在react中建構d3力導向圖方法分享
- 小云云原創
- 2018-01-15 09:23:222092瀏覽
本文主要介紹如何在react中搭建d3力導向圖,小編覺得挺不錯的,現在分享給大家,也給大家做個參考。一起跟著小編過來看看吧,希望能幫助大家,
D3js力導向圖搭建
d3js是一個可以基於資料來操作文件的JavaScript函式庫。可以使用HTML,CSS,SVG以及Canvas來展示資料。力導向圖能夠用來表示節點間多對多的關係。
實現效果:連線有箭頭,點選節點能改變該節點顏色和所連接的線的粗細,縮放、拖曳。
版本:4.X
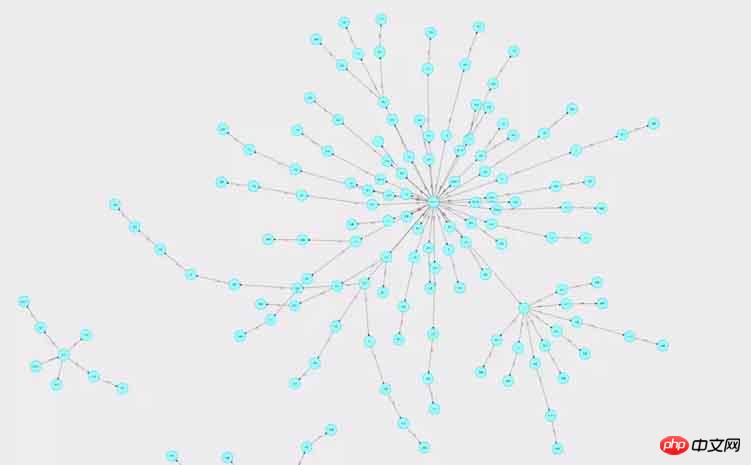
#安裝與導入
npm安裝:npm install d3
前端導入:import * as d3 from 'd3';
##一、完整程式碼
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import { push } from 'react-router-redux';
import * as d3 from 'd3';
import { Row, Form } from 'antd';
import { chartReq} from './actionCreator';
import './Chart.less';
const WIDTH = 1900;
const HEIGHT = 580;
const R = 30;
let simulation;
class Chart extends Component {
constructor(props, context) {
super(props, context);
this.print = this.print.bind(this);
this.forceChart = this.forceChart.bind(this);
this.state = {
};
}
componentWillMount() {
this.props.dispatch(push('/Chart'));
}
componentDidMount() {
this.print();
}
print() {
let callback = (res) => { // callback获取后台返回的数据,并存入state
let nodeData = res.data.nodes;
let relationData = res.data.rels;
this.setState({
nodeData: res.data.nodes,
relationData: res.data.rels,
});
let nodes = [];
for (let i = 0; i < nodeData.length; i++) {
nodes.push({
id: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].id) || '',
name: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].name) || '',
type: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].type) || '',
definition: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].definition) || '',
});
}
let edges = [];
for (let i = 0; i < relationData.length; i++) {
edges.push({
id: (relationData[i] && (relationData[i].id)) || '',
source: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].start.id) || '',
target: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].end.id) || '',
tag: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].name) || '',
});
}
this.forceChart(nodes, edges); // d3力导向图内容
};
this.props.dispatch(chartReq({ param: param }, callback));
}
// func
forceChart(nodes, edges) {
this.refs['theChart'].innerHTML = '';
// 函数内其余代码请看拆解代码
}
render() {
return (
<Row style={{ minWidth: 900 }}>
<p className="outerp">
<p className="theChart" id="theChart" ref="theChart">
</p>
</p>
</Row>
);
}
}
Chart.propTypes = {
dispatch: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
};
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return {
};
}
const WrappedChart = Form.create({})(Chart);
export default connect(mapStateToProps)(WrappedChart);二、拆解程式碼1.元件
<p className="theChart" id="theChart" ref="theChart"> </p>整個圖都將在p裡繪製。
2.建構節點與連線
#
let nodes = []; // 节点
for (let i = 0; i < nodeData.length; i++) {
nodes.push({
id: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].id) || '',
name: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].name) || '', // 节点名称
});
}
let edges = []; // 连线
for (let i = 0; i < relationData.length; i++) {
edges.push({
id: (relationData[i] && (relationData[i].id)) || '',
source: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].start.id) || '', // 开始节点
target: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].end.id) || '', // 结束节点
tag: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].name) || '', // 连线名称
});
} 具體怎麼建構依據你們的專案資料。 3.定義力模型
