關於js中this、原型與閉包的深入理解
- 王林轉載
- 2019-08-21 15:34:542422瀏覽
1、this關鍵字
a、有物件指向物件;
b、沒物件指向全域變數(window);
c、有new指向new出的新物件;
##d、bind,call&apply改變this的指向;e、setTimeout/setInterval this指向window;f、箭頭函數this 是由函數定義時候決定的;##
var adder = {
base : 1,
add : function(a) {
var f = v => v + this.base;
return f(a);
},
addThruCall: function inFun(a) {
var f = v => v + this.base;
var b = {
base : 2
};
return f.call(b, a);
}
};var obj = {
i: 10,
b: () => console.log(this.i, this),
c: function() {
console.log( this.i, this)
}
}
obj.b(); // undefined window{...}原型
obj.c(); // 10 Object {...}2、原型
prototype:
prototype:每一個物件都會在其內部初始化一個屬性:即prototype;
原型鏈:當我們存取一個物件的屬性時,如果這個物件內部不存在這個屬性,那麼就回去
__proto__#裡找這個屬性,這樣一直找下去就是:原型鏈;
原理是判斷實例物件的__proto__和產生該實例的建構子的prototype是不是引用的同一個地址。
是 JavaScript 中唯一一個處理屬性但不尋找原型鏈的函數。
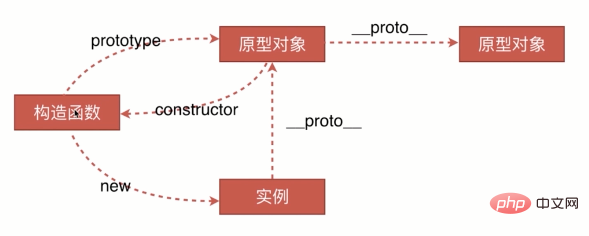 建構子 ->prototype-> 原型物件-> constructor -> 建構子
建構子 ->prototype-> 原型物件-> constructor -> 建構子
建構子-> new ->實例物件
實例物件-> __proto__-> 原型物件-> __proto__->原型物件->->null
#執行上下文:變數宣告與函數聲明,其作用域會提升到方法體的頂端;
作用域:
# a、javascript沒有區塊級作用域
b、javascript除了全域作用域之外,只有函數可以創建的作用域。作用域在函數定義時就已經確定了。而不是在函數呼叫時確定。
閉包:
概念: 內部函數可以存取外部函數中的變數;
使用:函數作為傳回值;函數作為參數;
作用:封裝變量,收斂權限;
缺點:消耗記憶體
建立物件的方法:物件字面量;
建構子;
立即執行函數;
Object.create();
new 物件過程:#建立新物件;
this指向這個新物件;
執行程式碼;
返回this;
##類別與繼承
:類別的宣告
:function Animal(){
this.name = 'name';
}
// es6
class Animal2{
constructor(){
this.name = 'name2';
}
}繼承:1.借助建構子實作繼承
function Parent(){
this.name = 'parent';
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child1';
}缺點:部分繼承;繼承不到父類別原型物件上的方法;(只有父類別的屬性掛載到子類別上了,Child的prototype沒變成Child.prototype繼承不了Parent的prototype)2.原型鏈繼function Parent(){
this.name = 'name';
}
function Child(){
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
缺点:原型链上原型对象是共用的。(原型的属性修改,所有继承自该原型的类的属性都会一起改变)
3.组合方式
function Parent(){
this.name = 'parent';
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();缺点:
父类执行函数执行两次;
constructor指向父类;
function Parent(){
this.name = 'parent';
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;缺点:
子类constructor指向父类
function Parent(){
this.name = 'parent';
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;优点:
子类的原型指向Object.create(Parent.prototype),实现了子类和父类构造函数的分离,但是这时子类中还是没有自己的构造函数,
所以紧接着又设置了子类的构造函数,由此实现了完美的组合继承。(也就是把父类的prototype写入子类的prototype,在定义子类的constructor)
4. es6
class Child extends Parent {
constructor(){
}
}希望本文中的内容能够帮到学习JavaScript的同学。谢谢!
更多JavaScript的相关问题请访问PHP中文网:https://www.php.cn/
以上是關於js中this、原型與閉包的深入理解的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

