加權圖類
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB原創
- 2024-09-06 06:01:02825瀏覽
WeightedGraph 類擴展了 AbstractGraph。
前面的章節設計了用於對圖進行建模的 Graph 介面、AbstractGraph 類別和 UnweightedGraph 類別。依照這個模式,我們將 WeightedGraph 設計為 AbstractGraph 的子類,如下圖所示。
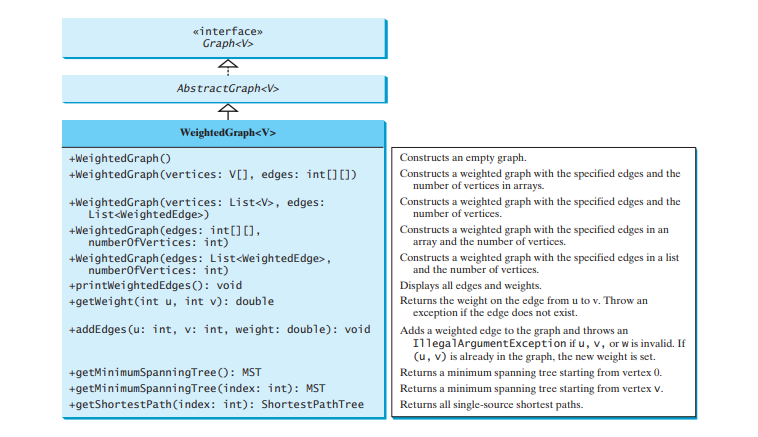
WeightedGraph 只需使用五個建構子擴充 AbstractGraph 即可建立特定的 WeightedGraph 實例。 WeightedGraph 繼承了AbstractGraph 的所有方法,重寫了clear 和addVertex 方法,實作了新的 > 方法新增加權邊,也引入了取得最小生成樹和尋找所有單一來源最短路徑的新方法。最小生成樹和最短路徑將在最小生成樹和最短路徑部分分別介紹。
下面的程式碼實現了WeightedGraph。邊鄰接清單(第 38-63 行)在內部用於儲存頂點的相鄰邊。當構造 WeightedGraph 時,會建立它的邊鄰接清單(第 47 和 57 行)。方法 getMinimumSpanningTree()(第 99-138 行)和 getShortestPath()(第 156-197 行)將在接下來的部分中介紹。
package demo;
import java.util.*;
public class WeightedGraph<V> extends AbstractGraph<V> {
/** Construct an empty */
public WeightedGraph() {}
/** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edged in arrays */
public WeightedGraph(V[] vertices, int[][] edges) {
createWeightedGraph(java.util.Arrays.asList(vertices), edges);
}
/** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edges in list */
public WeightedGraph(int[][] edges, int numberOfVertices) {
List<V> vertices = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfVertices; i++)
vertices.add((V)(new Integer(i)));
createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
}
/** Construct a WeightedGraph for vertices 0, 1, 2 and edge list */
public WeightedGraph(List<V> vertices, List<WeightedEdge> edges) {
createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
}
/** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices 0, 1, and edge array */
public WeightedGraph(List<WeightedEdge> edges, int numberOfVertices) {
List<V> vertices = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfVertices; i++)
vertices.add((V)(new Integer(i)));
createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
}
/** Create adjacency lists from edge arrays */
private void createWeightedGraph(List<V> vertices, int[][] edges) {
this.vertices = vertices;
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.size(); i++) {
neighbors.add(new ArrayList<Edge>()); // Create a list for vertices
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
neighbors.get(edges[i][0]).add(new WeightedEdge(edges[i][0], edges[i][1], edges[i][2]));
}
}
/** Create adjacency lists from edge lists */
private void createWeightedGraph(List<V> vertices, List<WeightedEdge> edges) {
this.vertices = vertices;
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.size(); i++) {
neighbors.add(new ArrayList<Edge>()); // Create a list for vertices
}
for (WeightedEdge edge: edges) {
neighbors.get(edge.u).add(edge); // Add an edge into the list
}
}
/** Return the weight on the edge (u, v) */
public double getWeight(int u, int v) throws Exception {
for (Edge edge : neighbors.get(u)) {
if (edge.v == v) {
return ((WeightedEdge)edge).weight;
}
}
throw new Exception("Edge does not exit");
}
/** Display edges with weights */
public void printWeightedEdges() {
for (int i = 0; i < getSize(); i++) {
System.out.print(getVertex(i) + " (" + i + "): ");
for (Edge edge : neighbors.get(i)) {
System.out.print("(" + edge.u + ", " + edge.v + ", " + ((WeightedEdge)edge).weight + ") ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/** Add edges to the weighted graph */
public boolean addEdge(int u, int v, double weight) {
return addEdge(new WeightedEdge(u, v, weight));
}
/** Get a minimum spanning tree rooted at vertex 0 */
public MST getMinimumSpanningTree() {
return getMinimumSpanningTree(0);
}
/** Get a minimum spanning tree rooted at a specified vertex */
public MST getMinimumSpanningTree(int startingVertex) {
