詳解Java的Hibernate框架中的註解與緩存
- 高洛峰原創
- 2017-01-23 11:53:301349瀏覽
註解
Hibernate註解是一個沒有使用XML檔案來定義映射的最新方法。可以在除或替換的XML映射元資料使用註解。
Hibernate的註解是強大的方式來提供元資料物件和關係表的對應。所有的元資料都被杵到一起的程式碼POJO java檔案這可以幫助使用者在開發過程中同時要了解表格的結構和POJO。
如果打算讓應用程式移植到其他EJB3規範的ORM應用程序,必須使用註解來表示映射信息,但仍然如果想要更大的靈活性,那麼應該使用基於XML的映射去。
環境設定Hibernate註解
首先,必須確保使用的是JDK5.0,否則,需要JDK升級到JDK5.0帶註解的原生支援的優勢。
其次,需要安裝Hibernate的3.x註解分發包,可從SourceForge上:(Download Hibernate Annotation) 並拷貝hibernate-annotations.jar, lib/hibernate-comons-annotations.jar 和lib/ejb3-persistence.從Hibernate註解分配到CLASSPATH
註釋的類別實例:
正如提到的,同時使用Hibernate註解工作的所有元資料杵成隨著程式碼的POJO java檔案上面這可以幫助使用者在開發過程中同時了解表結構和POJO。
考慮到將要使用下面的EMPLOYEE表來儲存的物件:
create table EMPLOYEE ( id INT NOT NULL auto_increment, first_name VARCHAR(20) default NULL, last_name VARCHAR(20) default NULL, salary INT default NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) );
下面是用註解來映射與定義的EMPLOYEE表的物件Employee類別的映射:
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "EMPLOYEE")
public class Employee {
@Id @GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "salary")
private int salary;
public Employee() {}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId( int id ) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName( String first_name ) {
this.firstName = first_name;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName( String last_name ) {
this.lastName = last_name;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary( int salary ) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}一個字段,並假設它應該直接透過在運行時域存取一個物件的屬性。如果將@Id註解getId()方法,將透過getter和setter方法預設允許存取屬性。因此,所有其他註釋也被放置在任一欄位或getter方法,以下所選的策略。下面的部分將解釋在上面的類別中使用的註釋。 @Entity 註解:在EJB3規範說明都包含在javax.persistence包,所以我們導入這個包作為第一步。其次,我們使用了@Entity註解來這標誌著這個類別作為一個實體bean Employee類,因此它必須有一個無參數的建構函數,總算是有保護的範圍可見。
@Table註解允許指定的表將被用於保存該實體在資料庫中的詳細資訊。
每個實體bean將有一個主鍵,註解在類別的@Id註解。主鍵可以是單一欄位或根據表格結構的多個欄位的組合。
@Column批註用於指定的列到一個欄位或屬性將被對應的細節。可以使用列註解以下最常用的屬性:
最後,我們將建立應用程式類別的main()方法來執行應用程式。我們將使用這個應用程序,以節省一些員工的記錄,然後我們將申請CRUD操作上的記錄。
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.hibernate.HibernateException;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class ManageEmployee {
private static SessionFactory factory;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
factory = new AnnotationConfiguration().
configure().
//addPackage("com.xyz") //add package if used.
addAnnotatedClass(Employee.class).
