Java中GUI程式設計講解(下)
- 巴扎黑原創
- 2017-07-23 13:47:332370瀏覽
一、事件監聽機制
-- 事件來源:awt 或swing套件中的那些圖形介面元件,即發生事件的元件
-- 事件:Event 使用者對元件的一個動作
-- 監聽器:Listener 負責處理事件的方法
二、java.awt.event 套件下的類別
WindowEvent //視窗事件,例如使用者點了半閉視窗,視窗得到或失去焦點,最大化最小化等
MouseEvent //滑鼠事件,滑鼠按下,滑鼠釋放,點選(按下後再鬆開)等
ActionEvent //動作事件,它不是代表一個具體動作,而是一種語義,比如按紐,或菜單被點擊,在文本框中按下回車等等,可以這樣理解:用戶的某一動作導致了某個組件本身的基本作用發生了,這就是ActionEvent事件
不同的事件類型,對應著不同的事件監聽器接口,接口的名稱和事件的名稱是相對應的。
WindowEvent - >WindowListener
MouseEvent ->MouseListener
ActionEvent ->ActionListener
程式碼範例:
import java.awt.Frame;import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;import java.awt.event.WindowListener;public class Test20 {public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame();
f.setSize(400, 400);
f.setVisible(true);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowListener() {
@Overridepublic void windowOpened(WindowEvent e) { // 窗口被打开// TODO Auto-generated method stub}
@Overridepublic void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { // 设置关闭事件// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.exit(0);
}
@Overridepublic void windowClosed(WindowEvent e) { // 用户已经关闭窗口// TODO Auto-generated method stub}
@Overridepublic void windowIconified(WindowEvent e) { // 被最小化的时候// TODO Auto-generated method stub}
@Overridepublic void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent e) { // 最小化被还原的时候// TODO Auto-generated method stub}
@Overridepublic void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) { // 窗体被激活// TODO Auto-generated method stub}
@Overridepublic void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) { // 失去焦点的时候// TODO Auto-generated method stub}
});
}
}有沒有發現,用WindowListener介面的時候,會引入一大堆不常用的程式碼(這裡我們只想設定關閉),藉口裡的方法只能被覆蓋,又不能刪掉,這樣就是的整個專案顯得很囉嗦,為了解決這個事情,就有了事件轉接器。
三、事件適配器
JDK 針對大多數事件監聽器介面類別定義了對應的實作類別(裡面有很多空實作的方法,方便我們建立偵聽器物件),我們稱為事件適配器類別。這裡我用到了WindowAdapter。
import java.awt.Frame;import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;public class Test21 {public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame("事件适配器的栗子");
f.setSize(400, 400);
f.setVisible(true);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}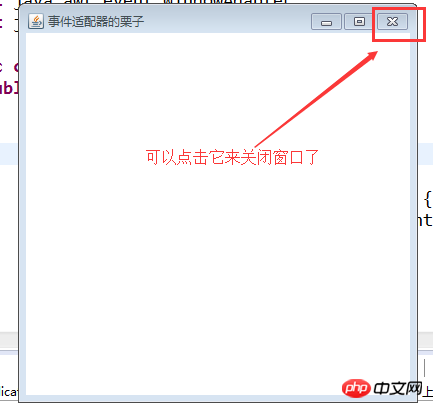
可以觀察一下WindowAdapter類別的原始碼,找出感覺。
public abstract class WindowAdapterimplements WindowListener, WindowStateListener, WindowFocusListener
{/** * Invoked when a window has been opened. */public void windowOpened(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when a window is in the process of being closed.
* The close operation can be overridden at this point. */public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when a window has been closed. */public void windowClosed(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when a window is iconified. */public void windowIconified(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when a window is de-iconified. */public void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when a window is activated. */public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when a window is de-activated. */public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when a window state is changed.
* @since 1.4 */public void windowStateChanged(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when the Window is set to be the focused Window, which means
* that the Window, or one of its subcomponents, will receive keyboard
* events.
*
* @since 1.4 */public void windowGainedFocus(WindowEvent e) {}/** * Invoked when the Window is no longer the focused Window, which means
* that keyboard events will no longer be delivered to the Window or any of
* its subcomponents.
