分析長輪詢的實作方式
現在各大中間件都使用了長輪詢的資料互動方式,目前比較流行的例如Nacos的配置中心,RocketMQ Pull(拉模式)訊息等等,它們都是採用了長輪詢方的式實現。就例如Nacos的配置中心,如何做到服務端感知配置變化即時推送給客戶端的呢?
長輪詢與短輪詢
說到長輪詢,肯定存在和它相對立的,我們暫且叫它短輪詢吧,我們簡單介紹一下短輪詢:
短輪詢也是拉模式。是指不管服務端資料有無更新,客戶端每隔定長時間請求拉取一次數據,可能有更新資料返回,也可能什麼都沒有。如果配置中心使用這樣的方式,會存在以下問題:
由於配置資料並不會頻繁變更,若是一直發請求,勢必會對服務端造成很大壓力。也會造成推送資料的延遲,例如:每10s請求一次配置,如果在第11s時配置更新了,那麼推送將會延遲9s,等待下一次請求;
無法在推送延遲和服務端壓力兩者之間中和。降低輪詢的間隔,延遲降低,壓力增加;增加輪詢的間隔,壓力降低,延遲增加。
長輪詢為了解決短輪詢存在的問題,客戶端發起長輪詢,如果服務端的資料沒有變更,會hold住請求,直到服務端的資料發生變化,或等待一定時間超時才會返回。返回後,客戶端再發起下一次長輪詢請求監聽。
這樣設計的好處:
相對於低延時,客戶端發起長輪詢,服務端感知到資料發生變更後,能立刻回傳回應給客戶端。
服務端的壓力減少,客戶端發起長輪詢,如果資料沒有發生變更,服務端會hold住此次客戶端的請求,hold住請求的時間一般會設定到30s或60s,且服務端hold住請求不會消耗太多服務端的資源。
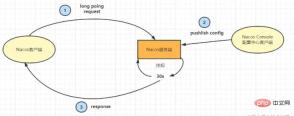
下面借用圖片來說明流程:

