使用Pytorch實現對比學習SimCLR 進行自我監督預訓練
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB轉載
- 2023-04-10 14:11:032206瀏覽
SimCLR(Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Representations)是一種學習影像表示的自監督技術。與傳統的監督學習方法不同,SimCLR 不依賴標記資料來學習有用的表示。它利用對比學習框架來學習一組有用的特徵,這些特徵可以從未標記的圖像中捕獲高級語義資訊。
SimCLR 已被證明在各種影像分類基準上優於最先進的無監督學習方法。並且它學習到的表示可以很容易地轉移到下游任務,例如物件檢測、語義分割和小樣本學習,只需在較小的標記資料集上進行最少的微調。
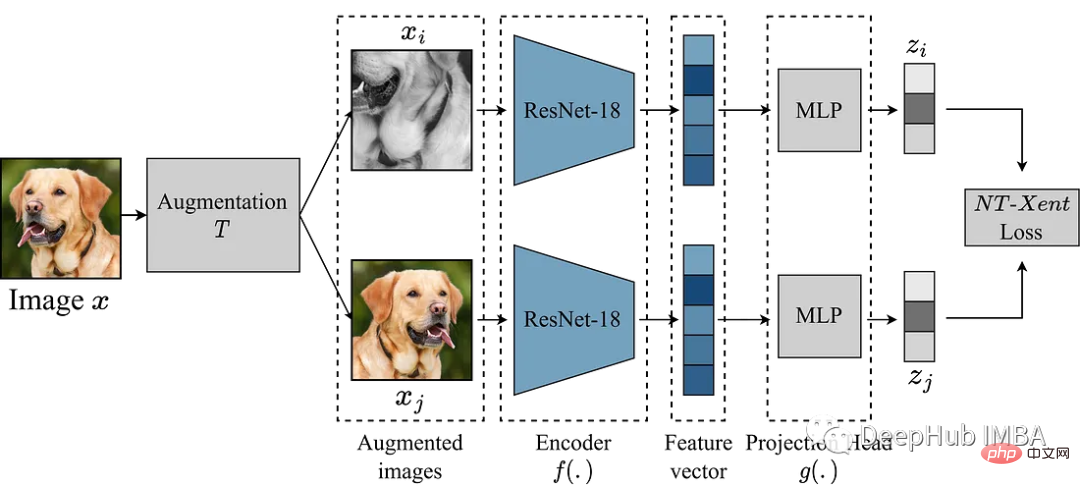
SimCLR 主要想法是透過增強模組 T 將影像與同一影像的其他增強版本進行對比,從而學習影像的良好表示。這是透過編碼器網路 f(.) 來映射影像,然後進行投影來完成的。 head g(.) 將學習到的特徵對應到低維空間。然後在同一圖像的兩個增強版本的表示之間計算對比損失,以鼓勵對同一圖像的相似表示和對不同圖像的不同表示。
本文我們將深入研究 SimCLR 框架並探索演算法的關鍵元件,包括資料增強、對比損失函數以及編碼器和投影的head 架構。
我們這裡使用來自 Kaggle 的垃圾分類資料集來進行實驗
增強模組
SimCLR 中最重要的就是轉換影像的增強模組。 SimCLR 論文的作者建議,強大的資料增強對於無監督學習很有用。因此,我們將遵循論文中推薦的方法。
- 調整大小的隨機裁切
- 50% 機率的隨機水平翻轉
- 隨機顏色失真(顏色抖動機率為80%,顏色下降機率為20% )
- 50% 機率為隨機高斯模糊
def get_complete_transform(output_shape, kernel_size, s=1.0): """ Color distortion transform Args: s: Strength parameter Returns: A color distortion transform """ rnd_crop = RandomResizedCrop(output_shape) rnd_flip = RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5) color_jitter = ColorJitter(0.8*s, 0.8*s, 0.8*s, 0.2*s) rnd_color_jitter = RandomApply([color_jitter], p=0.8) rnd_gray = RandomGrayscale(p=0.2) gaussian_blur = GaussianBlur(kernel_size=kernel_size) rnd_gaussian_blur = RandomApply([gaussian_blur], p=0.5) to_tensor = ToTensor() image_transform = Compose([ to_tensor, rnd_crop, rnd_flip, rnd_color_jitter, rnd_gray, rnd_gaussian_blur, ]) return image_transform class ContrastiveLearningViewGenerator(object): """ Take 2 random crops of 1 image as the query and key. """ def __init__(self, base_transform, n_views=2): self.base_transform = base_transform self.n_views = n_views def __call__(self, x): views = [self.base_transform(x) for i in range(self.n_views)] return views
下一步就是定義一個PyTorch 的Dataset 。
class CustomDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, list_images, transform=None): """ Args: list_images (list): List of all the images transform (callable, optional): Optional transform to be applied on a sample. """ self.list_images = list_images self.transform = transform def __len__(self): return len(self.list_images) def __getitem__(self, idx): if torch.is_tensor(idx): idx = idx.tolist() img_name = self.list_images[idx] image = io.imread(img_name) if self.transform: image = self.transform(image) return image
作為範例,我們使用比較小的模型ResNet18 作為主幹,所以他的輸入是224x224 映像,我們按照要求設定一些參數並產生dataloader
#
out_shape = [224, 224]
kernel_size = [21, 21] # 10% of out_shape
# Custom transform
base_transforms = get_complete_transform(output_shape=out_shape, kernel_size=kernel_size, s=1.0)
custom_transform = ContrastiveLearningViewGenerator(base_transform=base_transforms)