// cost[v] stores the cost by adding v to the tree
double[] cost = new double[getSize()];
for (int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
cost[i] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // Initial cost
}
cost[startingVertex] = 0; // Cost of source is 0
int[] parent = new int[getSize()]; // Parent of a vertex
parent[startingVertex] = -1; // startingVertex is the root
double totalWeight = 0; // Total weight of the tree thus far
List<Integer> T = new ArrayList<>();
// Expand T
while (T.size() < getSize()) {
// Find smallest cost v in V - T
int u = -1; // Vertex to be determined
double currentMinCost = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < getSize(); i++) {
if (!T.contains(i) && cost[i] < currentMinCost) {
currentMinCost = cost[i];
u = i;
}
}
T.add(u); // Add a new vertex to T
totalWeight += cost[u]; // Add cost[u] to the tree
// Adjust cost[v] for v that is adjacent to u and v in V - T
for (Edge e : neighbors.get(u)) {
if (!T.contains(e.v) && cost[e.v] > ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) {
cost[e.v] = ((WeightedEdge)e).weight;
parent[e.v] = u;
}
}
} // End of while
return new MST(startingVertex, parent, T, totalWeight);
}
/** MST is an inner class in WeightedGraph */
public class MST extends Tree {
private double totalWeight; // Total weight of all edges in the tree
public MST(int root, int[] parent, List<Integer> searchOrder, double totalWeight) {
super(root, parent, searchOrder);
this.totalWeight = totalWeight;
}
public double getTotalWeight() {
return totalWeight;
}
}
/** Find single source shortest paths */
public ShortestPathTree getShortestPath(int sourceVertex) {
// cost[v] stores the cost of the path from v to the source
double[] cost = new double[getSize()];
for (int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
cost[i] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // Initial cost set to infinity
}
cost[sourceVertex] = 0; // Cost of source is 0
// parent[v] stores the previous vertex of v in the path
int[] parent = new int[getSize()];
parent[sourceVertex] = -1; // The parent of source is set to -1
// T stores the vertices whose path found so far
List<Integer> T = new ArrayList<>();
// Expand T
while (T.size() < getSize()) {
// Find smallest cost v in V - T
int u = -1; // Vertex to be determined
double currentMinCost = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < getSize(); i++) {
if (!T.contains(i) && cost[i] < currentMinCost) {
currentMinCost = cost[i];
u = i;
}
}
T.add(u); // Add a new vertex to T
// Adjust cost[v] for v that is adjacent to u and v in V - T
for (Edge e : neighbors.get(u)) {
if (!T.contains(e.v) && cost[e.v] > cost[u] + ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) {
cost[e.v] = cost[u] + ((WeightedEdge)e).weight;
parent[e.v] = u;
}
}
} // End of while
// Create a ShortestPathTree
return new ShortestPathTree(sourceVertex, parent, T, cost);
}
/** ShortestPathTree is an inner class in WeightedGraph */
public class ShortestPathTree extends Tree {
private double[] cost; // cost[v] is the cost from v to source
/** Construct a path */
public ShortestPathTree(int source, int[] parent, List<Integer> searchOrder, double[] cost) {
super(source, parent, searchOrder);
this.cost = cost;
}
/** Return the cost for a path from the root to vertex v */
public double getCost(int v) {
return cost[v];
}
/** Print paths from all vertices to the source */
public void printAllPaths() {
System.out.println("All shortest paths from " + vertices.get(getRoot()) + " are:");
for (int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