#首先客戶端發起長輪詢請求,服務端收到客戶端的請求,這時會掛起客戶端的請求,如果在服務端設計的30s之內都沒有發生變更,服務端會回應回客戶端資料沒有變更,客戶端會繼續傳送請求。
如果在30s之內服務資料發生了變更,服務端會推送變更的資料到客戶端。
配置中心長輪詢設計
#上面我們已經介紹了整個思路,下面我們用程式碼實作一下:
首先客戶端發送一個HTTP請求到服務端;服務端會開啟一個非同步線程,如果一直沒有資料變更會掛起目前請求(一個Tomcat 也就200 個線程,長輪詢也不應該阻塞Tomcat 的業務線程,所以需要配置中心在實現長輪詢時往往採用異步響應的方式來實現,而比較方便實現異步HTTP 的常見手段便是Servlet3.0 提供的AsyncContext 機制.)
在服務端設定的逾時時間內仍然沒有資料變更,那就傳回客戶端一個沒有變更的標識。例如回應304狀態碼;
在服務端設定的逾時時間內有資料變更了,就傳回客戶端變更的內容;
配置中心長輪詢實作
下面用程式碼實作長輪詢:
客戶端實作
@Slf4j
public class ConfigClientWorker {
private final CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
private final ScheduledExecutorService executorService;
public ConfigClientWorker(String url, String dataId) {
this.executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(runnable -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.setName("client.worker.executor-%d");
thread.setDaemon(true);
return thread;
});
// ① httpClient 客户端超时时间要大于长轮询约定的超时时间
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom().setSocketTimeout(40000).build();
this.httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig).build();
executorService.execute(new LongPollingRunnable(url, dataId));
}
class LongPollingRunnable implements Runnable {
private final String url;
private final String dataId;
public LongPollingRunnable(String url, String dataId) {
this.url = url;
this.dataId = dataId;
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
String endpoint = url + "?dataId=" + dataId;
log.info("endpoint: {}", endpoint);
HttpGet request = new HttpGet(endpoint);
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request);
switch (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()) {
case 200: {
BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(response.getEntity()
.getContent()));
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = rd.readLine()) != null) {
result.append(line);
}
response.close();
String configInfo = result.toString();
log.info("dataId: [{}] changed, receive configInfo: {}", dataId, configInfo);
break;
}
// ② 304 响应码标记配置未变更
case 304: {
log.info("longPolling dataId: [{}] once finished, configInfo is unchanged, longPolling again", dataId);
break;
}
default: {
throw new RuntimeException("unExcepted HTTP status code");
}
}
executorService.execute(this);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new ConfigClientWorker("http://127.0.0.1:8080/listener", "user");
System.in.read();
}
}httpClient 用戶端逾時時間大於長輪詢約定的逾時時間,不然還沒等到服務端返回,客戶端自己就超時了。
304 回應碼標記配置未變更;
http://127.0.0.1:8080/listener 是服務端位址;
服務端實作
@RestController
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigServer {
@Data
private static class AsyncTask {
// 长轮询请求的上下文,包含请求和响应体
private AsyncContext asyncContext;
// 超时标记
private boolean timeout;
public AsyncTask(AsyncContext asyncContext, boolean timeout) {
this.asyncContext = asyncContext;
this.timeout = timeout;
}
}
// guava 提供的多值 Map,一个 key 可以对应多个 value
private Multimap<String, AsyncTask> dataIdContext = Multimaps.synchronizedSetMultimap(HashMultimap.create());
private ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("longPolling-timeout-checker-%d")
.build();
private ScheduledExecutorService timeoutChecker = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, threadFactory);
// 配置监听接入点
@RequestMapping("/listener")
public void addListener(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String dataId = request.getParameter("dataId");
// 开启异步!!!
AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync(request, response);
AsyncTask asyncTask = new AsyncTask(asyncContext, true);
// 维护 dataId 和异步请求上下文的关联
dataIdContext.put(dataId, asyncTask);
// 启动定时器,30s 后写入 304 响应
timeoutChecker.schedule(() -> {
if (asyncTask.isTimeout()) {
dataIdContext.remove(dataId, asyncTask);
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
// 标志此次异步线程完成结束!!!
asyncContext.complete();
}
}, 30000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 配置发布接入点
@RequestMapping("/publishConfig")
@SneakyThrows
public String publishConfig(String dataId, String configInfo) {
log.info("publish configInfo dataId: [{}], configInfo: {}", dataId, configInfo);
Collection<AsyncTask> asyncTasks = dataIdContext.removeAll(dataId);