#
const simulation = d3.forceSimulation(nodes) // 指定被引用的nodes数组 .force('link', d3.forceLink(edges).id(d => d.id).distance(150)) .force('collision', d3.forceCollide(1).strength(0.1)) .force('center', d3.forceCenter(WIDTH / 2, HEIGHT / 2)) .force('charge', d3.forceManyBody().strength(-1000).distanceMax(800));透過simulation.force()設定力,可以設定這幾種力:
- Centering:中心力,設定圖中心點位置。
- Collision:節點碰撞作用力,.strength參數範圍為[0,1]。
- Links:連線的作用力;.distance設定連線兩端節點的距離。
- Many-Body:.strength的參數為正時,模擬重力,為負時,模擬電荷力;.distanceMax的參數設定最大距離。
4.繪製svg
#
const svg = d3.select('#theChart').append('svg') // 在id为‘theChart'的标签内创建svg
.style('width', WIDTH)
.style('height', HEIGHT * 0.9)
.on('click', () => {
console.log('click', d3.event.target.tagName);
})
.call(zoom); // 缩放
const g = svg.append('g'); // 则svg中创建g建立svg,在svg裡建立g,將節點連線等內容放在g內。
- select:選擇第一個對應的元素
- selectAll:選擇所有對應的元素
- append:建立元素
5.繪製連線
const edgesLine = svg.select('g')
.selectAll('line')
.data(edges) // 绑定数据
.enter() // 添加数据到选择集edgepath
.append('path') // 生成折线
.attr('d', (d) => { return d && 'M ' + d.source.x + ' ' + d.source.y + ' L ' + d.target.x + ' ' + d.target.y; }) // 遍历所有数据,d表示当前遍历到的数据,返回绘制的贝塞尔曲线
.attr('id', (d, i) => { return i && 'edgepath' + i; }) // 设置id,用于连线文字
.attr('marker-end', 'url(#arrow)') // 根据箭头标记的id号标记箭头
.style('stroke', '#000') // 颜色
.style('stroke-width', 1); // 粗细連線以貝塞爾曲線繪製:(M 起點X 起點y L 終點x 終點y)6.繪製連線上的箭頭
const defs = g.append('defs'); // defs定义可重复使用的元素 const arrowheads = defs.append('marker') // 创建箭头 .attr('id', 'arrow') // .attr('markerUnits', 'strokeWidth') // 设置为strokeWidth箭头会随着线的粗细进行缩放 .attr('markerUnits', 'userSpaceOnUse') // 设置为userSpaceOnUse箭头不受连接元素的影响 .attr('class', 'arrowhead') .attr('markerWidth', 20) // viewport .attr('markerHeight', 20) // viewport .attr('viewBox', '0 0 20 20') // viewBox .attr('refX', 9.3 + R) // 偏离圆心距离 .attr('refY', 5) // 偏离圆心距离 .attr('orient', 'auto'); // 绘制方向,可设定为:auto(自动确认方向)和 角度值 arrowheads.append('path') .attr('d', 'M0,0 L0,10 L10,5 z') // d: 路径描述,贝塞尔曲线 .attr('fill', '#000'); // 填充颜色
viewport:視覺區域
#
const nodesCircle = svg.select('g')
.selectAll('circle')
.data(nodes)
.enter()
.append('circle') // 创建圆
.attr('r', 30) // 半径
.style('fill', '#9FF') // 填充颜色
.style('stroke', '#0CF') // 边框颜色
.style('stroke-width', 2) // 边框粗细
.on('click', (node) => { // 点击事件
console.log('click');
})
.call(drag); // 拖拽单个节点带动整个图建立圓形作為節點。
.call()呼叫拖曳函數。
8.節點名稱
#
const nodesTexts = svg.select('g')
.selectAll('text')
.data(nodes)
.enter()
.append('text')
.attr('dy', '.3em') // 偏移量
.attr('text-anchor', 'middle') // 节点名称放在圆圈中间位置
.style('fill', 'black') // 颜色
.style('pointer-events', 'none') // 禁止鼠标事件
.text((d) => { // 文字内容
return d && d.name; // 遍历nodes每一项,获取对应的name
});因為文字在節點上層,如果沒有設定禁止滑鼠事件,點擊文字將無法回應點擊節點的效果,也無法拖曳節點。 9.連線名稱
#
const edgesText = svg.select('g').selectAll('.edgelabel')
.data(edges)
.enter()
.append('text') // 为每一条连线创建文字区域
.attr('class', 'edgelabel')
.attr('dx', 80)
.attr('dy', 0);
edgesText.append('textPath')// 设置文字内容
.attr('xlink:href', (d, i) => { return i && '#edgepath' + i; }) // 文字布置在对应id的连线上
.style('pointer-events', 'none')
.text((d) => { return d && d.tag; });
10.滑鼠移到節點上有氣泡提示
nodesCircle.append('title')
.text((node) => { // .text设置气泡提示内容
return node.definition;
});
#11.監聽圖元素的位置變化
simulation.on('tick', () => {
// 更新节点坐标
nodesCircle.attr('transform', (d) => {
return d && 'translate(' + d.x + ',' + d.y + ')';
});
// 更新节点文字坐标
nodesTexts.attr('transform', (d) => {
return 'translate(' + (d.x) + ',' + d.y + ')';
