Python中單線程、多線程和多進程的效率對比實驗
- 高洛峰原創
- 2016-11-22 10:45:011335瀏覽
對比實驗
資料顯示,如果多執行緒的進程是CPU密集型的,那多執行緒並不能有多少效率上的提升,相反還可能會因為執行緒的頻繁切換,導致效率下降,推薦使用多進程;如果是IO密集型,多執行緒程序可以利用IO阻塞等待時的空閒時間執行其他執行緒,提升效率。所以我們根據實驗比較不同場景的效率

(1)引入所需要的模組
import requests import time from threading import Thread from multiprocessing import Process
(2)定義CPU密集的計算函數
def count(x, y):
# 使程序完成150万计算
c = 0
while c < 500000:
c += 1
x += x
y += y(3)定義IO密集的文件讀寫函數
reee(4) 定義網路請求函數
def write():
f = open("test.txt", "w")
for x in range(5000000):
f.write("testwrite\n")
f.close()
def read():
f = open("test.txt", "r")
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()(5)測試線性執行IO密集操作、CPU密集操作所需時間、網路請求密集操作所需時間
_head = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/48.0.2564.116 Safari/537.36'}
url = "http://www.tieba.com"
def http_request():
try:
webPage = requests.get(url, headers=_head)
html = webPage.text
return {"context": html}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": e}輸出
CPU密集操作所需時間、網路請求密集操作所需時間
# CPU密集操作
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
count(1, 1)
print("Line cpu", time.time() - t)
# IO密集操作
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
write()
read()
print("Line IO", time.time() - t)
# 网络请求密集型操作
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
http_request()
print("Line Http Request", time.time() - t)輸出
CPU密集操作:95.6059999466、91.57039862095386395095. 99.96799993515015
IO密集:24.25、21.76699995994568、21.76999980926514、22.060999876999980926514、22.060999870300293319893896. 563999891281128、4.371000051498413、4.522000074386597、14.67100003814697
(6)測試多執行緒並發執行密集作業所需的時間99.9240000248 、101.26400017738342、102.32200002670288
(7)測試多執行緒並發執行IO密集操作所需時間
counts = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
thread = Thread(target=count, args=(1,1))
counts.append(thread)
thread.start()
e = counts.__len__()
while True:
for th in counts:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print(time.time() - t)put: 測試多執行緒並發執行IO密集作業所需時間
def io():
write()
read()
t = time.time()
ios = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
thread = Thread(target=count, args=(1,1))
ios.append(thread)
thread.start()
e = ios.__len__()
while True:
for th in ios:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print(time.time() - t)68
(8)測試多執行緒並發執行網路密集操作所需時間
t = time.time()
ios = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
thread = Thread(target=http_request)
ios.append(thread)
thread.start()
e = ios.__len__()
while True:
for th in ios:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print("Thread Http Request", time.time() - t)Output: 0.7419998645782471、0.3839998245239258、0.3900001049041748
(9)測試多進程並發執行CPU密集操作所需時間
rr 963760376(10)測試多進程並發執行IO密集型操作counts = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
process = Process(target=count, args=(1,1))
counts.append(process)
process.start()
e = counts.__len__()
while True:
for th in counts:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print("Multiprocess cpu", time.time() - t)Output: 12.509000062942505、 13.059000015258789(11)測試多重進程並發執行Http請求密集型操作t = time.time()
ios = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
process = Process(target=io)
ios.append(process)
process.start()
e = ios.__len__()
while True:
for th in ios:
if not th.is_alive():
e -= 1
if e <= 0:
break
print("Multiprocess IO", time.time() - t)Output: 0.53299999923706055、0.476000070571899457100007057600007057 透過上面的結果,我們可以看到:
多執行緒在IO密集型的操作下似乎也沒有很大的優勢(也許IO操作的任務再繁重一些就能體現出優勢),在CPU密集型的操作下明顯地比單線程線性執行性能更差,但是對於網絡請求這種忙等阻塞執行緒的操作,多執行緒的優勢便非常顯著了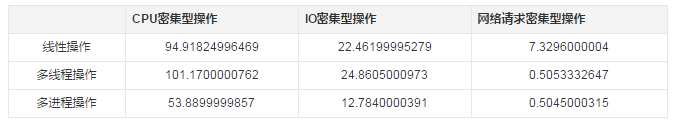
多進程無論是在CPU密集型或IO密集型以及網路請求密集型(經常發生執行緒阻塞的操作)中,都能體現出效能的優勢。不過在類似網路請求密集的操作上,與多執行緒相差無幾,但卻更佔用CPU等資源,所以對於這種情況下,我們可以選擇多執行緒來執行