PHP中引入檔案的方法有哪些? PHP引入檔案的四種方法介紹(程式碼)
- 不言原創
- 2018-07-23 17:09:374438瀏覽
PHP引入檔案的方式有哪些? PHP引入檔案有四個語句:include、require、include_once、require_once,我們來看看PHP引入檔案的具體實例。
基本語法
require:require函數一般放在PHP腳本的最前面,PHP執行前就會先讀入require指定引入的文件,包含並嘗試執行引入的腳本文件。 require的工作方式是提高PHP的執行效率,當它在同一個網頁中解釋過一次後,第二次就不會解釋。但同樣的,正因為它不會重複解釋引入文件,所以當PHP中使用循環或條件語句來引入文件時,需要用到include。
include:可以放在PHP腳本的任何位置,一般放在流程控制的處理部分。當PHP腳本執行到include指定引入的檔案時,才將它包含並嘗試執行。這種方式可以把程式執行時的流程簡單化。當第二次遇到相同檔案時,PHP還是會重新解釋一次,include相對於require的執行效率下降很多,同時在引入檔案中包含使用者自訂函數時,PHP在解釋過程中會發生函數重複定義問題。
require_once / include_once:分別與require / include作用相同,不同的是他們在執行到時會先檢查目標內容是不是在之前已經導入過,如果導入過了,那麼便不會再重複引入其同樣的內容。
相互差異
#include與require:
## include有傳回值,而require沒有回傳值 include在載入檔案失敗時,會產生一個警告(E_WARNING),在錯誤發生後腳本繼續執行。所以include用在希望繼續執行並向使用者輸出結果時。//test1.php
<?php
include './tsest.php';
echo 'this is test1';
?>
//test2.php
<?php
echo 'this is test2\n';
function test() {
echo 'this is test\n';
}
?>
//结果:
this is test1 require在載入失敗時會產生一個致命錯誤(E_COMPILE_ERROR),在錯誤發生後腳本停止執行。一般用在後續程式碼依賴於載入的檔案的時候。 //test1.php
<?php
require './tsest.php';
echo 'this is test1';
?>
//test2.php
<?php
echo 'this is test2\n';
function test() {
echo 'this is test\n';
}
?>結果:
include與include_once:
include載入的檔案不會判斷是否重複,只要有include語句,就會載入一次(即使可能出現重複載入)。而include_once載入檔案時會有內部判斷機制判斷前面程式碼是否已經載入過。這裡要注意的是include_once是根據前面有無引入相同路徑的文件為判斷的,而不是根據文件中的內容(即兩個待引入的文件內容相同,使用include_once還是會引入兩個)。//test1.php <?php include './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1this is test2 //test1.php <?php include './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include_once './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1 //test1.php <?php include_once './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1this is test2 //test1.php <?php include_once './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include_once './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1
require和require_once:同include和include_once的差別相同。
載入時執行程序
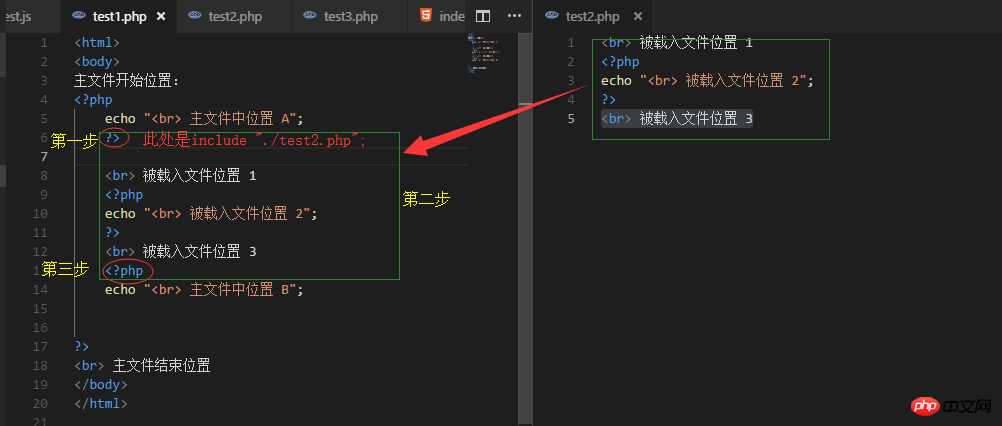
