看看 MySQL令人咋舌的隱式轉換
- coldplay.xixi轉載
- 2021-01-13 09:20:412080瀏覽
mysql教學欄位介紹相關的隱含轉換

更多相關免費學習推薦:mysql教學(影片)
一、問題描述
root@mysqldb 22:12: [xucl]> show create table t1\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t1
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
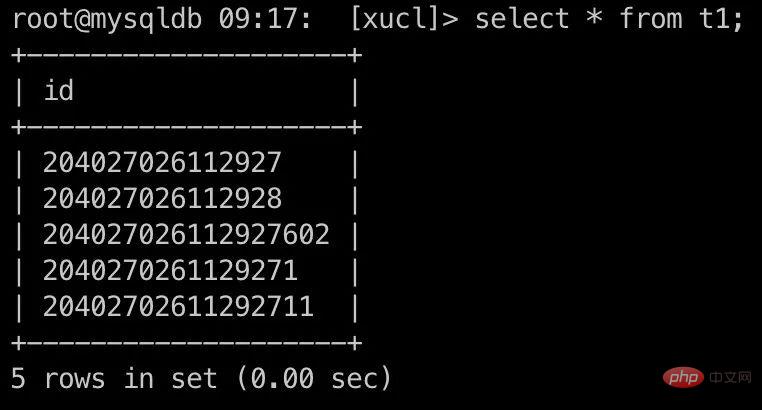
root@mysqldb 22:19: [xucl]> select * from t1;
+--------------------+
| id |
+--------------------+
| 204027026112927605 |
| 204027026112927603 |
| 2040270261129276 |
| 2040270261129275 |
| 100 |
| 101 |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)奇怪的現象:
root@mysqldb 22:19: [xucl]> select * from t1 where id=204027026112927603; +--------------------+ | id | +--------------------+ | 204027026112927605 | | 204027026112927603 | +--------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)

什麼鬼,明明查的是204027026112927603,為什麼204027026112927605也出來了
二、原始碼解釋
堆疊呼叫關係如下所示:
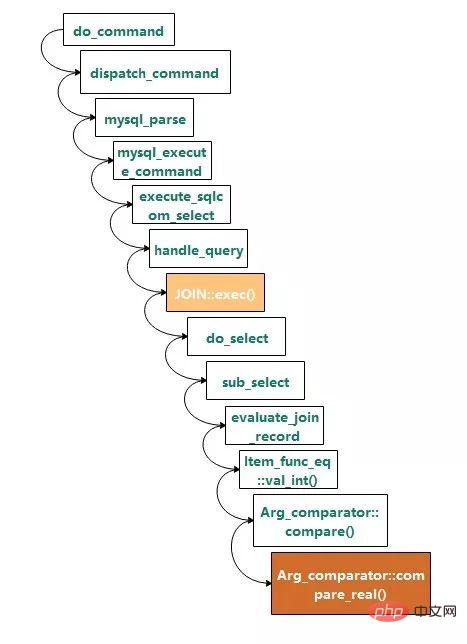
#其中JOIN::exec( )是執行的入口,Arg_comparator::compare_real()是進行等值判斷的函數,其定義如下
int Arg_comparator::compare_real()
{
/*
Fix yet another manifestation of Bug#2338. 'Volatile' will instruct
gcc to flush double values out of 80-bit Intel FPU registers before
performing the comparison.
*/
volatile double val1, val2;
val1= (*a)->val_real();
if (!(*a)->null_value)
{
val2= (*b)->val_real();
if (!(*b)->null_value)
{
if (set_null)
owner->null_value= 0;
if (val1 < val2) return -1;
if (val1 == val2) return 0;
return 1;
}
}
if (set_null)
owner->null_value= 1;
return -1;
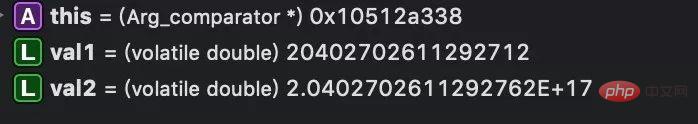
}比較步驟如下圖所示,逐行讀取t1表的id列放入val1,而常數204027026112927603存在於cache中,型別為double型別(2.0402702611292762E 17),所以到這裡傳值給val2後val2=2.04027026112926117。
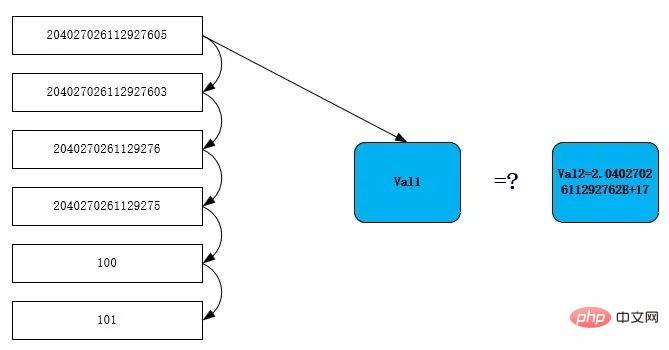
當掃描到第一行時,204027026112927605轉成doule的值為2.0402702611292762e17,等式成立,繼續判定為符合條件的行,繼續往下掃描,同理204027026112927603也同樣符合
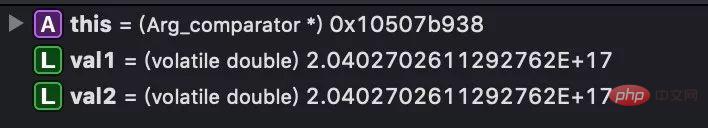
如何檢測string類型的數字轉成doule類型是否溢出呢?這裡經過測試,當數字超過16位以後,轉成double型別就已經不準確了,例如20402702611292711會表示成20402702611292712(如圖中val1)
{
char buf[DTOA_BUFF_SIZE];
double res;
DBUG_ASSERT(end != NULL && ((str != NULL && *end != NULL) ||
(str == NULL && *end == NULL)) &&
error != NULL);
res= my_strtod_int(str, end, error, buf, sizeof(buf));
return (*error == 0) ? res : (res < 0 ? -DBL_MAX : DBL_MAX);
}
真正轉換函數my_strtod_int位置在dtoa.c(太複雜了,簡單貼個註解)
/*
strtod for IEEE--arithmetic machines.