});
// 更新连线位置
edgesLine.attr('d', (d) => {
const path = 'M ' + d.source.x + ' ' + d.source.y + ' L ' + d.target.x + ' ' + d.target.y;
return path;
});
// 更新连线文字位置
edgesText.attr('transform', (d, i) => {
return 'rotate(0)';
});
});12.拖曳
function onDragStart(d) {
// console.log('start');
// console.log(d3.event.active);
if (!d3.event.active) {
simulation.alphaTarget(1) // 设置衰减系数,对节点位置移动过程的模拟,数值越高移动越快,数值范围[0,1]
.restart(); // 拖拽节点后,重新启动模拟
}
d.fx = d.x; // d.x是当前位置,d.fx是静止时位置
d.fy = d.y;
}
function dragging(d) {
d.fx = d3.event.x;
d.fy = d3.event.y;
}
function onDragEnd(d) {
if (!d3.event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0);
d.fx = null; // 解除dragged中固定的坐标
d.fy = null;
}
const drag = d3.drag()
.on('start', onDragStart)
.on('drag', dragging) // 拖拽过程
.on('end', onDragEnd);
13.縮放
function onZoomStart(d) {
// console.log('start zoom');
}
function zooming(d) {
// 缩放和拖拽整个g
// console.log('zoom ing', d3.event.transform, d3.zoomTransform(this));
g.attr('transform', d3.event.transform); // 获取g的缩放系数和平移的坐标值。
}
function onZoomEnd() {
// console.log('zoom end');
}
const zoom = d3.zoom()
// .translateExtent([[0, 0], [WIDTH, HEIGHT]]) // 设置或获取平移区间, 默认为[[-∞, -∞], [+∞, +∞]]
.scaleExtent([1 / 10, 10]) // 设置最大缩放比例
.on('start', onZoomStart)
.on('zoom', zooming)
.on('end', onZoomEnd);三、其它效果
1.點選節點時讓連接線加粗
##nodesCircle.on('click, (node) => {
edges_line.style("stroke-width",function(line){
if(line.source.name==node.name || line.target.name==node.name){
return 4;
}else{
return 0.5;
}
});
})2.被點擊的節點變色
#
nodesCircle.on('click, (node) => {
nodesCircle.style('fill', (nodeOfSelected) => { // nodeOfSelected:所有节点, node: 选中的节点
if (nodeOfSelected.id === node.id) { // 被点击的节点变色
console.log('node')
return '#36F';
} else {
return '#9FF';
}
});
})1、在react中使用注意事項
componentDidMount() {
this.print();
}
print() {
let callback = (res) => { // callback获取后台返回的数据,并存入state
let nodeData = res.data.nodes;
let relationData = res.data.rels;
this.setState({
nodeData: res.data.nodes,
relationData: res.data.rels,
});
let nodes = [];
for (let i = 0; i < nodeData.length; i++) {
nodes.push({
id: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].id) || '',
name: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].name) || '',
type: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].type) || '',
definition: (nodeData[i] && nodeData[i].definition) || '',
});
}
let edges = [];
for (let i = 0; i < relationData.length; i++) {
edges.push({
id: (relationData[i] && (relationData[i].id)) || '',
source: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].start.id) || '',
target: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].end.id) || '',
tag: (relationData[i] && relationData[i].name) || '',
});
}
this.forceChart(nodes, edges); // d3力导向图内容
};
this.props.dispatch(getDataFromNeo4J({
neo4jrun: 'match p=(()-[r]-()) return p limit 300',
}, callback));
}######在哪裡建構圖###因為圖表是動態的,如果渲染多次(render執行多次,渲染多次),不會覆寫前面渲染的圖,反而會造成渲染多次,出現多個圖的現象。把建構圖的函式print()放到componentDidMount()內執行,只會渲染一次。 ###對節點和連線資料進行增刪改操作後,需要再次呼叫print()函數,重新建構圖。 ############從哪裡取得資料### 資料不會從redux取得,發送請求後callback直接取得。 ######相關推薦:############如何實作d3力導向圖聚焦############使用D3.js製作表格方法介紹## ##########使用Python讀取和寫入mp3檔案的id3v1資訊################以上是在react中建構d3力導向圖方法分享的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
陳述:
本文內容由網友自願投稿,版權歸原作者所有。本站不承擔相應的法律責任。如發現涉嫌抄襲或侵權的內容,請聯絡admin@php.cn