1. 從include(require)語句退出php腳本模式(進入html程式碼模式)2. 載入include語句所設定的檔案中的程式碼,並嘗試執行3. 退出html模式,重新進入php腳本模式,繼續後面腳本程式的執行
//test1.php
<html>
<body>
主文件开始位置:
<?php
echo "<br> 主文件中位置 A";
include "./test2.php"; //要载入的文件
echo "<br> 主文件中位置 B";
?>
<br> 主文件结束位置
</body>
</html>
//test2.php
<br> 被载入文件位置 1
<?php
echo "<br> 被载入文件位置 2";
?>
<br> 被载入文件位置 3結果:
#載入時的路徑問題
相對路徑:
相對於目前網頁檔案所在位置來定位某個被載入的檔案位置。./ 表示表示当前位置,即当前网页文件所在的目录 . . / 表示上一级位置,即当前网页文件所在目录的上一级目录 //例如: include "./test2.php"; require "../../test3.html";
絕對路徑:
分為本機絕對路徑與網路絕對路徑本地絕對路徑:
從本地的根目錄逐層遞歸向下找,直到找到對應目錄下的待引入檔案。include "C:/PHP/test/test2.php";我們都知道,絕對路徑不利於專案的移植和可維護性,所以一般很少在程式碼中直接這樣寫絕對路徑,但是如果我們需要用到絕對路徑,該怎麼辦? ? PHP中有魔術常數__DIR__和全域陣列$_SERVER,用法如下:
<?php define('DS') or define('DS',DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR); echo "使用绝对路径引入(方法一)"; include __DIR__ . DS . 'test2.php'; echo "使用绝对路径载入方法(方法二)"; $root = $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT']; // 获得当前站点的根目录 include $root.DS.'node_test'.DS.'inAndRe'.DS. 'test2.php'; ?>
網路絕對路徑:
透過網址連結到檔案下,伺服器會將網址指向的檔案執行後回傳回來include "http://www.lishnli/index.php"
無路徑:
只給檔名而沒有給予路徑訊息,此時PHP會在目前網頁目錄下找該文件,如果找到相同名字的文件,執行並引入。需要注意:无论采用哪种路径,必须要加上文件后缀名,这四种文件载入方式不能识别无后缀的文件。
//test1.php include "./test2.php"; //结果:this is test2 //test1.php include "./test2"; //结果:
返回值的比较
上文说道include有返回值,而require无返回值
对于include,如果载入成功,有返回值,返回值为1;如果载入失败,则返回false.
对于require,如果载入成功,有返回值,返回值为1;如果载入失败,无返回值。
//test1.php <?php $a = include "./test2.php"; var_dump($a); echo "<br>"; $b = include "./test2.phps"; var_dump($b); echo "<br>"; $c = require "./test2.php"; var_dump($c); echo "<br>"; $d = require "./test2.phps"; var_dump($d); ?>
输出:

当文件中有return:
当被载入文件中有return语句时,会有另外的机制,此时return语句的作用是终止载入过程,即被载入文件中return语句的后续代码不再载入。return语句也可以用于被载入文件载入时返回一个数据。
//test1.php <?php $a = include "./test2.php"; echo "<br>"; var_dump($a); ?> //test2.php //该文件中有return语句 <?php $b = 'test2'; echo "被载入的文件:A 位置"; return $b; echo "<br 被载入的文件: B 位置"; ?>
结果:

相关推荐:
php 字符串写入文件或追加入文件(file_put_contents)
以上是PHP中引入檔案的方法有哪些? PHP引入檔案的四種方法介紹(程式碼)的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

