詳細解析線性表的原理及簡單實作方法
- ringa_lee原創
- 2017-10-15 10:43:573091瀏覽
下面小編就為大家帶來一篇淺談線性表的原理及簡單實作方法。小編覺得蠻不錯的,現在就分享給大家,也給大家做個參考。一起跟著小編過來看看吧
一、線性表
原理:零個或多個同類資料元素的有限序列
原理圖:
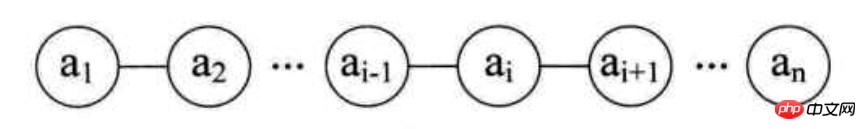
特點:
##1、有序性2、有限性3、同型元素4、第一個元素無前驅,最後一個元素無後繼,中間的元素有一個前驅並且有一個後繼線性表是一種邏輯上的資料結構,在物理上一般有兩種實作順序實作和鍊錶實作二、基於陣列的線性表順序實作
原則: 用一段位址連續的儲存單元依序儲存線性表資料元素。 原理圖: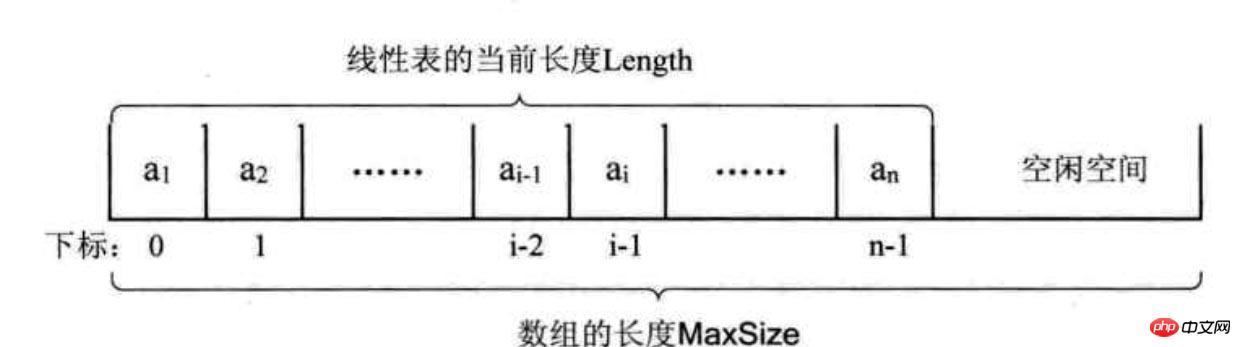
總結:
1、無需為表示表中元素之間的邏輯關係增加額外的儲存空間#2、可以快速存取表中任一位置元素 #3、插入和刪除需要進行陣列複製(即大量元素的移動)#4、線性表長度變化較大時,需要頻繁擴容,並造成儲存空間碎片實作程式碼:
介面定義:
package online.jfree.base;
/**
* author : Guo LiXiao
* date : 2017-6-14 11:46
*/
public interface LineList <E>{
/**
* lineList 是否为空
* @return
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 清空 lineList
*/
void clear();
/**
* 获取指定位置元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
E get(int index);
/**
* 获取元素第一次出现的位置
* @param e
* @return
*/
int indexOf(E e);
/**
* 判断 lineList是否包含指定元素
* @param e
* @return
*/
boolean contains(E e);
/**
* 设置指定位置数据,如数据已存在 则覆盖原数据
* @param index
* @param e
* @return
*/
E set(int index, E e);
/**
* 移除指定位置元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
E remove(int index);
/**
* 在lineList结尾插入元素
* @param e
* @return
*/
E add(E e);
/**
* 在index后面插入元素
* @param index
* @param e
* @return
*/
E add(int index, E e);
/**
* 返回lineList长度
* @return
*/
int size();
}
演算法實作:
package online.jfree.base;
/**
* author : Guo LiXiao
* date : 2017-6-15 13:44
*/
public class OrderedLineList<E> implements LineList<E> {
private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 10;
private transient E[] elementData;
private transient int elementLength;
private int size;
public OrderedLineList() {
this(0);
}
public OrderedLineList(int initCapacity) {
init(initCapacity);
}
private void init(int initCapacity) {
if (initCapacity >= 0) {
this.elementData = (E[]) new Object[initCapacity];
this.elementLength = initCapacity;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " +
initCapacity);
}
this.size = 0;
}
/**
* 扩容
*/
private void dilatation() {
int oldCapacity = this.elementLength;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity;
if (oldCapacity <= this.size) {
newCapacity = oldCapacity + INIT_CAPACITY;
}else if(oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY > this.size){
newCapacity = oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY;
}
if (oldCapacity != newCapacity){
E[] newElementData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newElementData, 0, oldCapacity);
this.elementLength = newCapacity;
this.elementData = newElementData;
}
}
/**
* 校验列表索引越界
* @param index
*/
private void checkCapacity(int index){
if (index > this.size - 1 || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(new StringBuffer("[index : ").append(index).append("] , [size : ").append(size).append("] ").toString());
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
this.init(0);
}
@Override
public E get(int index) {
this.checkCapacity(index);
return this.elementData[index];
}
@Override
public int indexOf(E e) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){
if (e == null && elementData[i] == null || e.equals(elementData[i])){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(E e) {
return this.indexOf(e) > 0;
}
@Override
public E set(int index, E e) {
this.checkCapacity(index);
this.dilatation();
E oldElement = this.elementData[index];
this.elementData[index] = e;
return oldElement;
}
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
this.dilatation();
E e = elementData[index];
if (index == size - 1) elementData[index] = null;
else {
int length = size - index - 1;
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, length);
}
size --;
return e;
}
@Override
public E add(E e) {
return this.add(size, e);
}
@Override
public E add(int index, E e) {
this.dilatation();
if (index == size) elementData[index] = e;
else {
index++;
int lastLength = size - index;
E[] lastElementData = (E[]) new Object[lastLength];
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, lastElementData, 0, lastLength);
elementData[index] = e;
System.arraycopy(lastElementData, 0, elementData, index + 1, lastLength);
}
size ++ ;
return e;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
}以上是詳細解析線性表的原理及簡單實作方法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
陳述:
本文內容由網友自願投稿,版權歸原作者所有。本站不承擔相應的法律責任。如發現涉嫌抄襲或侵權的內容,請聯絡admin@php.cn