for (AsyncTask asyncTask : asyncTasks) {
asyncTask.setTimeout(false);
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)asyncTask.getAsyncContext().getResponse();
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
response.getWriter().println(configInfo);
asyncTask.getAsyncContext().complete();
}
return "success";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServer.class, args);
}
}客戶端請求過來,先開啟一個非同步執行緒
request.startAsync(request, response);保證不佔用Tomcat線程。此時Tomcat線程以及釋放。配合asyncContext.complete()使用。dataIdContext.put(dataId, asyncTask);會將dataId 和非同步請求上下文給關聯起來,方便配置發佈時,拿到對應的上下文Multimap<string asynctask> dataIdContext</string>它是一個多值Map,一個key 可以對應多個value,你也可以理解為Map<string list>></string>#timeoutChecker.schedule()啟動計時器,30s 後寫入304 回應@RequestMapping("/publishConfig"),配置发布的入口。配置变更后,根据 dataId 一次拿出所有的长轮询,为之写入变更的响应。asyncTask.getAsyncContext().complete();表示这次异步请求结束了。
启动配置监听
先启动 ConfigServer,再启动 ConfigClient。30s之后控制台打印第一次超时之后收到服务端304的状态码
16:41:14.824 [client.worker.executor-%d] INFO cn.haoxiaoyong.poll.ConfigClientWorker - longPolling dataId: [user] once finished, configInfo is unchanged, longPolling again
请求一下配置发布,请求localhost:8080/publishConfig?dataId=user&configInfo=helloworld
服务端打印日志:
2022-08-25 16:45:56.663 INFO 90650 --- [nio-8080-exec-2] cn.haoxiaoyong.poll.ConfigServer : publish configInfo dataId: [user], configInfo: helloworld
以上是如何用Java實作簡單的長輪詢?的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
 平台獨立性如何使企業級的Java應用程序受益?May 03, 2025 am 12:23 AM
平台獨立性如何使企業級的Java應用程序受益?May 03, 2025 am 12:23 AMJava在企業級應用中被廣泛使用是因為其平台獨立性。 1)平台獨立性通過Java虛擬機(JVM)實現,使代碼可在任何支持Java的平台上運行。 2)它簡化了跨平台部署和開發流程,提供了更大的靈活性和擴展性。 3)然而,需注意性能差異和第三方庫兼容性,並採用最佳實踐如使用純Java代碼和跨平台測試。
 考慮到平台獨立性,Java在物聯網(物聯網)設備的開發中扮演什麼角色?May 03, 2025 am 12:22 AM
考慮到平台獨立性,Java在物聯網(物聯網)設備的開發中扮演什麼角色?May 03, 2025 am 12:22 AMJavaplaysigantroleiniotduetoitsplatFormentence.1)itallowscodeTobewrittenOnCeandrunonVariousDevices.2)Java'secosystemprovidesuseusefidesusefidesulylibrariesforiot.3)
 描述一個方案,您在Java中遇到了一個特定於平台的問題以及如何解決。May 03, 2025 am 12:21 AM
描述一個方案,您在Java中遇到了一個特定於平台的問題以及如何解決。May 03, 2025 am 12:21 AMThesolutiontohandlefilepathsacrossWindowsandLinuxinJavaistousePaths.get()fromthejava.nio.filepackage.1)UsePaths.get()withSystem.getProperty("user.dir")andtherelativepathtoconstructthefilepath.2)ConverttheresultingPathobjecttoaFileobjectifne
 Java平台獨立對開發人員有什麼好處?May 03, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Java平台獨立對開發人員有什麼好處?May 03, 2025 am 12:15 AMJava'splatFormIndenceistificantBecapeitAllowSitallowsDevelostWriTecoDeonCeandRunitonAnyPlatFormwithAjvm.this“ writeonce,runanywhere”(era)櫥櫃櫥櫃:1)交叉plat formcomplibility cross-platformcombiblesible,enablingDeploymentMentMentMentMentAcrAptAprospOspOspOssCrossDifferentoSswithOssuse; 2)
 將Java用於需要在不同服務器上運行的Web應用程序的優點是什麼?May 03, 2025 am 12:13 AM
將Java用於需要在不同服務器上運行的Web應用程序的優點是什麼?May 03, 2025 am 12:13 AMJava適合開發跨服務器web應用。 1)Java的“一次編寫,到處運行”哲學使其代碼可在任何支持JVM的平台上運行。 2)Java擁有豐富的生態系統,包括Spring和Hibernate等工具,簡化開發過程。 3)Java在性能和安全性方面表現出色,提供高效的內存管理和強大的安全保障。
 JVM如何促進Java的'寫作一次,在任何地方運行”(WORA)功能?May 02, 2025 am 12:25 AM
JVM如何促進Java的'寫作一次,在任何地方運行”(WORA)功能?May 02, 2025 am 12:25 AMJVM通過字節碼解釋、平台無關的API和動態類加載實現Java的WORA特性:1.字節碼被解釋為機器碼,確保跨平台運行;2.標準API抽像操作系統差異;3.類在運行時動態加載,保證一致性。
 Java的較新版本如何解決平台特定問題?May 02, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Java的較新版本如何解決平台特定問題?May 02, 2025 am 12:18 AMJava的最新版本通過JVM優化、標準庫改進和第三方庫支持有效解決平台特定問題。 1)JVM優化,如Java11的ZGC提升了垃圾回收性能。 2)標準庫改進,如Java9的模塊系統減少平台相關問題。 3)第三方庫提供平台優化版本,如OpenCV。
 說明JVM執行的字節碼驗證的過程。May 02, 2025 am 12:18 AM
說明JVM執行的字節碼驗證的過程。May 02, 2025 am 12:18 AMJVM的字節碼驗證過程包括四個關鍵步驟:1)檢查類文件格式是否符合規範,2)驗證字節碼指令的有效性和正確性,3)進行數據流分析確保類型安全,4)平衡驗證的徹底性與性能。通過這些步驟,JVM確保只有安全、正確的字節碼被執行,從而保護程序的完整性和安全性。


熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

Atom編輯器mac版下載
最受歡迎的的開源編輯器

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
這個專案正在遷移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的過程中,你可以繼續在那裡關注我們。 MinGW:GNU編譯器集合(GCC)的本機Windows移植版本,可自由分發的導入函式庫和用於建置本機Windows應用程式的頭檔;包括對MSVC執行時間的擴展,以支援C99功能。 MinGW的所有軟體都可以在64位元Windows平台上運作。

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser是一個安全的瀏覽器環境,安全地進行線上考試。該軟體將任何電腦變成一個安全的工作站。它控制對任何實用工具的訪問,並防止學生使用未經授權的資源。