buildSessionFactory();
}catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println("Failed to create sessionFactory object." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
ManageEmployee ME = new ManageEmployee();
/* Add few employee records in database */
Integer empID1 = ME.addEmployee("Zara", "Ali", 1000);
Integer empID2 = ME.addEmployee("Daisy", "Das", 5000);
Integer empID3 = ME.addEmployee("John", "Paul", 10000);
/* List down all the employees */
ME.listEmployees();
/* Update employee's records */
ME.updateEmployee(empID1, 5000);
/* Delete an employee from the database */
ME.deleteEmployee(empID2);
/* List down new list of the employees */
ME.listEmployees();
}
/* Method to CREATE an employee in the database */
public Integer addEmployee(String fname, String lname, int salary){
Session session = factory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
Integer employeeID = null;
try{
tx = session.beginTransaction();
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setFirstName(fname);
employee.setLastName(lname);
employee.setSalary(salary);
employeeID = (Integer) session.save(employee);
tx.commit();
}catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx!=null) tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
session.close();
}
return employeeID;
}
/* Method to READ all the employees */
public void listEmployees( ){
Session session = factory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try{
tx = session.beginTransaction();
List employees = session.createQuery("FROM Employee").list();
for (Iterator iterator =
employees.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();){
Employee employee = (Employee) iterator.next();
System.out.print("First Name: " + employee.getFirstName());
System.out.print(" Last Name: " + employee.getLastName());
System.out.println(" Salary: " + employee.getSalary());
}
tx.commit();
}catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx!=null) tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
session.close();
}
}
/* Method to UPDATE salary for an employee */
public void updateEmployee(Integer EmployeeID, int salary ){
Session session = factory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try{
tx = session.beginTransaction();
Employee employee =
(Employee)session.get(Employee.class, EmployeeID);
employee.setSalary( salary );
session.update(employee);
tx.commit();
}catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx!=null) tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
session.close();
}
}
/* Method to DELETE an employee from the records */
public void deleteEmployee(Integer EmployeeID){
Session session = factory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try{
tx = session.beginTransaction();
Employee employee =
(Employee)session.get(Employee.class, EmployeeID);
session.delete(employee);
tx.commit();
}catch (HibernateException e) {
if (tx!=null) tx.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
session.close();
}
}
}
資料庫設定:現在,讓我們建立hibernate.cfg.xml設定檔來定義資料庫的相關參數。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration SYSTEM "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <property name="hibernate.dialect"> org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class"> com.mysql.jdbc.Driver </property> <!-- Assume students is the database name --> <property name="hibernate.connection.url"> jdbc:mysql://localhost/test </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username"> root </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password"> cohondob </property> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>編譯和執行:
下面是步驟來編譯並運行上述應用程式。請確保已在進行的編譯和執行之前,適當地設定PATH和CLASSPATH。
$java ManageEmployee .......VARIOUS LOG MESSAGES WILL DISPLAY HERE........ First Name: Zara Last Name: Ali Salary: 1000 First Name: Daisy Last Name: Das Salary: 5000 First Name: John Last Name: Paul Salary: 10000 First Name: Zara Last Name: Ali Salary: 5000 First Name: John Last Name: Paul Salary: 10000如果檢查EMPLOYEE表,它應該有以下記錄:
mysql> select * from EMPLOYEE; +----+------------+-----------+--------+ | id | first_name | last_name | salary | +----+------------+-----------+--------+ | 29 | Zara | Ali | 5000 | | 31 | John | Paul | 10000 | +----+------------+-----------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec mysql>快取
快取是所有關於應用程式的效能最佳化和它位於應用程式和資料庫之間,以避免資料庫存取多次,讓效能關鍵型應用程式有更好的表現。
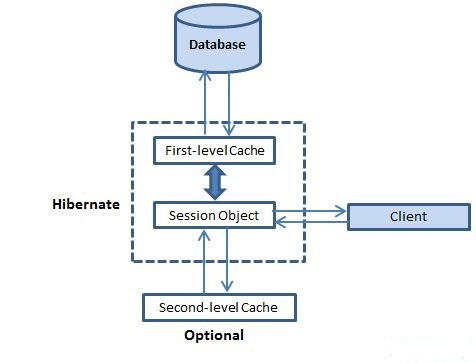
第一级缓存:
第一级缓存是Session的缓存,是一个强制性的缓存,通过它所有的请求都必须通过。 Session对象不断自身的动力的对象,提交到数据库之前。
如果发出多个更新一个对象,Hibernate试图拖延尽可能长的时间做了更新,以减少发出的更新SQL语句的数量。如果您关闭会话,所有被缓存的对象都将丢失,要么持久,或在数据库中更新。
二级缓存:
二级缓存是可选的缓存和一级缓存,总是会征询任何试图找到一个对象的二级缓存之前。第二级缓存可以在每个类和每个集合基础上进行配置,主要负责在会话缓存的对象。
任何第三方缓存可以使用Hibernate。org.hibernate.cache.CacheProvider接口提供,必须实施提供Hibernate一个句柄缓存实现。
查询级别缓存:
Hibernate也实现了查询结果集缓存与二级缓存的紧密集成在一起。
这是一个可选功能,需要两个额外的物理缓存中保存缓存的查询结果和地区当一个表的最后更新的时间戳。这只是针对那些使用相同的参数经常运行的查询非常有用。
二级缓存:
Hibernate使用一级缓存,默认情况下,你什么都没有做使用第一级缓存。让我们直接进入可选的第二级缓存。并不是所有的类受益于缓存,这样一来就能禁用二级缓存是很重要的
Hibernate二级缓存被设置为两个步骤。首先,必须决定要使用的并发策略。在此之后,可以配置缓存过期和使用缓存提供物理缓存属性。
并发策略:
并发策略是一个中介的负责存储数据项在缓存并从缓存中检索它们。如果要启用二级缓存,将必须决定,为每个持久化类和集合,要使用的缓存并发策略。
Transactional: 使用这种策略的主要读取数据的地方,以防止过时的数据的并发事务,在更新的罕见情况下是至关重要的。
Read-write: 再次使用这种策略的主要读取数据的地方,以防止并发事务陈旧的数据是至关重要的,在更新的罕见情况。
Nonstrict-read-write: 这种策略不保证缓存与数据库之间的一致性。使用此策略,如果数据很少改变和陈旧数据的可能性很小关键是不关注。
Read-only: 并发策略适用于数据,永远不会改变。使用数据仅供参考。
如果我们要使用第二级缓存为我们的Employee类,让我们添加告诉Hibernate使用可读写的高速缓存策略Employee实例所需的映射元素。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="Employee" table="EMPLOYEE">
<meta attribute="class-description">
This class contains the employee detail.