printPath(i); // Print a path from i to the source
System.out.println("(cost: " + cost[i] + ")"); // Path cost
}
}
}
}
WeightedGraph 類擴展了 AbstractGraph 類(第 3 行)。 AbstractGraph 中的屬性 vertices 和 neighbors 繼承於 WeightedGraph.neighbors 是一個清單。列表中的每個元素都是另一個包含邊的列表。對於未加權圖,每條邊都是 AbstractGraph.Edge 的實例。對於加權圖,每條邊都是 WeightedEdge 的實例。 WeightedEdge 是 Edge 的子類型。因此,您可以將加權邊加到 neighbors.get(i) 以獲得加權圖(第 47 行)。
下面的程式碼給出了一個測試程序,該程序為下圖中的圖建立一個圖,並為下圖a中的圖建立另一個圖。
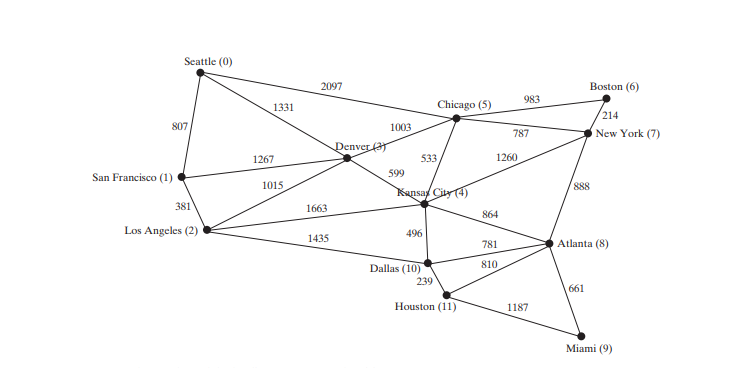
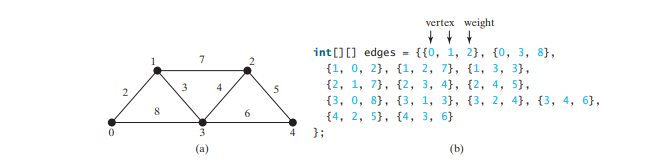
package demo;
public class TestWeightedGraph {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"};
int[][] edges = {
{0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097},
{1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267},
{2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435},
{3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003},
{4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496},
{5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787},
{6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214},
{7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888},
{8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810},
{9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187},
{10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239},
{11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239}
};
WeightedGraph<String> graph1 = new WeightedGraph<>(vertices, edges);
System.out.println("The number of vertices in graph1: " + graph1.getSize());
System.out.println("The vertex with index 1 is " + graph1.getVertex(1));
System.out.println("The index for Miami is " + graph1.getIndex("Miami"));
System.out.println("The edges for graph1:");
graph1.printWeightedEdges();
edges = new int[][] {
{0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8},
{1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3},
{2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5},
{3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6},
{4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6}
};
WeightedGraph<Integer> graph2 = new WeightedGraph<>(edges, 5);
System.out.println("\nThe edges for graph2:");
graph2.printWeightedEdges();
}
}
graph1 的頂點數量:12
索引為 1 的頂點是舊金山
邁阿密的指數是 9
graph1 的邊:
頂點 0: (0, 1, 807) (0, 3, 1331) (0, 5, 2097)
頂點 1: (1, 2, 381) (1, 0, 807) (1, 3, 1267)
頂點 2: (2, 1, 381) (2, 3, 1015) (2, 4, 1663) (2, 10, 1435)
頂點 3: (3, 4, 599) (3, 5, 1003) (3, 1, 1267)
(3, 0, 1331) (3, 2, 1015)
頂點 4: (4, 10, 496) (4, 8, 864) (4, 5, 533) (4, 2, 1663)
(4, 7, 1260) (4, 3, 599)
頂點 5: (5, 4, 533) (5, 7, 787) (5, 3, 1003)
(5, 0, 2097) (5, 6, 983)
頂點 6: (6, 7, 214) (6, 5, 983)
頂點 7: (7, 6, 214) (7, 8, 888) (7, 5, 787) (7, 4, 1260)
頂點 8: (8, 9, 661) (8, 10, 781) (8, 4, 864)
(8, 7, 888) (8, 11, 810)
頂點 9: (9, 8, 661) (9, 11, 1187)
頂點 10: (10, 11, 239) (10, 4, 496) (10, 8, 781) (10, 2, 1435)
頂點 11: (11, 10, 239) (11, 9, 1187) (11, 8, 810)
頂點 0: (0, 1, 2) (0, 3, 8)
頂點 1: (1, 0, 2) (1, 2, 7) (1, 3, 3)
頂點 2: (2, 3, 4) (2, 1, 7) (2, 4, 5)
頂點 3: (3, 1, 3) (3, 4, 6) (3, 2, 4) (3, 0, 8)
頂點 4: (4, 2, 5) (4, 3, 6)
程式為上圖第 3-27 行的圖表建立 graph1。 graph1 的頂點在第 3-5 行定義。 graph1 的邊在第 7-24 行定義。邊緣使用二維數組表示。對於陣列中的每一行i,edges[i][0] 和edges[i][1] 表示從頂點edges[i] 有一條邊[0 ] 到頂點edges[i][1],邊的權重為edges[i][2]。例如,{0, 1, 807}(第8 行)表示來自頂點0 的邊(edges[ 0][0]) 到頂點1 (邊[0][1]),權重807 (邊[0] [2])。 {0, 5, 2097}(第8 行)表示從頂點0 開始的邊(edges[🎜>0 開始的邊(edges[22 ][ 0]) 到頂點5 (邊[2][1]),權重2097 (邊[2][ 2] )。第 35 行呼叫 graph1 上的 printWeightedEdges() 方法來顯示
graph1中的所有邊。 程式為上圖 a 中第 37-44 行中的圖形建立 graph2 的邊。第 46 行呼叫 graph2 上的 printWeightedEdges() 方法來顯示
graph2 中的所有邊。以上是加權圖類的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