garbage_ds = CustomDataset(
list_images=glob.glob("/kaggle/input/garbage-classification/garbage_classification/*/*.jpg"),
transform=custom_transform
)
BATCH_SZ = 128
# Build DataLoader
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
garbage_ds,
batch_size=BATCH_SZ,
shuffle=True,
drop_last=True,
pin_memory=True)
SimCLR
我們已經準備好了數據,開始對模型進行複現。上面的增強模組提供了圖像的兩個增強視圖,它們透過編碼器前向傳遞以獲得相應的表示。 SimCLR 的目標是透過鼓勵模型從兩個不同的增強視圖中學習物件的一般表示來最大化這些不同學習表示之間的相似性。
編碼器網路的選擇不受限制,可以是任何架構。上面已經說了,為了簡單演示,我們使用 ResNet18。編碼器模型學習到的表示決定了相似性係數,為了提高這些表示的質量,SimCLR 使用投影頭將編碼向量投影到更豐富的潛在空間。這裡我們將ResNet18的512維度的特徵投影到256的空間中,看著很複雜,其實就是加了一個帶relu的mlp。
class Identity(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Identity, self).__init__() def forward(self, x): return x class SimCLR(nn.Module): def __init__(self, linear_eval=False): super().__init__() self.linear_eval = linear_eval resnet18 = models.resnet18(pretrained=False) resnet18.fc = Identity() self.encoder = resnet18 self.projection = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(512, 512), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(512, 256) ) def forward(self, x): if not self.linear_eval: x = torch.cat(x, dim=0) encoding = self.encoder(x) projection = self.projection(encoding) return projection
對比損失
對比損失函數,也稱為歸一化溫度標度交叉熵損失(NT-Xent),是SimCLR 的關鍵組成部分,它鼓勵模型學習相同圖像的相似表示和不同圖像的不同表示。
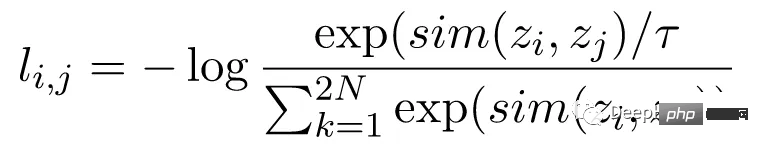
NT-Xent 損失是使用一對透過編碼器網路傳遞的圖像的增強視圖來計算的,以獲得它們相應的表示。對比損失的目標是鼓勵同一圖像的兩個增強視圖的表示相似,同時迫使不同圖像的表示不相似。
NT-Xent 將 softmax 函數套用至增強視圖表示的配對相似性。 softmax 函數應用於小批量內的所有表示對,得到每個影像的相似性機率分佈。溫度參數temperature 用於在應用 softmax 函數之前縮放成對相似性,這有助於在最佳化過程中獲得更好的梯度。
在獲得相似性的機率分佈後,透過最大化相同影像的匹配表示的對數似然和最小化不同影像的不匹配表示的對數似然來計算 NT-Xent 損失。
LABELS = torch.cat([torch.arange(BATCH_SZ) for i in range(2)], dim=0) LABELS = (LABELS.unsqueeze(0) == LABELS.unsqueeze(1)).float() #one-hot representations LABELS = LABELS.to(DEVICE) def ntxent_loss(features, temp): """ NT-Xent Loss. Args: z1: The learned representations from first branch of projection head z2: The learned representations from second branch of projection head Returns: Loss """ similarity_matrix = torch.matmul(features, features.T) mask = torch.eye(LABELS.shape[0], dtype=torch.bool).to(DEVICE) labels = LABELS[~mask].view(LABELS.shape[0], -1) similarity_matrix = similarity_matrix[~mask].view(similarity_matrix.shape[0], -1) positives = similarity_matrix[labels.bool()].view(labels.shape[0], -1) negatives = similarity_matrix[~labels.bool()].view(similarity_matrix.shape[0], -1) logits = torch.cat([positives, negatives], dim=1) labels = torch.zeros(logits.shape[0], dtype=torch.long).to(DEVICE) logits = logits / temp return logits, labels
所有的準備都完成了,讓我們訓練 SimCLR 看看效果!