</meta>
<cache usage="read-write"/>
<id name="id" type="int" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="firstName" column="first_name" type="string"/>
<property name="lastName" column="last_name" type="string"/>
<property name="salary" column="salary" type="int"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
usage="read-write" 属性告诉Hibernate使用一个可读写的并发策略定义的缓存。
缓存提供者:
考虑到会用你的缓存候选类的并发策略后,下一步就是选择一个缓存提供程序。Hibernate迫使选择一个缓存提供整个应用程序。
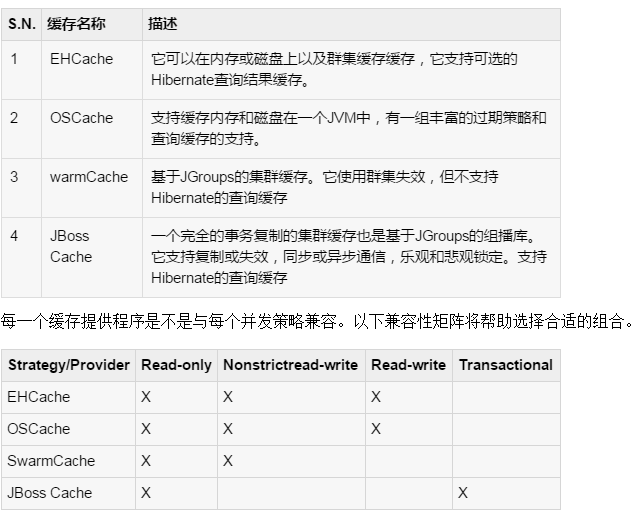
在指定hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件中的缓存提供。选择EHCache作为第二级缓存提供程序:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration SYSTEM "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <property name="hibernate.dialect"> org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class"> com.mysql.jdbc.Driver </property> <!-- Assume students is the database name --> <property name="hibernate.connection.url"> jdbc:mysql://localhost/test </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username"> root </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password"> root123 </property> <property name="hibernate.cache.provider_class"> org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider </property> <!-- List of XML mapping files --> <mapping resource="Employee.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
现在,需要指定缓存区域的属性。EHCache都有自己的配置文件ehcache.xml,在应用程序在CLASSPATH中。在ehcache.xml中Employee类高速缓存配置可能看起来像这样:
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="1000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="true" /> <cache name="Employee" maxElementsInMemory="500" eternal="true" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="0" overflowToDisk="false" />
就这样,现在启用Employee类的二级缓存和Hibernate现在二级缓存,每当浏览到一个雇员或当通过标识符加载雇员。
应该分析你所有的类,并选择适当的缓存策略为每个类。有时,二级缓存可能降级的应用程序的性能。所以建议到基准应用程序第一次没有启用缓存,非常适合缓存和检查性能。如果缓存不提高系统性能再有就是在使任何类型的缓存是没有意义的。
查询级别缓存:
使用查询缓存,必须先使用 hibernate.cache.use_query_cache="true"属性配置文件中激活它。如果将此属性设置为true,让Hibernate的在内存中创建所需的高速缓存来保存查询和标识符集。
接下来,使用查询缓存,可以使用Query类的setCacheable(Boolean)方法。例如:
Session session = SessionFactory.openSession();
Query query = session.createQuery("FROM EMPLOYEE");
query.setCacheable(true);
List users = query.list();
SessionFactory.closeSession();
Hibernate也支持通过一个缓存区域的概念非常细粒度的缓存支持。缓存区是这是给定一个名称缓存的一部分。
Session session = SessionFactory.openSession();
Query query = session.createQuery("FROM EMPLOYEE");
query.setCacheable(true);
query.setCacheRegion("employee");
List users = query.list();
SessionFactory.closeSession();
此程式碼使用方法告訴Hibernate來儲存和尋找在快取中的員工方面的查詢。
更多詳解Java的Hibernate框架中的註解與快取相關文章請關注PHP中文網!

