C# 物件序列化
- PHPz原創
- 2024-09-03 15:05:54733瀏覽
要將物件轉換為序列或位元組流,所使用的過程稱為序列化。為了將物件傳輸到資料庫、檔案或內存,我們使用序列化。為了在需要時精確地重新創建或恢復對象,序列化起著至關重要的作用,因為它保存了對象的狀態。透過這項聲明,我們的意思是,使用 Web 服務,只需將物件從一個網域傳輸到另一個網域,就可以將物件傳輸到任何遠端位置。序列化的逆過程稱為反序列化,因為它是將序列化的位元組序列轉換為物件的過程。
C# 物件序列化語法:
對於C#中物件的序列化,有一個屬性叫做[Serialized]。如果未以正確的方式提及該屬性,則在執行時會引發 SerializedException。
文法如下:
public static void SomeData()
{
string aoo = "Heyoo! Thank you for visiting us....";
FileStream boo = new FileStream(@"D:\EduCBA.txt", FileMode.Create,FileAccess.Write, FileShare.None);
BinaryFormatter coo = new BinaryFormatter();
coo.Serialize(boo, aoo);
boo.Close();
}
C# 物件反序列化語法:
文法如下:
public static void AnotherData()
{
FileStream boo = new FileStream(@"D:\EduCBA.txt", FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read);
BinaryFormatter doo = new BinaryFormatter();
string eoo = "";
eoo = (string)doo.Deserialize(boo);
boo.Close();
Console.WriteLine("EduCBA’s-se-ria-li-za-tion-&-de-se-ria-li-za-tion-in-C#-exam-ple");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine(eoo);
}
C# 物件序列化使用範例
讓我們討論 C# 物件序列化的範例。
範例#1
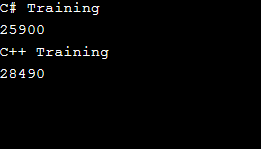
在下面的程式碼中,我們必須序列化 EduCBA 類,因此我們使用了 [Serialized]。為了阻止程式碼執行後發生任何錯誤,應該提及此屬性。在提到我們要序列化的類別的屬性之後,我們描述了類別的四個屬性,“CourseName1”是一個字串,“CoursePrice1”是一個整數值,類似地,“CourseName2”是一個字串,“ CoursePrice2」是一個整數價值。要以唯讀模式開啟檔案“E:EDUCBA.txt”,會建立一個物件 hello 物件“hello”,最後,我們使用前面提到的屬性顯示“yum”。
代碼:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Careerplan
{
[Serializable]
class EduCBA
{
public String CourseName1;
public int CoursePrice1;
public String CourseName2;
public int CoursePrice2;
static void Main(string[] rahul)
{
EduCBA yum = new EduCBA();
yum.CourseName1 = "C# Training";
yum.CoursePrice1 = 25900;
yum.CourseName2 = "C++ Training";
yum.CoursePrice2 = 28490;
IFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
Stream hello = new FileStream(@"E:\EDUCBA.txt",FileMode.Create,FileAccess.Write, FileShare.None);
formatter.Serialize(hello, yum);
hello.Close();
hello = new FileStream(@"E:\EDUCBA.txt",FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read);
hello.Close();
Console.WriteLine(yum.CourseName1);
Console.WriteLine(yum.CoursePrice1);
Console.WriteLine(yum.CourseName2);
Console.WriteLine(yum.CoursePrice2);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
輸出:
範例#2
在下面的程式碼中,我們必須序列化類別 CBA,因此我們使用了 [Serializable]。為了阻止程式碼執行後發生任何錯誤,應該提及此屬性。在提到我們要序列化的類別的屬性之後,我們描述了類別的九個屬性,其中「student_ID1」是一個整數值,「student_name1」是一個字串,「CGPA1」是一個雙精確值,這意味著它包含數字值小數點,類似地,“student_ID2”是整數值,“student_name2”是字串,“CGPA2”是雙精度值,“student_ID3”值是整數,“student_name3”是字串,“ CGPA3”是雙精度值。要以唯讀模式開啟檔案“E:EDUCBA.txt”,將建立一個物件hello 和一個物件“learn”,最後,我們使用先前在不同行中提到的屬性顯示“ID”以及提及資料實際代表什麼的文本。
代碼:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Text;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
namespace StudentData
{
[Serializable]
class CBA
{
public int student_ID1;
public String student_name1;
public double CGPA1;
public int student_ID2;
public String student_name2;
public double CGPA2;
public int student_ID3;
public String student_name3;
public double CGPA3;
