Java內省機制怎麼實現
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB轉載
- 2023-04-24 08:04:061674瀏覽
概念
JavaBean
在實際程式設計中,我們常常需要一些用來包裝值物件的類別,例如Student、 Employee 、Order,這些類別中往往沒有業務方法,只是為了把需要處理的實體物件進行封裝,有這樣的特徵:
- ##屬性都是私有的;
- 有無參的public建構方法;
- 對私有屬性依需求提供公有的getXxx方法以及setXxx方法;
 # #符合這些特徵的類,稱為JavaBean;
# #符合這些特徵的類,稱為JavaBean;
內省
內省(Inspector)機制就是基於反射的基礎, Java語言對Bean類別屬性、事件的一種缺失省處理方法。
只要類別中有getXXX方法,或setXXX方法,或同時有getXXX及setXXX方法,其中getXXX方法沒有方法參數,有回傳值;setXXX方法沒有回傳值,有一個方法參數;那麼內省機制就認為XXX為一個屬性;
例如下面程式碼
Employee類別中根本沒有聲明age屬性,只是聲明了這樣的getter和setter.內省機制就認為age是屬性
package com.shixun.introspector;
public class Employee {
private String name;
private Double score;
// age将被内省认为是属性
public int getAge(){
return 30;
}
// name将被内省认为是属性
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// score将被内省认为是属性
public Double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}相關API
與Java內省有關的主要類別及介面有:
- java.beans.Introspector類別
: 為取得JavaBean屬性、事件、方法提供了標準方法;通常使用其中的getBeanInfo方法傳回BeanInfo物件;
- Java.beans.BeanInfo介面
:不能直接實例化,通常透過Introspector類別傳回該類型對象,提供了傳回屬性描述子物件(PropertyDescriptor)、方法描述子物件(MethodDescriptor) 、 bean描述子(BeanDescriptor)物件的方法;
- #Java.beans.PropertyDescriptor類別
:用來描述一個屬性,該屬性有getter及setter方法;
##可以使用PropertyDescriptor類別的方法取得屬性相關的信息,例如getName方法傳回屬性的名字:
| Method getReadMethod() | |
|---|---|
| Method getWriteMethod() | |
//获取BeanInfo的对象
BeanInfo employeeBeanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Employee.class);
//通过BeanInfo对象获取PropertyDescriptor属性描述
PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = employeeBeanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
System.out.println("通过Inspector内省机制获取JavaBean属性======= 打印所有信息 ====================");
Arrays.stream(propertyDescriptors).forEach(f->{
System.out.println("====================================");
System.out.println("属性名:"+f.getName());
System.out.println("类型:"+f.getPropertyType());
System.out.println("get方法:"+f.getReadMethod());
System.out.println("set方法:"+f.getWriteMethod());
});
// 或者用增强for
System.out.println("通过Inspector内省机制获取JavaBean属性======= 打印所有信息 ====================");
for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {
System.out.println("====================================");
System.out.println("名字:" + propertyDescriptor.getName());
System.out.println("类型:" + propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType());
System.out.println("get方法:" + propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod());
System.out.println("set方法:" + propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod());
}運行結果如下:
我們也可以透過反射來呼叫這裡取得的get或set方法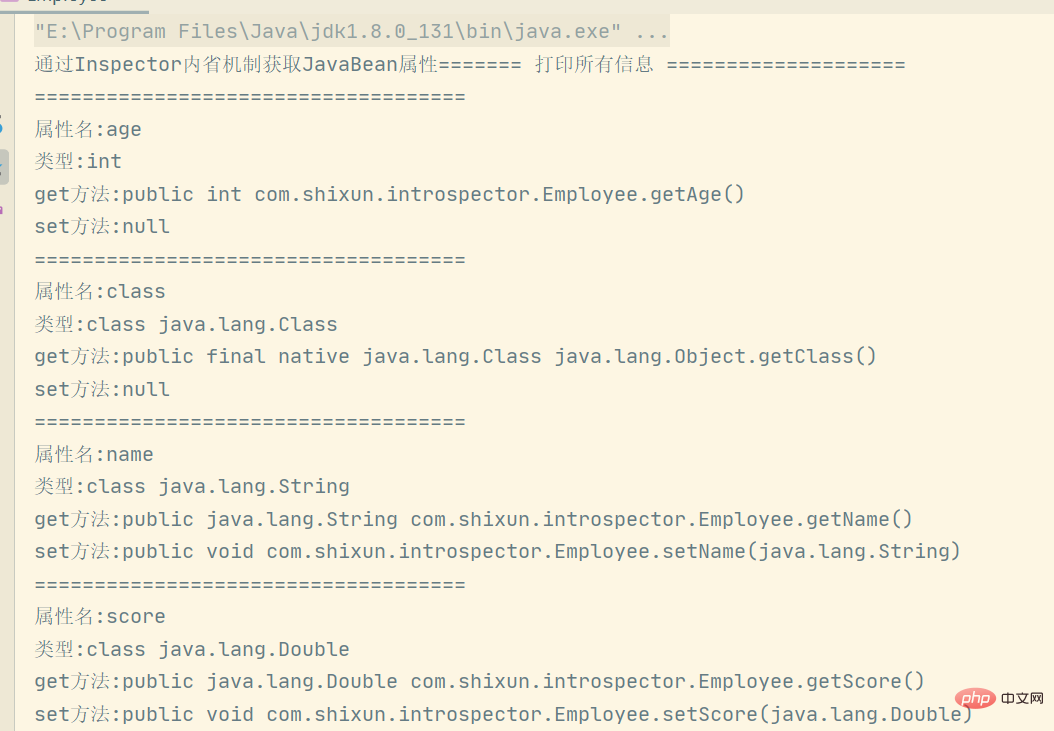
//创建Employee的对象
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.shixun.introspector.Employee");
Object employee = clazz.newInstance();
//遍历属性描述对象
for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {
//打印属性名称
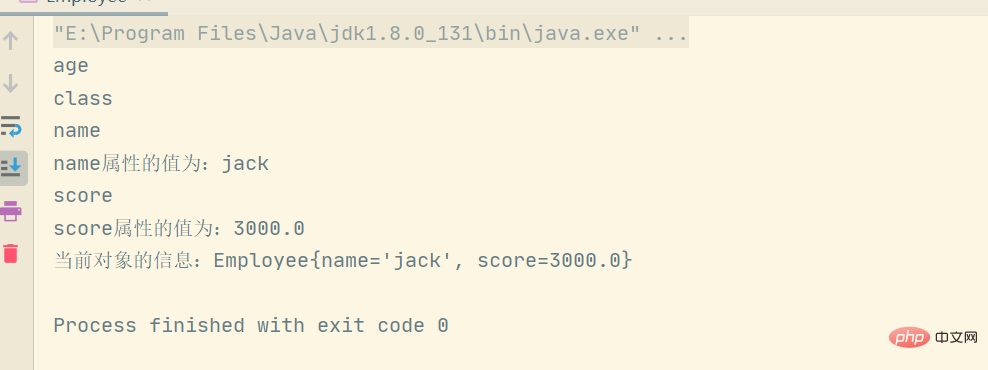
System.out.println(propertyDescriptor.getName());
//判断属性名称是不是name
if (propertyDescriptor.getName().equals("name")) {
//setter方法
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
//调用setName方法
writeMethod.invoke(employee, "jack");
//getter方法
Method readMethod = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod();
//调用getName方法
Object nameValue = readMethod.invoke(employee);
System.out.println("name属性的值为:" + nameValue);
}
//判断属性名称是否为score
if (propertyDescriptor.getName().equals("score")) {
//setter方法
