Java棧與佇列怎麼實現
- PHPz轉載
- 2023-04-20 10:43:061348瀏覽
1、實作循環佇列
【OJ連結】
循環佇列一般透過陣列實作。我們需要解決幾個問題。
(1)陣列下標實作迴圈
a、下標最後再往後(offset 小於 array.length): index = (index offset) % array.length。通俗一點,就是如果我們的陣列大小為8,下標走到了7,再往後如何回到0,我們可以(index 1)%8來實現。
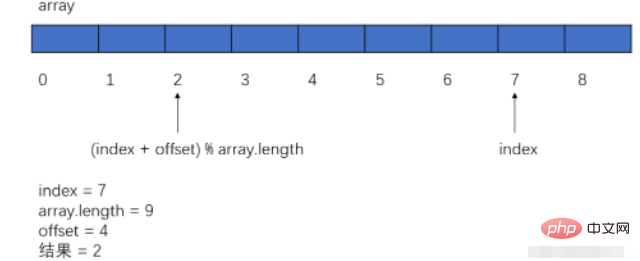
b、下標最前再往前的時候,我們特別判斷一下,將其置為陣列大小減一即可。
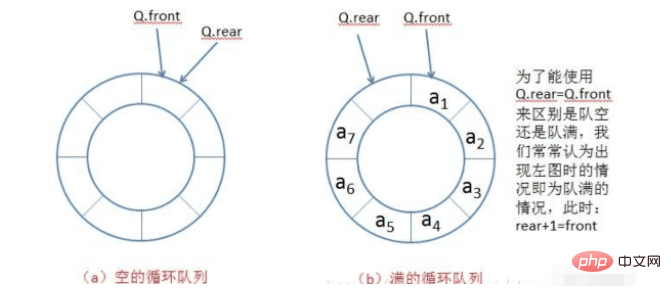
(2)區分隊列的滿與空
我們可以為陣列預留一個位置,如果rear 1=front,則表示隊列已滿;如果rear=front,表示隊列為空。這個情況下,我們需要考慮佇列大小的問題,在定義數組大小時,需要比原有的大一。
【程式碼如下】
class MyCircularQueue {
public int front;
public int rear;
public int[] array;
//构造方法
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
//因为预留位置的缘故,数组的大小要定义为k+1
this.array=new int[k+1];
}
//入队
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
this.array[this.rear]=value;
this.rear=(this.rear+1)%this.array.length;
return true;
}
//出队
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
this.front=(this.front+1)%this.array.length;
return true;
}
//获取队头
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return this.array[front];
}
//获取队尾
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
int index=-1;
if(this.rear==0){
index=this.array.length-1;
}else{
index=this.rear-1;
}
return this.array[index];
}
//判断是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(this.front==this.rear){
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull() {
if((this.rear+1)%this.array.length==this.front){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}2、佇列實作堆疊
【OJ連結】
因為堆疊的先進後出、隊列的先進先出原則。我們需要兩個佇列來實作堆疊。當兩個佇列都為空時,棧為空。
入棧(push):第一次入棧無所謂,兩個佇列都為空,隨便選一個隊列入隊即可;後面入棧時,一定會有一個隊列不為空,找到不為空的隊列,進行入隊操作。
出棧(pop):當先棧為空時,不能進行出棧操作;棧不為空時,肯定有一個佇列為空(queue1),一個佇列不為空(queue2),將queue1中的size-1個元素出棧到queue2中(特別注意不能將求queue1大小的函數放進循環裡,queue進行出隊操作時,其大小是改變的),最後將queue1中最後一個元素進行出隊最為回傳值。
取得棧頂元素(top):跟出棧差不多,就不細說了
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue1;
private Queue<Integer> queue2;
//构造方法
public MyStack() {
queue1=new LinkedList<>();
queue2=new LinkedList<>();
}
//入栈
public void push(int x) {
if(!queue2.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(x);
}else{
queue1.offer(x);
}
}
//出栈
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(queue1.isEmpty()){
int size=queue2.size();
for(int i=0;i<size-1;++i){
int x=queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(x);
}
return queue2.poll();
}else{
int size=queue1.size();
for(int i=0;i<size-1;++i){
int x=queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(x);
}
return queue1.poll();
}
}
//获取栈顶元素
public int top() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(queue1.isEmpty()){
int x=-1;
int size=queue2.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
x=queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(x);
}
return x;
}else{
int size=queue1.size();
int x=-1;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
x=queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(x);
}
return x;
}
}
//判断栈是否为空
public boolean empty() {
if(queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
} 3、堆疊實作佇列【OJ連結】還是跟上面一樣,需要用到兩個堆疊(stack1、stack2)。和實作棧列不同的是,入隊只能對同一個堆疊進行操作。如果兩個堆疊都為空,則佇列為空。
- 入隊(push):規定stack1用來入隊。每次入隊時,請對stack1進行入棧操作即可。
- 出隊(pop):規定stack2進行出隊操作。如果佇列為空時,不能進行出隊操作。當stack2為空時,我們需要將stack1中所有元素出棧,放入stack2中,然後對stack2進行出棧操作。如果stack2不為空,則直接對stack2進行出棧操作即可。
- 取得佇列開頭元素(peek):和出棧操作相同,最後只需要取得stack2的堆疊頂元素即可。
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
//构造方法
public MyQueue() {
stack1=new Stack<>();
stack2=new Stack<>();
}
//入队操作
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
//出队操作
public int pop() {
if(stack2.empty()){
int size=stack1.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
int x=stack1.pop();
stack2.push(x);
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
//获取队列开头的元素
public int peek() {
if(stack2.empty()){
int size=stack1.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
int x=stack1.pop();
stack2.push(x);
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean empty() {
if(stack1.empty()&&stack2.empty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}4、實作最小堆疊【OJ連結】##其實就是要在O( 1)的時間複雜度內找到堆疊的最小元素。需要兩個堆疊來實現,一個堆疊來進行出棧、入棧操作。只需要保證不管如何操作,另一個堆疊的棧頂元素都是目前堆疊的最小元素即可。
兩個堆疊stack1、stack2,站的操作都在stack1中:
- 入棧:如果第一次入棧,我們需要也放入stack2中,之後的入棧,將入棧元素與stack2的棧頂元素進行比較,如果其小於stack2的棧頂元素,則將其放入stack2中。
- 出棧:對stack1出棧時,將其與stack2的棧頂元素進行比較,如果其等於stack2的棧頂元素,則對stack2進行出棧操作。
- 這樣就能保證stack2的堆疊頂部元素總是stack1的最小元素。注意:如果stack1中入堆疊兩個相同的最小元素,都需要對stack2進行入堆疊。
【程式碼如下】
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
//构造方法
public MinStack() {
stack1=new Stack<>();
stack2=new Stack<>();
}
//入栈
public void push(int val) {
stack1.push(val);
if(stack2.empty()){
stack2.push(val);
}else{
if(val<=stack2.peek()){
stack2.push(val);
}
}
}
//出栈
public void pop() {
int x=stack1.pop();
if(x==stack2.peek()){
stack2.pop();
}
}
//获取栈顶元素
public int top() {
return stack1.peek();
}
//获取栈的最小元素
public int getMin() {
return stack2.peek();
}
}以上是Java棧與佇列怎麼實現的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