simclr_model = SimCLR().to(DEVICE)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(DEVICE)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(simclr_model.parameters())
epochs = 10
with tqdm(total=epochs) as pbar:
for epoch in range(epochs):
t0 = time.time()
running_loss = 0.0
for i, views in enumerate(train_dl):
projections = simclr_model([view.to(DEVICE) for view in views])
logits, labels = ntxent_loss(projections, temp=2)
loss = criterion(logits, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print stats
running_loss += loss.item()
if i%10 == 9: # print every 10 mini-batches
print(f"Epoch: {epoch+1} Batch: {i+1} Loss: {(running_loss/100):.4f}")
running_loss = 0.0
pbar.update(1)
print(f"Time taken: {((time.time()-t0)/60):.3f} mins")
上面程式碼訓練了10輪,假設我們已經完成了預訓練過程,可以將預先訓練的編碼器用於我們想要的下游任務。這可以透過下面的程式碼來完成。
from torchvision.transforms import Resize, CenterCrop
resize = Resize(255)
ccrop = CenterCrop(224)
ttensor = ToTensor()
custom_transform = Compose([
resize,
ccrop,
ttensor,
])
garbage_ds = ImageFolder(
root="/kaggle/input/garbage-classification/garbage_classification/",
transform=custom_transform
)
classes = len(garbage_ds.classes)
BATCH_SZ = 128
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
garbage_ds,
batch_size=BATCH_SZ,
shuffle=True,
drop_last=True,
pin_memory=True,
)
class Identity(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Identity, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x
class LinearEvaluation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model, classes):
super().__init__()
simclr = model
simclr.linear_eval=True
simclr.projection = Identity()
self.simclr = simclr
for param in self.simclr.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
self.linear = nn.Linear(512, classes)
def forward(self, x):
encoding = self.simclr(x)
pred = self.linear(encoding)
return pred
eval_model = LinearEvaluation(simclr_model, classes).to(DEVICE)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(DEVICE)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(eval_model.parameters())
preds, labels = [], []
correct, total = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
t0 = time.time()
for img, gt in tqdm(train_dl):
image = img.to(DEVICE)
label = gt.to(DEVICE)
pred = eval_model(image)
_, pred = torch.max(pred.data, 1)
total += label.size(0)
correct += (pred == label).float().sum().item()
print(f"Time taken: {((time.time()-t0)/60):.3f} mins")
print(
"Accuracy of the network on the {} Train images: {} %".format(
total, 100 * correct / total
)
)
上面的程式碼最主要的部分就是讀取剛剛訓練的simclr模型,然後凍結所有的權重,然後再建立一個分類頭self.linear ,進行下游的分類任務
總結
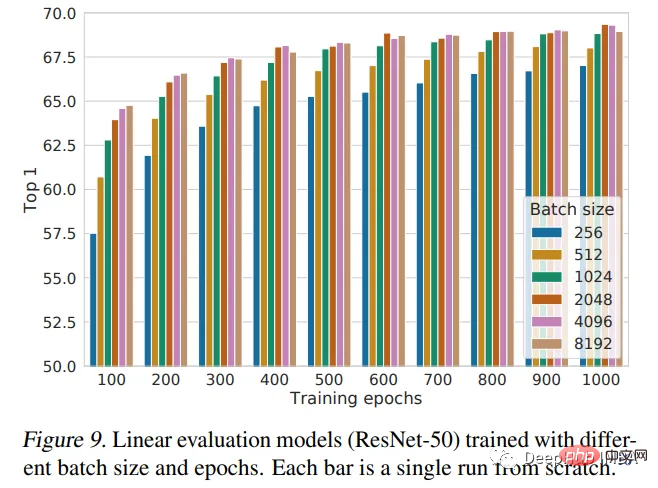
本文介紹了SimCLR框架,並使用它來預先訓練隨機初始化權重的ResNet18。預訓練是深度學習中使用的一種強大的技術,用於在大型資料集上訓練模型,學習可以轉移到其他任務中的有用特徵。 SimCLR論文認為,批量越大,效能越好。我們的實現只使用128個批次大小,只訓練10個epoch。所以這不是模型的最佳性能,如果需要性能對比還需要進一步的訓練。
下圖是論文作者給出的表現結論:
以上是使用Pytorch實現對比學習SimCLR 進行自我監督預訓練的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