Method scoreWriteMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
//调用setScore方法
scoreWriteMethod.invoke(employee, new Double(3000));
//getter方法
Method scoreReadMethod = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod();
Object scoreValue = scoreReadMethod.invoke(employee);
System.out.println("score属性的值为:" + scoreValue);
}
}
System.out.println("当前对象的信息:"+employee.toString());運行結果如下所示:
很多框架都使用了內省機制來擷取物件的屬性,定義屬性名稱時,名字最好起碼以兩個小寫字母開頭,例如stuName,而不要使用sName,某些情況下,可能會導致檢索屬性失敗;內省屬性的注意事項
- 內省機制檢索屬性時,是根據getter和setter方法確認屬性名字,而不是根據類別裡宣告的成員變數名稱決定;
- 完整程式碼
package com.shixun.introspector;
import java.beans.BeanInfo;
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Employee {
private String name;
private Double score;
// age将被内省认为是属性
public int getAge() {
return 30;
}
// name将被内省认为是属性
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// score将被内省认为是属性
public Double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IntrospectionException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
//获取BeanInfo的对象
BeanInfo employeeBeanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Employee.class);
//通过BeanInfo对象获取PropertyDescriptor属性描述
PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = employeeBeanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
// System.out.println("通过Inspector内省机制获取JavaBean属性======= 打印所有信息 ====================");
// Arrays.stream(propertyDescriptors).forEach(f->{
// System.out.println("====================================");
// System.out.println("属性名:"+f.getName());
// System.out.println("类型:"+f.getPropertyType());
// System.out.println("get方法:"+f.getReadMethod());
// System.out.println("set方法:"+f.getWriteMethod());
// });
//
//
//
// System.out.println("通过Inspector内省机制获取JavaBean属性======= 打印所有信息 ====================");
//
// for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {
// System.out.println("名字:" + propertyDescriptor.getName());
// System.out.println("类型:" + propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType());
// System.out.println("get方法:" + propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod());
// System.out.println("set方法:" + propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod());
// }
//创建Employee的对象
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.shixun.introspector.Employee");
Object employee = clazz.newInstance();
//遍历属性描述对象
for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {
//打印属性名称
System.out.println(propertyDescriptor.getName());
//判断属性名称是不是name
if (propertyDescriptor.getName().equals("name")) {
//setter方法
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
//调用setName方法
writeMethod.invoke(employee, "jack");
//getter方法
Method readMethod = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod();
//调用getName方法
Object nameValue = readMethod.invoke(employee);
System.out.println("name属性的值为:" + nameValue);
}
//判断属性名称是否为score
if (propertyDescriptor.getName().equals("score")) {
//setter方法
Method scoreWriteMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
//调用setScore方法
scoreWriteMethod.invoke(employee, new Double(3000));
//getter方法
Method scoreReadMethod = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod();
Object scoreValue = scoreReadMethod.invoke(employee);
System.out.println("score属性的值为:" + scoreValue);
}
}
System.out.println("当前对象的信息:"+employee.toString());
}
}以上是Java內省機制怎麼實現的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
陳述:
本文轉載於:yisu.com。如有侵權,請聯絡admin@php.cn刪除

