怎麼使用react redux中間件
- php中世界最好的语言原創
- 2018-05-26 15:36:071445瀏覽
這次帶給大家怎麼使用react redux中間件,使用react redux中間件的注意事項有哪些,以下就是實戰案例,一起來看一下。
用過react的同學都知道在redux的存在,redux就是一種前端用來儲存資料的倉庫,並對改倉庫進行增刪改查操作的一種框架,它不僅適用於react ,也使用於其他前端框架。研究過redux原始碼的人都覺得該原始碼很精妙,而本博文就針對redux中對中間件的處理進行介紹。
在講redux中間件之前,先用兩張圖來大致介紹一下redux的基本原理:
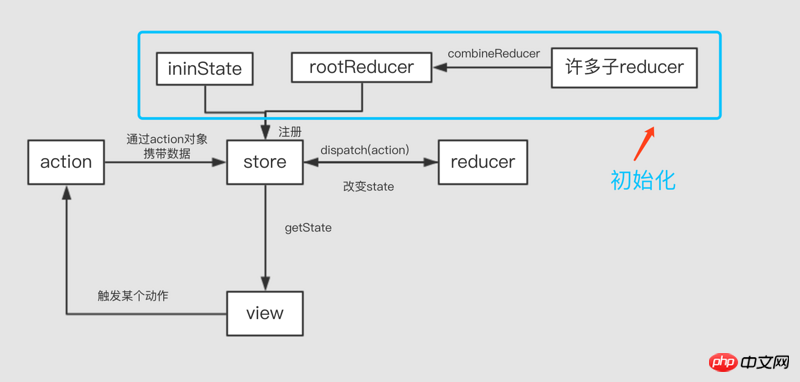
圖中就是redux的基本流程,這裡就不細說。
一般在react中不只利用redux,還利用到react-redux:
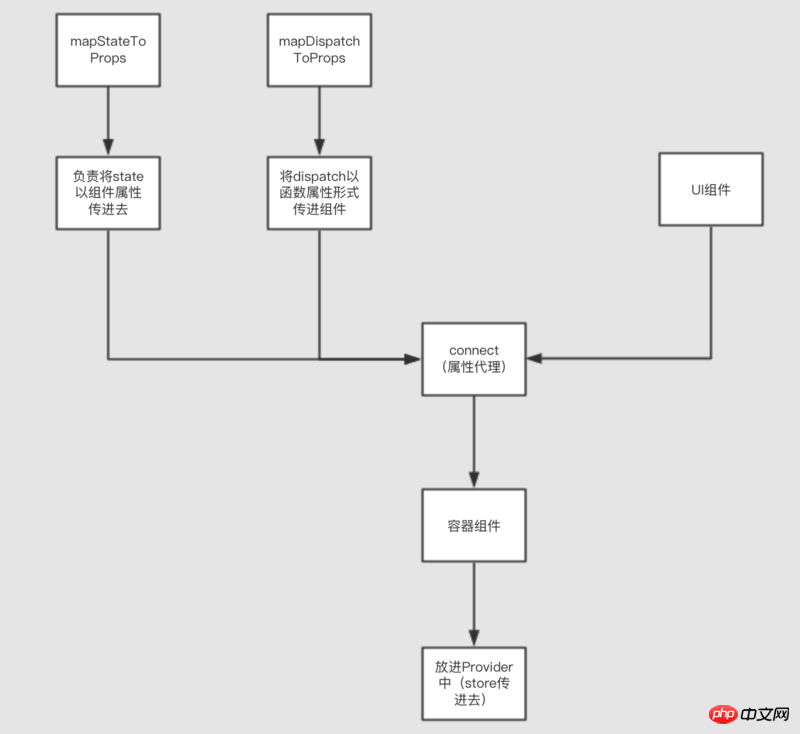
react-redux這裡也不細說。
redux中間件
一般情況下,redux是不具備處理非同步請求的能力,稚嫩溝通過間接或者添加中間件的方式,加強了對dispatch的能力,是的redux具備非同步的能力;
一般來說,redux處理非同步的方式有兩種:間接方式和中間件方式;
間接方式:
間接方式就死自訂非同步的行為,保留dispatch同步的功能。
想法:就是講非同步回傳的結果塞進action中,然後在透過dispatch同步到reduce中,再改變state;
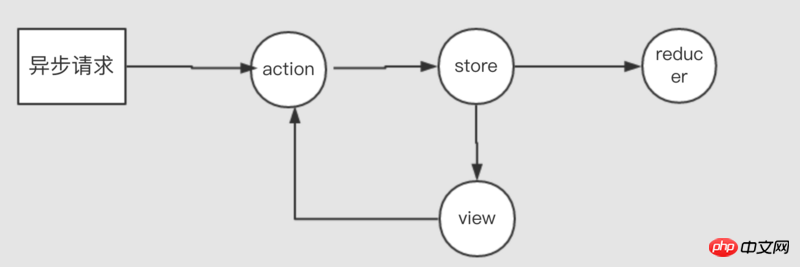
request.get(API)
.then(d => {
store.dispatch(type: xxx, playload: d)
}) 這種方式沒有破壞dispatch的同步機制,原汁原味的使用dispatch將資料同步到state中,但不好的地方就是每次呼叫都會寫很長的一段。
中間件方式
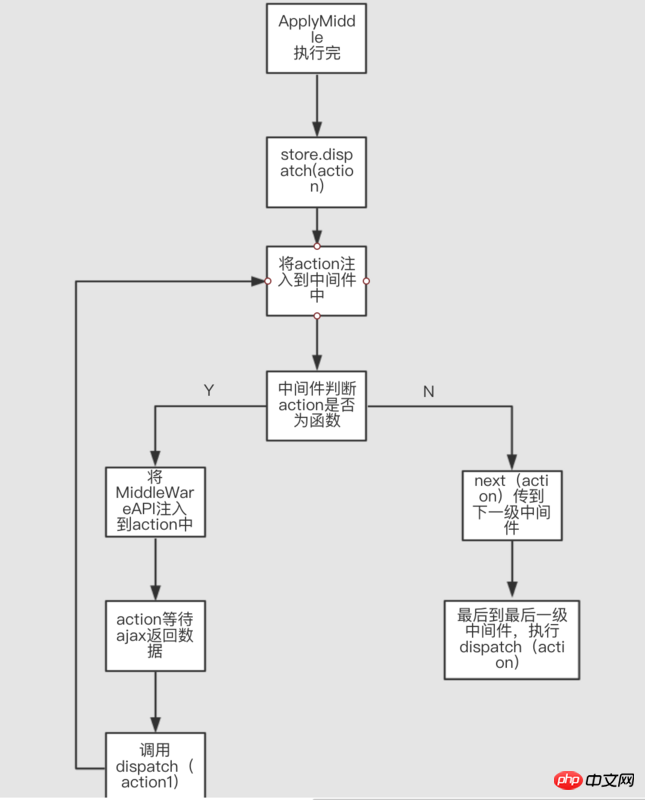
中間件方式中核心部分就是redux提供的applyMiddleWare這個高階函數,它透過多層呼叫後悔傳回一個全新的store對象,在全新的store物件和原始物件中,唯一的不同就是dispatch具備了非同步的功能;const applyMiddleWare = (...middlewares) => createStore => (reducer, initState) =>{
const store = createStore(reducer, initState);
const _dispatch = store.dispatch;
const MiddleWareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: action => _dispatch(action) 1)
};
const chain = [];
chain = middlewares.map(middleware => {middleware(MiddleWareAPI)}); 2)
let dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch); 3)
return {
dispatch,
...store
}
}短短十幾行程式碼,其中卻蘊含著不少精妙之處,部落客選擇了其中三個地方進行分析其精妙之處:M = [M1,M2,M3] ----> M1(M2(M3(store.dispatch)));從這裡其實就知道中間件大致是什麼樣子的了:
const MiddleWare = store => next => action => {
...
} 參數解釋:
- store:其實就是MiddleWareAPI;
- next: 這裡有兩種情況,如果改中間件是在middlewares數組裡最右邊,則next就是store.dispatch;否則就是它相鄰左邊的一個中間件回傳值(閉包函數,就是action => {}這個函數);