static void Main(string[] annie)
{
CBA ID = new CBA();
ID.student_ID1 = 15023456;
ID.student_name1 = "Rahul Kashyap";
ID.CGPA1 = 9.5;
ID.student_ID2 = 18023950;
ID.student_name2 = "Ankush Rajput";
ID.CGPA2 = 8.7;
ID.student_ID3 = 19084653;
ID.student_name3 = "Aadarsh Rajput";
ID.CGPA3 = 7.5;
IFormatter eduCBA = new BinaryFormatter();
Stream learn = new FileStream(@"E:\EDUCBA.txt",FileMode.Create,FileAccess.Write, FileShare.None);
eduCBA.Serialize(learn, ID);
learn.Close();
learn = new FileStream(@"E:\EDUCBA.txt",FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read);
learn.Close();
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("Welcome! Desired data is below");
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("::TABLE::");
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("::ROW1::");
Console.WriteLine("Student_ID: {0}", ID.student_ID1);
Console.Write("::ROW2::");
Console.WriteLine("Student_Name: {0}", ID.student_name1);
Console.Write("::ROW3::");
Console.WriteLine("CGPA Scored: {0}", ID.CGPA1);
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("::ROW1::");
Console.WriteLine("Student_ID: {0}", ID.student_ID2);
Console.Write("::ROW2::");
Console.WriteLine("Student_Name: {0}", ID.student_name2);
Console.Write("::ROW3::");
Console.WriteLine("CGPA Scored: {0}", ID.CGPA2);
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("\n");
Console.Write("::ROW1::");
Console.WriteLine("Student_ID: {0}", ID.student_ID3);
Console.Write("::ROW2::");
Console.WriteLine("Student_Name: {0}", ID.student_name3);
Console.Write("::ROW3::");
Console.WriteLine("CGPA Scored: {0}", ID.CGPA3);
}
}
}
輸出:

範例 #3
在下面的範例中,為了物件的序列化,我們首先建立了一個流(FileStream)物件“boo”,然後我們為BinaryFormatter 物件“coo”建立了一個對象,然後我們呼叫了“coo.Serialize (boo, aoo)”,這是一個BinaryFormatter.Serialize() 方法,用於在C# 中序列化物件。
類似地,對於對象的反序列化,首先我們創建了一個流(FileStream)對象“boo”,用於讀取序列化輸出,然後我們為BinaryFormatter 對象“doo”創建了一個對象,然後我們呼叫了 “Du. Deserialize(boo)”,這是一個BinaryFormatter.Deserialize() 方法,用於C# 中物件的反序列化。
代碼:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
namespace EDUCBA
{
class Rahul
{
public static void SomeData()
{
string aoo = "Heyoo! Thank you for visiting us....";
FileStream boo = new FileStream(@"D:\EduCBA.txt", FileMode.Create,FileAccess.Write, FileShare.None);
BinaryFormatter coo = new BinaryFormatter();
coo.Serialize(boo, aoo);
boo.Close();
}
public static void AnotherData()
{
FileStream boo = new FileStream(@"D:\EduCBA.txt", FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read);
BinaryFormatter doo = new BinaryFormatter();
string eoo = "";
eoo = (string)doo.Deserialize(boo);
boo.Close();
Console.WriteLine("EduCBA’s-se-ria-li-za-tion-&-de-se-ria-li-za-tion-in-C#-exam-ple");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine(eoo);
}
static void Main(string[] foo)
{
SomeData();
AnotherData();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
輸出:

結論
基於上面的討論,我們了解了C#中物件的序列化以及C#中同一物件的反序列化。我們也了解序列化的重要性。我們已經討論了與 C# 序列化和 C# 反序列化相關的各種範例以及兩者的語法。
以上是C# 物件序列化的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

