劍鋒1.3B
Janus 是一個新的自回歸框架,整合了多模態理解和生成。與先前的模型使用單一視覺編碼器來執行理解和生成任務不同,Janus 為這些功能引入了兩個獨立的視覺編碼路徑。
理解和產生編碼的差異
- 在多模態理解任務中,視覺編碼器會擷取高階語意訊息,例如物件類別和視覺屬性。此編碼器專注於推斷複雜的含義,強調高維語義元素。
- 另一方面,在視覺生成任務中,重點放在生成精細細節並保持整體一致性。因此,需要能夠捕捉空間結構和紋理的低維編碼。
設定環境
以下是在 Google Colab 中執行 Janus 的步驟:
git clone https://github.com/deepseek-ai/Janus cd Janus pip install -e . # If needed, install the following as well # pip install wheel # pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
願景任務
載入模型
使用以下程式碼載入視覺任務所需的模型:
import torch from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM from janus.models import MultiModalityCausalLM, VLChatProcessor from janus.utils.io import load_pil_images # Specify the model path model_path = "deepseek-ai/Janus-1.3B" vl_chat_processor = VLChatProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer vl_gpt = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) vl_gpt = vl_gpt.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda().eval()
載入和準備圖像以進行編碼
接下來,載入圖片並將其轉換為模型可以理解的格式:
conversation = [
{
"role": "User",
"content": "<image_placeholder>\nDescribe this chart.",
"images": ["images/pie_chart.png"],
},
{"role": "Assistant", "content": ""},
]
# Load the image and prepare input
pil_images = load_pil_images(conversation)
prepare_inputs = vl_chat_processor(
conversations=conversation, images=pil_images, force_batchify=True
).to(vl_gpt.device)
# Run the image encoder and obtain image embeddings
inputs_embeds = vl_gpt.prepare_inputs_embeds(**prepare_inputs)
</image_placeholder>
產生回應
最後,運行模型以產生回應:
# Run the model and generate a response
outputs = vl_gpt.language_model.generate(
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
attention_mask=prepare_inputs.attention_mask,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
bos_token_id=tokenizer.bos_token_id,
eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
max_new_tokens=512,
do_sample=False,
use_cache=True,
)
answer = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0].cpu().tolist(), skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"{prepare_inputs['sft_format'][0]}", answer)
範例輸出
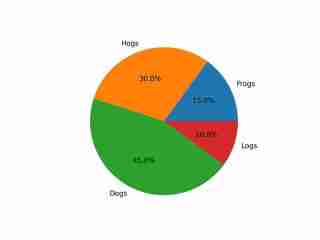
The image depicts a pie chart that illustrates the distribution of four different categories among four distinct groups. The chart is divided into four segments, each representing a category with a specific percentage. The categories and their corresponding percentages are as follows: 1. **Hogs**: This segment is colored in orange and represents 30.0% of the total. 2. **Frog**: This segment is colored in blue and represents 15.0% of the total. 3. **Logs**: This segment is colored in red and represents 10.0% of the total. 4. **Dogs**: This segment is colored in green and represents 45.0% of the total. The pie chart is visually divided into four segments, each with a different color and corresponding percentage. The segments are arranged in a clockwise manner starting from the top-left, moving clockwise. The percentages are clearly labeled next to each segment. The chart is a simple visual representation of data, where the size of each segment corresponds to the percentage of the total category it represents. This type of chart is commonly used to compare the proportions of different categories in a dataset. To summarize, the pie chart shows the following: - Hogs: 30.0% - Frog: 15.0% - Logs: 10.0% - Dogs: 45.0% This chart can be used to understand the relative proportions of each category in the given dataset.