- action:可以是函數,也可以是含有promise的物件;
export const MiddleForTest = store => next => action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
action(store);
} else {
next(action);
}
};
export const MiddleForTestTwo = store => next => action => {
next(action);
};
export function AjaxAction(store) {
setTimeout(function () {
store.dispatch({
type: 'up',
playload: '异步信息'
})
}, 1000)
}
store.dispatch(AjaxAction);說這裡應該會對中間件有個大致的認識,接下來介紹一下常用的中間件以及自己寫一個中間件。
redux-thunk:主要是适用于action是一个函数的情况,它是对原有的中间件模式再封装多一层,原则上是支持promise为主的action函数;
export function AjaxThunk (url, type) {
return dispatch => {
Ajax(url)
.then(d => {
dispatch({
type,
playload: d
})
})
}
}
store.dispatch(AjaxThunk(url1, 'add'));redux-promise:主要就是针对action对象,action对象是一个promise的异步请求函数:
它的大概实现思路是:
const promiseAction = store => next => action => {
const {type, playload} = action;
if (playload && typeof playload.then === 'function') {
playload.then(result => {
store.dispatch({type, playload: result});
}).catch(e => {})
} else {
next(action);
}
}
action = {
type: 'xxx',
playload: Ajax(url)
}自定义中间件:很多时候网上的redux中间件可能不太符合项目中的需要,所以这时候可以自己写一套适合项目的中间件,以下指示本博主的一个demo,形式不唯一:
export const PromiseWares = store => next => action => {
next({type: 'right', playload: 'loading'});
if (typeof action === 'function') {
const {dispatch} = store;
action(dispatch);
} else {
const {type, playload} = action;
if (playload && typeof playload.then === 'function') {
playload.then(result => {
store.dispatch({type, playload: result});
}).catch(e => {})
} else {
next(action);
next({type: 'right', playload: 'noLoading'});
}
}
};相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
以上是怎麼使用react redux中間件的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

