分享用MongoDB中oplog機制實作資料監控實例
- 零下一度原創
- 2017-07-03 16:43:592144瀏覽
MongoDB 的Replication是透過一個日誌來儲存寫入作業的,這個日誌就叫做oplog,而下面這篇文章主要給大家介紹了利用MongoDB中oplog機制實現準實時數據的操作監控的相關資料,需要的朋友可以參考借鑒,下面來一起看看吧。
前言
最近有一個需求是要即時取得到新插入到MongoDB的數據,而插入程式本身已經有一套處理邏輯,所以不方便直接在插入程序裡寫相關程序,傳統的資料庫大多自帶這種觸發器機制,但是Mongo沒有相關的函數可以用(也可能我了解的太少了,求修正),當然還有一點是需要python實現,於是收集整理了一個對應的實作方法。
一、引子
#首先可以想到,這種需求其實很像資料庫的主從備份機制,從資料庫之所以能夠同步主函式庫是因為有某些指標來做控制,我們知道MongoDB雖然沒有現成觸發器,但是它能夠實現主從備份,所以我們就從它的主從備份機制入手。
二、OPLOG
首先,需要以master模式來開啟mongod守護,命令列使用–master,或設定檔增加master鍵為true。
此時,我們可以在Mongo的系統函式庫local裡見到新增的collection-oplog,此時oplog.$main裡就會儲存進oplog訊息,如果此時還有充當從資料庫的Mongo存在,就會還有一些slaves的信息,由於我們這裡並不是主從同步,所以不存在這些集合。
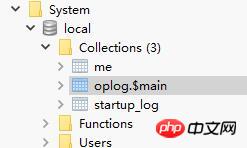
再來看看oplog結構:
"ts" : Timestamp(6417682881216249, 1), 时间戳
"h" : NumberLong(0), 长度
"v" : 2,
"op" : "n", 操作类型
"ns" : "", 操作的库和集合
"o2" : "_id" update条件
"o" : {} 操作值,即document這裡要知道op的幾個屬性:
insert,'i' update, 'u' remove(delete), 'd' cmd, 'c' noop, 'n' 空操作
從上面的資訊可以看出,我們只要不斷讀取到ts來做對比,然後根據op可以判斷當前出現的是什麼操作,相當於使用程式實作了一個從資料庫的接收端。
三、CODE
#在Github上找到了別人的實作方式,不過它的函式庫太老舊,所以在他的基礎上進行修改。
Github位址:github.com/RedBeard0531/mongo-oplog-watcher
mongo_oplog_watcher.py如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
import pymongo
import re
import time
from pprint import pprint # pretty printer
from pymongo.errors import AutoReconnect
class OplogWatcher(object):
def init(self, db=None, collection=None, poll_time=1.0, connection=None, start_now=True):
if collection is not None:
if db is None:
raise ValueError('must specify db if you specify a collection')
self._ns_filter = db + '.' + collection
elif db is not None:
self._ns_filter = re.compile(r'^%s\.' % db)
else:
self._ns_filter = None
self.poll_time = poll_time
self.connection = connection or pymongo.Connection()
if start_now:
self.start()
@staticmethod
def get_id(op):
id = None
o2 = op.get('o2')
if o2 is not None:
id = o2.get('_id')
if id is None:
id = op['o'].get('_id')
return id
def start(self):
oplog = self.connection.local['oplog.$main']
ts = oplog.find().sort('$natural', -1)[0]['ts']
while True:
if self._ns_filter is None:
filter = {}
else:
filter = {'ns': self._ns_filter}
filter['ts'] = {'$gt': ts}
try:
cursor = oplog.find(filter, tailable=True)
while True:
for op in cursor:
ts = op['ts']
id = self.get_id(op)
self.all_with_noop(ns=op['ns'], ts=ts, op=op['op'], id=id, raw=op)
time.sleep(self.poll_time)
if not cursor.alive:
break
except AutoReconnect:
time.sleep(self.poll_time)
def all_with_noop(self, ns, ts, op, id, raw):
if op == 'n':
self.noop(ts=ts)
else:
self.all(ns=ns, ts=ts, op=op, id=id, raw=raw)
def all(self, ns, ts, op, id, raw):
if op == 'i':
self.insert(ns=ns, ts=ts, id=id, obj=raw['o'], raw=raw)
elif op == 'u':
self.update(ns=ns, ts=ts, id=id, mod=raw['o'], raw=raw)
elif op == 'd':
self.delete(ns=ns, ts=ts, id=id, raw=raw)
elif op == 'c':
self.command(ns=ns, ts=ts, cmd=raw['o'], raw=raw)
elif op == 'db':
self.db_declare(ns=ns, ts=ts, raw=raw)
def noop(self, ts):
pass
def insert(self, ns, ts, id, obj, raw, **kw):
pass
def update(self, ns, ts, id, mod, raw, **kw):
pass
def delete(self, ns, ts, id, raw, **kw):
pass
def command(self, ns, ts, cmd, raw, **kw):
pass
def db_declare(self, ns, ts, **kw):
pass
class OplogPrinter(OplogWatcher):
def all(self, **kw):
pprint (kw)
print #newline
if name == 'main':
OplogPrinter()首先是實作一個資料庫的初始化,設定一個延遲時間(準實時):
self.poll_time = poll_time self.connection = connection or pymongo.MongoClient()
主要的函數是start() ,實現一個時間的比對並進行對應欄位的處理:
def start(self):
oplog = self.connection.local['oplog.$main']
#读取之前提到的库
ts = oplog.find().sort('$natural', -1)[0]['ts']
#获取一个时间边际
while True:
if self._ns_filter is None:
filter = {}
else:
filter = {'ns': self._ns_filter}
filter['ts'] = {'$gt': ts}
try:
cursor = oplog.find(filter)
#对此时间之后的进行处理
while True:
for op in cursor:
ts = op['ts']
id = self.get_id(op)
self.all_with_noop(ns=op['ns'], ts=ts, op=op['op'], id=id, raw=op)
#可以指定处理插入监控,更新监控或者删除监控等
time.sleep(self.poll_time)
if not cursor.alive:
break
except AutoReconnect:
time.sleep(self.poll_time)循環這個start函數,在all_with_noop這裡就可以寫出對應的監控處理邏輯。
這樣就可以實作一個簡易的準實時Mongo資料庫操作監控器,下一步就可以配合其他操作來對新入庫的程式進行對應處理。
以上是分享用MongoDB中oplog機制實作資料監控實例的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