This strtod returns a nearest machine number to the input decimal
string (or sets errno to EOVERFLOW). Ties are broken by the IEEE round-even
rule.
Inspired loosely by William D. Clinger's paper "How to Read Floating
Point Numbers Accurately" [Proc. ACM SIGPLAN '90, pp. 92-101].
Modifications:
1. We only require IEEE (not IEEE double-extended).
2. We get by with floating-point arithmetic in a case that
Clinger missed -- when we're computing d * 10^n
for a small integer d and the integer n is not too
much larger than 22 (the maximum integer k for which
we can represent 10^k exactly), we may be able to
compute (d*10^k) * 10^(e-k) with just one roundoff.
3. Rather than a bit-at-a-time adjustment of the binary
result in the hard case, we use floating-point
arithmetic to determine the adjustment to within
one bit; only in really hard cases do we need to
compute a second residual.
4. Because of 3., we don't need a large table of powers of 10
for ten-to-e (just some small tables, e.g. of 10^k
for 0 <= k <= 22).
*/既然是這樣,我們測試下沒有溢出的案例root@mysqldb 23:30: [xucl]> select * from t1 where id=2040270261129276; +------------------+ | id | +------------------+ | 2040270261129276 | +------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) root@mysqldb 23:30: [xucl]> select * from t1 where id=101; +------+ | id | +------+ | 101 | +------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)結果符合預期,而在本例中,正確的寫法應當是
root@mysqldb 22:19: [xucl]> select * from t1 where id='204027026112927603'; +--------------------+ | id | +--------------------+ | 204027026112927603 | +--------------------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
#三、結論
#避免發生隱含型別轉換,隱含轉換的型別主要有欄位型別不一致、in參數包含多個型別、字元集型別或校對規則不一致等
隱含型別轉換可能導致無法使用索引、查詢結果不準確等,因此在使用時必須仔細甄別
數字類型的建議在欄位定義時就定義為int或bigint,表格關聯時關聯欄位必須保持類型、字元集、校對規則都一致
最後貼一下官網對於隱式類型轉換的說明吧
1、If one or both arguments are NULL, the result of the comparison is NULL, except for the NULL-safe <=> equality comparison operator. For NULL <=> NULL, the result is true. No conversion is needed. 2、If both arguments in a comparison operation are strings, they are compared as strings. 3、If both arguments are integers, they are compared as integers. 4、Hexadecimal values are treated as binary strings if not compared to a number. 5、If one of the arguments is a TIMESTAMP or DATETIME column and the other argument is a constant, the constant is converted to a timestamp before the comparison is performed. This is done to be more ODBC-friendly. This is not done for the arguments to IN(). To be safe, always use complete datetime, date, or time strings when doing comparisons. For example, to achieve best results when using BETWEEN with date or time values, use CAST() to explicitly convert the values to the desired data type. A single-row subquery from a table or tables is not considered a constant. For example, if a subquery returns an integer to be compared to a DATETIME value, the comparison is done as two integers. The integer is not converted to a temporal value. To compare the operands as DATETIME values, use CAST() to explicitly convert the subquery value to DATETIME. 6、If one of the arguments is a decimal value, comparison depends on the other argument. The arguments are compared as decimal values if the other argument is a decimal or integer value, or as floating-point values if the other argument is a floating-point value. 7、In all other cases, the arguments are compared as floating-point (real) numbers.
以上是看看 MySQL令人咋舌的隱式轉換的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