輸出展示了對圖像的適當理解,包括其顏色和文字。
影像生成任務
載入模型
使用以下程式碼載入影像產生任務所需的模型:
import os import PIL.Image import torch import numpy as np from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM from janus.models import MultiModalityCausalLM, VLChatProcessor # Specify the model path model_path = "deepseek-ai/Janus-1.3B" vl_chat_processor = VLChatProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer vl_gpt = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) vl_gpt = vl_gpt.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda().eval()
準備提示
接下來,依照使用者的要求準備提示:
# Set up the prompt
conversation = [
{
"role": "User",
"content": "cute japanese girl, wearing a bikini, in a beach",
},
{"role": "Assistant", "content": ""},
]
# Convert the prompt into the appropriate format
sft_format = vl_chat_processor.apply_sft_template_for_multi_turn_prompts(
conversations=conversation,
sft_format=vl_chat_processor.sft_format,
system_prompt="",
)
prompt = sft_format + vl_chat_processor.image_start_tag
產生影像
以下函數用於產生影像。預設情況下,產生 16 張影像:
@torch.inference_mode()
def generate(
mmgpt: MultiModalityCausalLM,
vl_chat_processor: VLChatProcessor,
prompt: str,
temperature: float = 1,
parallel_size: int = 16,
cfg_weight: float = 5,
image_token_num_per_image: int = 576,
img_size: int = 384,
patch_size: int = 16,
):
input_ids = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer.encode(prompt)
input_ids = torch.LongTensor(input_ids)
tokens = torch.zeros((parallel_size*2, len(input_ids)), dtype=torch.int).cuda()
for i in range(parallel_size*2):
tokens[i, :] = input_ids
if i % 2 != 0:
tokens[i, 1:-1] = vl_chat_processor.pad_id
inputs_embeds = mmgpt.language_model.get_input_embeddings()(tokens)
generated_tokens = torch.zeros((parallel_size, image_token_num_per_image), dtype=torch.int).cuda()
for i in range(image_token_num_per_image):
outputs = mmgpt.language_model.model(
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
use_cache=True,
past_key_values=outputs.past_key_values if i != 0 else None,
)
hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
logits = mmgpt.gen_head(hidden_states[:, -1, :])
logit_cond = logits[0::2, :]
logit_uncond = logits[1::2, :]
logits = logit_uncond + cfg_weight * (logit_cond - logit_uncond)
probs = torch.softmax(logits / temperature, dim=-1)
next_token = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)
generated_tokens[:, i] = next_token.squeeze(dim=-1)
next_token = torch.cat([next_token.unsqueeze(dim=1), next_token.unsqueeze(dim=1)], dim=1).view(-1)
img_embeds = mmgpt.prepare_gen_img_embeds(next_token)
inputs_embeds = img_embeds.unsqueeze(dim=1)
dec = mmgpt.gen_vision_model.decode_code(
generated_tokens.to(dtype=torch.int),
shape=[parallel_size, 8, img_size // patch_size, img_size // patch_size],
)
dec = dec.to(torch.float32).cpu().numpy().transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
dec = np.clip((dec + 1) / 2 * 255, 0, 255)
visual_img = np.zeros((parallel_size, img_size, img_size, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
visual_img[:, :, :] = dec
os.makedirs('generated_samples', exist_ok=True)
for i in range(parallel_size):
save_path = os.path.join('generated_samples', f"img_{i}.jpg")
PIL.Image.fromarray(visual_img[i]).save(save_path)
# Run the image generation
generate(vl_gpt, vl_chat_processor, prompt)
產生的影像將保存在 generated_samples 資料夾中。
產生結果範例
以下是產生影像的範例:

- 狗的描繪相對較好。
- 建築物保持整體形狀,但某些細節(例如窗戶)可能顯得不切實際。
- 人類,然而,要很好地生成是很有挑戰性的,在真實感和類似動畫的風格中都存在明顯的扭曲。
以上是Janus B:多模態理解與生成任務的統一模型的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
 python中兩個列表的串聯替代方案是什麼?May 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
python中兩個列表的串聯替代方案是什麼?May 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM可以使用多種方法在Python中連接兩個列表:1.使用 操作符,簡單但在大列表中效率低;2.使用extend方法,效率高但會修改原列表;3.使用 =操作符,兼具效率和可讀性;4.使用itertools.chain函數,內存效率高但需額外導入;5.使用列表解析,優雅但可能過於復雜。選擇方法應根據代碼上下文和需求。
 Python:合併兩個列表的有效方法May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python:合併兩個列表的有效方法May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM有多種方法可以合併Python列表:1.使用 操作符,簡單但對大列表不內存高效;2.使用extend方法,內存高效但會修改原列表;3.使用itertools.chain,適用於大數據集;4.使用*操作符,一行代碼合併小到中型列表;5.使用numpy.concatenate,適用於大數據集和性能要求高的場景;6.使用append方法,適用於小列表但效率低。選擇方法時需考慮列表大小和應用場景。
 編譯的與解釋的語言:優點和缺點May 09, 2025 am 12:06 AM
編譯的與解釋的語言:優點和缺點May 09, 2025 am 12:06 AMCompiledLanguagesOffersPeedAndSecurity,而interneterpretledlanguages provideeaseafuseanDoctability.1)commiledlanguageslikec arefasterandSecureButhOnderDevevelmendeclementCyclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesandentency.2)cransportedeplatectentysenty
 Python:對於循環,最完整的指南May 09, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Python:對於循環,最完整的指南May 09, 2025 am 12:05 AMPython中,for循環用於遍歷可迭代對象,while循環用於條件滿足時重複執行操作。 1)for循環示例:遍歷列表並打印元素。 2)while循環示例:猜數字遊戲,直到猜對為止。掌握循環原理和優化技巧可提高代碼效率和可靠性。
 python concatenate列表到一個字符串中May 09, 2025 am 12:02 AM
python concatenate列表到一個字符串中May 09, 2025 am 12:02 AM要將列表連接成字符串,Python中使用join()方法是最佳選擇。 1)使用join()方法將列表元素連接成字符串,如''.join(my_list)。 2)對於包含數字的列表,先用map(str,numbers)轉換為字符串再連接。 3)可以使用生成器表達式進行複雜格式化,如','.join(f'({fruit})'forfruitinfruits)。 4)處理混合數據類型時,使用map(str,mixed_list)確保所有元素可轉換為字符串。 5)對於大型列表,使用''.join(large_li
 Python的混合方法:編譯和解釋合併May 08, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python的混合方法:編譯和解釋合併May 08, 2025 am 12:16 AMpythonuseshybridapprace,ComminingCompilationTobyTecoDeAndInterpretation.1)codeiscompiledtoplatform-Indepententbybytecode.2)bytecodeisisterpretedbybythepbybythepythonvirtualmachine,增強效率和通用性。
 了解python的' for”和' then”循環之間的差異May 08, 2025 am 12:11 AM
了解python的' for”和' then”循環之間的差異May 08, 2025 am 12:11 AMtheKeyDifferencesBetnewpython's“ for”和“ for”和“ loopsare:1)” for“ loopsareIdealForiteringSequenceSquencesSorkNowniterations,而2)”,而“ loopsareBetterforConterContinuingUntilacTientInditionIntionismetismetistismetistwithOutpredefinedInedIterations.un
 Python串聯列表與重複May 08, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python串聯列表與重複May 08, 2025 am 12:09 AM在Python中,可以通過多種方法連接列表並管理重複元素:1)使用 運算符或extend()方法可以保留所有重複元素;2)轉換為集合再轉回列表可以去除所有重複元素,但會丟失原有順序;3)使用循環或列表推導式結合集合可以去除重複元素並保持原有順序。


熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

SublimeText3 英文版
推薦:為Win版本,支援程式碼提示!

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
將Eclipse與SAP NetWeaver應用伺服器整合。

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser是一個安全的瀏覽器環境,安全地進行線上考試。該軟體將任何電腦變成一個安全的工作站。它控制對任何實用工具的訪問,並防止學生使用未經授權的資源。





