } }}結果:
與while不同的是,do while是先執行一次再判斷這裡先執行一次輸出,再判斷。所以條件i結果:
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; do { i++; System.out.println(i); } while (i < 0); }}
 #break continue
#break continue
終止目前循環語句continue; 結束這次循環,立即準備開啟下一次循環
當i被2整除就跳過這次,進行下一次循環。當i大於10就結束循環。int i = 0;while (++i < 20) { if (i % 2 == 0) continue; System.out.println(i); if (i > 10) break;}
以上是JAVA流程控制的方法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
陳述:
本文轉載於:yisu.com。如有侵權,請聯絡admin@php.cn刪除

