在webpack中詳細解讀入口函數run
- 亚连原創
- 2018-06-15 14:35:462384瀏覽
Webpack 是一個前端資源載入/打包工具。它將根據模組的依賴關係進行靜態分析,然後將這些模組按照指定的規則產生對應的靜態資源。這篇文章主要介紹了webpack源碼之compile流程-入口函數run,需要的朋友可以參考下
Webpack是目前基於React和Redux開發的應用的主要打包工具。我想使用Angular 2或其他框架開發的應用程式也有很多在使用Webpack。
本節流程如圖:
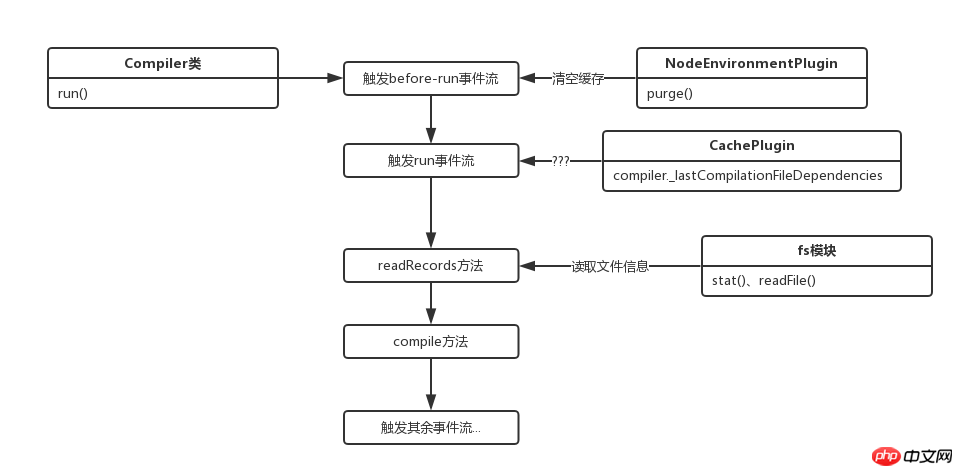
現在正式進入打包流程,起步方法為run:
Compiler.prototype.run = (callback) => {
const startTime = Date.now();
const onCompiled = (err, compilation) => { /**/ };
this.applyPluginsAsync("before-run", this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.applyPluginsAsync("run", this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.readRecords(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.compile(onCompiled);
});
});
});
}為什麼不介紹compiler對象?因為建構函式中並沒有一個初始化的方法,只是普通的變數聲明,沒啥好講的。
在run方法中,首先是呼叫了tapable的applyPluginsAsync執行了before-run事件流,該事件流的定義地點如下:
// NodeEnvironmentPlugin
compiler.plugin("before-run", (compiler, callback) => {
if (compiler.inputFileSystem === inputFileSystem)
inputFileSystem.purge();
callback();
});在對compiler物件的檔案系統方法的掛載插件中,注入了before-run這個事件流,這裡首先看一下applyPluginsAsync(做了小幅度的修改以適應webpack源碼):
// tapable
Tapable.prototype.applyPluginsAsync = (name, ...args, callback) => {
var plugins = this._plugins[name];
if (!plugins || plugins.length === 0) return callback();
var i = 0;
var _this = this;
// args为[args,next函数]
args.push(copyProperties(callback, function next(err) {
// 事件流出错或者全部执行完后调用回调函数
if (err) return callback(err);
i++;
if (i >= plugins.length) {
return callback();
}
// 执行下一个事件
plugins[i].apply(_this, args);
}));
// 执行第一个事件
plugins[0].apply(this, args);
};當時在第八節沒有講這個系列的事件流觸發方式,這裡簡單說下:
1、copyProperties用於物件屬性的拷貝,類似於Object.assign,然而在這裡傳入的是兩個函數,一點用都沒有! ! ! ! ! (當時沒寫講解就是因為一直卡在這個物件拷貝方法在這裡有什麼毛用)
2、在webpack中,args為一個this,指向compiler的上下文
3、注入該事件流的事件必須要執行callback方法(如上例),此時執行的並不是外部的callback,而是next函數
4、有兩種情況下會執行外部callback,中途出錯或者所有事件流執行完畢
這樣就很明白了,注入before-run中的函數形參的意義如下:
// before-run
// compiler => this
// callback => next
(compiler, callback) => {
if (compiler.inputFileSystem === inputFileSystem)
inputFileSystem.purge();
callback();
}由於before-run中只有一個事件,所以在調用內部callback的next方法後,會因為i大於事件長度而直接呼叫外部callback。
這裡的purge方法之前見過,這裡複習下內容:
// NodeEnvironmentPlugin
compiler.inputFileSystem = new CachedInputFileSystem(new NodeJsInputFileSystem(), 60000);
// CachedInputFileSystem
CachedInputFileSystem.prototype.purge = function(what) {
this._statStorage.purge(what);
this._readdirStorage.purge(what);
this._readFileStorage.purge(what);
this._readlinkStorage.purge(what);
this._readJsonStorage.purge(what);
};
// CachedInputFileSystem => Storage
Storage.prototype.purge = function(what) {
if (!what) {
this.count = 0;
clearInterval(this.interval);
this.nextTick = null;
this.data.clear();
this.levels.forEach(function(level) {
level.clear();
});
} else if (typeof what === "string") { /**/ } else { /**/ }
};一句話概括就是:清除所有打包中緩存的資料。
由於假設是第一次,所以這裡並沒有什麼實際操作,接著呼叫外部callback,用同樣的方式觸發了run事件流。
run事件流也只有一個方法,來自CachePlugin插件:
Compiler.plugin("run", (compiler, callback) => {
// 这个属性我暂时也不知道是啥 反正直接callback了
if (!compiler._lastCompilationFileDependencies) return callback();
const fs = compiler.inputFileSystem;
const fileTs = compiler.fileTimestamps = {};
asyncLib.forEach(compiler._lastCompilationFileDependencies, (file, callback) => {
// ...
}, err => {
// ...
});
});在第一次觸發run事件流時,那個屬性是undefined,所以會直接跳過,因為我是邊看原始碼邊解析,所以也不知道是啥,哈哈。
接下來下一個callback是這個:
this.readRecords(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.compile(onCompiled);
});這是另一個原型方法,源碼如下:
Compiler.prototype.readRecords = (callback) => {
// 这个属性也没有
if (!this.recordsInputPath) {
this.records = {};
return callback();
}
this.inputFileSystem.stat(this.recordsInputPath, err => {
// ...
});
}這裡第一次也會跳過並直接callback,看源碼大概是傳入一個路徑並讀取裡面的檔案資訊快取到records。
這下連跳兩步,直接進入原型方法compile中,預覽一下這個函數:
Compiler.prototype.compile = (callback) => {
const params = this.newCompilationParams();
// 依次触发事件流
this.applyPluginsAsync("before-compile", params, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.applyPlugins("compile", params);
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
this.applyPluginsParallel("make", compilation, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
compilation.finish();
compilation.seal(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.applyPluginsAsync("after-compile", compilation, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
return callback(null, compilation);
});
});
});
});
}編譯打包的核心流程已經一覽無遺,方法中依次觸發了before-compile、 compile、make、after-compile事件流,最後呼叫了回調函數。
上面是我整理給大家的,希望今後對大家有幫助。
相關文章:
在VueJs中如何監聽window.resize具體該怎麼實現?
React-native橋接Android如何實現,具體步驟又是什麼?
以上是在webpack中詳細解讀入口函數run的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