*
* @since 1.4 */public void windowLostFocus(WindowEvent e) {}
}練習幾個事件處理程序的栗子吧。
例一:
import java.awt.Button;import java.awt.FlowLayout;import java.awt.Frame;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;//例一:在窗体中放置一个按纽,点击后让程序退出class TestFrame implements ActionListener { // ActionListener接口里面只有一个方法,下面会重写private Frame f;public TestFrame() {
f = new Frame("窗口");
init();
}private void init() {
f.setSize(300, 300);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());// 布局模式Button b = new Button("退出程序");
b.addActionListener(this);
f.add(b);
f.setVisible(true);
}
@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubf.setVisible(false);
f.dispose();// 在关闭的时候,可以用它来销毁窗体资源System.exit(0);// 退出 }
}public class Test22 {public static void main(String[] args) {new TestFrame();
}
}
上面的,點選退出程式按鈕才可以退出,點選右上角的X,是不可以退出的哦。因為沒有設定WindowListener哦。
這個範例用到ActionListener接口,可以看它的原始碼,如下:
public interface ActionListener extends EventListener {/** * Invoked when an action occurs. */public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e);
}#例二:
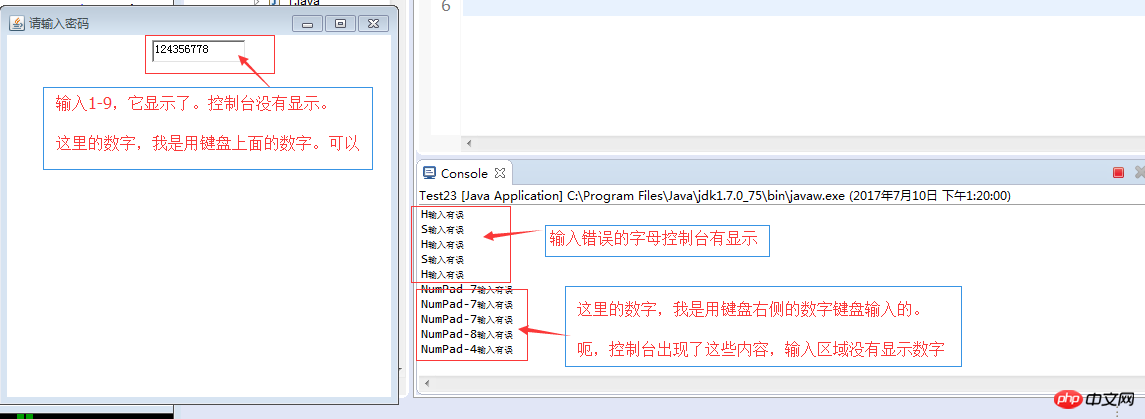
TextField txtNo;= Frame("请输入密码"f.setBounds(50, 50, 400, 400);f.setLayout( FlowLayout());= TextField(10); code = (!(code >= KeyEvent.VK_0 && code <= KeyEvent.VK_9)) {System.out.println(KeyEvent.getKeyText(code) + "输入有误" 0測試類別:
public class Test23 {public static void main(String[] args) {new TestFrame();
}
}
範例三:
列出指定目錄的內容:
import java.awt.Button;import java.awt.FlowLayout;import java.awt.Frame;import java.awt.TextArea;import java.awt.TextField;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;import java.io.File;public class Test24 {public static void main(String[] args) {new MyWindow();
}
}class MyWindow {
MyWindow() {
init();
}private Frame f;private Button b;private TextField txtDir;// 用来输入目录名称private TextArea txtFileList;// 用来显示文件列表private void init() {
f = new Frame("窗口");
f.setBounds(44, 44, 500, 500);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
txtDir = new TextField(8);
b = new Button("显示");
txtFileList = new TextArea(20, 30);// 用来显示文件列表的区域f.add(txtDir);
f.add(b);
f.add(txtFileList);
initEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}private void initEvent() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubf.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {/** * Invoked when a window is in the process of being closed. The
* close operation can be overridden at this point. */public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {/** * Invoked when an action occurs. */public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
txtFileList.setText("");
String dirStr = txtDir.getText();// 取出用户输入的路径File file = new File(dirStr);if (file.isDirectory() && file.exists()) {
String[] fileNameList = file.list();for (String s : fileNameList) {
txtFileList.append(s + "\r\n");// 别忘了换行符 }
} else {
txtFileList.append("输入有误,请重新输入");
}
}
});
}
} 結果:(我讓它顯示我D碟的目錄)

#
#以上是Java中GUI程式設計講解(下)的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

