在XML佈局裡給View設定點擊事件的案例分享
- 黄舟原創
- 2017-03-17 17:25:491690瀏覽
給一個View設定監聽點擊事件是再普通不過的事情,例如
view.setOnClickListener(onClickListener);
另外一種做法是直接在XML佈局裡面指定View點擊時候的回呼方法,首先需要在Activity中寫一個回呼的方法,例如
public void onClickView(View view){
// do something
}然後在XML設定View的android:onClick屬性
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:onClick="onClickView" />有的時候從XML佈局裡直接設定點擊事件會比較方便(特別是在寫DEMO項目的時候),這種做法平時用的人並不多,從使用方式上大致能猜出來, View應該是在運作的時候,使用反射的方式從Activity找到「onClickView」方法並調用,因為這種做法並沒有用到任何介面。
接下來,我們可以從原始碼中分析出View是怎麼觸發回呼方法的。 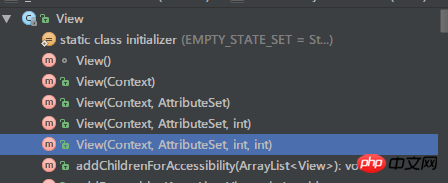
View有5個
,第一個是內部使用的,平常在Java程式碼中直接建立View實例用的是第二種方法,而從XML佈局渲染出來的View實例最後都是要呼叫第五種方法。
public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
this(context);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(
attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.View, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch (attr) {
……
// 处理onClick属性
case R.styleable.View_onClick:
if (context.isRestricted()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The android:onClick attribute cannot "
+ "be used within a restricted context");
}
final String handlerName = a.getString(attr);
if (handlerName != null) {
// 给当前View实例设置一个DeclaredOnClickListener监听器
setOnClickListener(new DeclaredOnClickListener(this, handlerName));
}
break;
}
}
}處理onClick屬性的時候,先判斷View的Context是否isRestricted,如果是就拋出一個IllegalStateException異常。看看isRestricted方法<pre class="brush:xml;toolbar:false;"> /**
* Indicates whether this Context is restricted.
*
* @return {@code true} if this Context is restricted, {@code false} otherwise.
*
* @see #CONTEXT_RESTRICTED
*/
public boolean isRestricted() {
return false;
}</pre>isRestricted是用來判斷目前的Context實例是否出於被限制的狀態,按照官方的解釋,處限制狀態的Context,會忽略某些特點的功能,例如XML的某些屬性,很明顯,我們在研究的
屬性也會被忽略。a restricted context may disable specific features. For instance, a View associated with a restricted context would ignore particular XML attributes.
 #isRestricted方法是Context中為數不符方法是Context中為數不符多的有具體實現的方法(其餘基本上是抽象方法),這裡直接回傳false,而且這個方法只有在ContextWrapper和MockContext中有重寫
#isRestricted方法是Context中為數不符方法是Context中為數不符多的有具體實現的方法(其餘基本上是抽象方法),這裡直接回傳false,而且這個方法只有在ContextWrapper和MockContext中有重寫
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
Context mBase;
@Override
public boolean isRestricted() {
return mBase.isRestricted();
}
}
public class MockContext extends Context {
@Override
public boolean isRestricted() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}ContextWrapper中也只是代理呼叫mBase的isRestricted,而MockContext是寫
單元測試的時候才會用到,所以這裡的isRestricted基本上只會回傳false,除非使用了自訂的ContextWrapper並重寫了isRestricted。 回到View,接著的final String handlerName = a.getString(attr);其實就是拿到了android:onClick="onClickView"中的「onClickView」這個
,接著使用了目前View的實例和「onClickView」建立了一個DeclaredOnClickListener實例,並設定為目前View的點擊監聽器。
/**
* An implementation of OnClickListener that attempts to lazily load a
* named click handling method from a parent or ancestor context.
*/
private static class DeclaredOnClickListener implements OnClickListener {
private final View mHostView;
private final String mMethodName;
private Method mMethod;
public DeclaredOnClickListener(@NonNull View hostView, @NonNull String methodName) {
mHostView = hostView;
mMethodName = methodName;
}
@Override
public void onClick(@NonNull View v) {
if (mMethod == null) {
mMethod = resolveMethod(mHostView.getContext(), mMethodName);
}
try {
mMethod.invoke(mHostView.getContext(), v);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not execute non-public method for android:onClick", e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not execute method for android:onClick", e);
}
}
@NonNull
private Method resolveMethod(@Nullable Context context, @NonNull String name) {
while (context != null) {
try {
if (!context.isRestricted()) {
return context.getClass().getMethod(mMethodName, View.class);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
// Failed to find method, keep searching up the hierarchy.
}
if (context instanceof ContextWrapper) {
context = ((ContextWrapper) context).getBaseContext();
} else {
// Can't search up the hierarchy, null out and fail.
context = null;
}
}
final int id = mHostView.getId();
final String idText = id == NO_ID ? "" : " with id '"
+ mHostView.getContext().getResources().getResourceEntryName(id) + "'";
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not find method " + mMethodName
+ "(View) in a parent or ancestor Context for android:onClick "
+ "attribute defined on view " + mHostView.getClass() + idText);
}
}到這裡就清楚了,當點擊View的時候,DeclaredOnClickListener實例的“onClick”方法會被調用,接著會調用“resolveMethod”方法,使用反射的方式從View的Context中找一個叫「onClickView」方法,這個方法有一個View類型的參數,最後再使用反射呼叫該方法。要注意的是,「onClickView」方法必須是public型別的,不然反射呼叫時會拋出IllegalAccessException異常。 同時從原始碼也能看出,使用
設定點擊事件的方式是從Context裡面查找回調方法的,所以如果對於在Fragment的XML裡創建的View,是無法透過這種方式綁定Fragment中的回呼方法的,因為Fragment本身並不是一個Context,這裡的View的Context其實是FragmentActivity,這也意味著使用這種方式能夠快速地從Fragment中回調到FragmentActivity。 此外,從DeclaredOnClickListener類別的註解也能看出android:onClick的功能,
,只有到點擊View的時候,才會知道哪個方法是用來點擊回呼的。 最後,特別需要補充說明的是,使用android:onClick給View設定點擊事件,就表示要在Activity裡加入一個非介面的public方法。現在Android的開發趨勢是“不要把業務邏輯寫在Activity類別裡面”,這樣做有利於專案的維護,防止Activity爆炸,所以盡量不要在Activity裡出現非介面、非生命週期的public方法。因此,貿然使用
可能會「污染」Activity。
以上是在XML佈局裡給View設定點擊事件的案例分享的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

