Java 中的多維數組
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB原創
- 2024-08-30 15:27:381264瀏覽
Java 多維數組的完整指南。數組是同質資料多維結構,是具有相似資料類型的元素的集合。它們儲存在連續的記憶體位置中。在陣列中,第一個元素儲存在索引 0 中;第二個元素儲存在索引 1 中,依此類推。數組可以是單維或多維的。在本文檔中,我們將研究 Java 中的多維數組。多維數組是可以容納多個行和列的數組的數組。現在,讓我們在以下部分中了解多維數組的語法和實作。
廣告 該類別中的熱門課程 JAVA 掌握 - 專業化 | 78 課程系列 | 15 次模擬測驗文法:
data_type[dimension 1][dimension 2][]…[dimension n] array_name= new data_type[size 1][size 2]…[size n]
- data_type:陣列的資料型,範例: int、char、float 等
- 維度:陣列的維度,範例: 1D、2D 等
- array_name:陣列的名稱。
- size1, size2, …, sizeN:維度的大小。
Java 中多維數組的型別
Java 中最常見的多維數組是:
- 二維數組或二維數組。
- 三維數組或 3D 數組。
1.二維數組
二維數組通常用於超級瑪利歐等平台電玩遊戲中來表示地形或螢幕。它們也可以用於繪製棋盤、表示電子表格等結構。
代碼:
int[][] array1 = new int[2][2];//Two dimensional Integer Array with 2 rows and 2 columns
範例:
9 10
7 66
這是一個兩行兩列的二維陣列。
2.三維數組
三維數組在即時應用程式中並不常用。因此,在程式設計範例中也更傾向於二維數組。
代碼:
int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Three dimensional Array
範例:
6 8 66
66 65 47
46 89 98
如何在 Java 中宣告多維數組?
如果知道普通數組,就很容易理解 Java 中的多維數組。多維數組可以如下聲明:
首先讓我們來看看二維陣列的宣告:
- int[][] array1 = new int[2][2]; //2行2列的二維整數陣列。
- String[][] array1 = new String[2][2]; //2行2列的二維字串陣列。
- char[][] array1 = new char[2][2]; //2行2列的二維char陣列。
- boolean[][] array1 = new boolean[2][2]; //2行2列的二維布林陣列。
- double[][] array1 = new double[2][2]; //2行2列的二維雙數組。
- float[][] array1 = new float[2][2]; //2行2列的二維浮點陣列。
- 長[][] array1 = new 長[2][2]; //2行2列的二維長數組
- short[][] array1 = new Short[2][2]; //2行2列的二維短數組。
- byte[][] array1 = new byte[2][2]; //2行2列的二維位元組陣列。
確保在 Java 程式設計時建立正確的聲明。
範例#1
代碼:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional 2D array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String args[]){
//2D array a is declared and initialized
int a[][]={{2,2,3},{8,4,5},{9,4,5}};
//Print the array elements
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}
輸出:

三維數組的聲明可以討論。
- int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //三維陣列
這些陣列可以是任何資料型態。以下是一些具有不同資料類型的三維數組。
- int [][][] IntArray; // 宣告整數的三維陣列。
- byte[][][] ByteArray; // 宣告三維位元組陣列。
- short[][][] ShortArray; // 宣告 Shorts 的三維陣列。
- long[][][] LongArray; // 宣告 Long 的三維陣列。
- float[][][] FloatArray; // 宣告 Floats 的三維陣列。
- double[][][] DoubleArray; // 宣告 Double 的三維陣列。
- boolean[][][] BooleanArray; // 宣告三維布林陣列。
- char[][][] CharArray; // 宣告 Chars 的三維陣列。
- String[][][] StringArray; // 宣告三維字串陣列。
範例#2
代碼:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3D array arr
int[][][] arr = { { { 1 , -9 , 3 } ,{ 2 , 7 , 4 } } , { { -45 , -5 , 6 , 75 } , { 88 } , { 29 , 30 } } };
// for..each loop to iterate through the elements of the 3d array arr
for (int[][] ar: arr) {
for (int[] a: ar) {
for(int finalarray: a) {
System.out.println(finalarray);
}
}
}
}
}
輸出:

如何在Java中初始化多維數組?
多維數組可以用多種方式初始化:
1. Declare and Create a Java Multidimensional Array
- int[][][] a= new int[3][5][4];
In a more traditional way, Initializing Array elements can be as follows.
- a[0][1][0] = 15; // Initializing Array elements at position [0][1][0]
- a[1][2][0] = 45; // Initializing Array elements at position [1][2][0]
- a[2][1][1] = 65; // Initializing Array elements at position [2][1][1]
2. Directly Specify the Elements
int[][][] a = { { { 11 , 23 , 30 }, { 5 ,65 , 70 } , { 0 , 80 , 10 } ,{ 10 , 12 , 450 } } ,{ { 33 , 2 , 4 } , {11, 66, 6}, {55, 11, 22}, {11, 57, 43} } };
In this case, even though the size of rows and columns are not mentioned, the java compiler is able to identify the size of rows and columns by counting the number of elements.
3. Nested For Loop
In the case of storing a large number of elements, Nested For Loop can be used as shown below:
int i, j, k;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
a[i][j][k] = i + j + k;} } }
4. Assigning Values to One Row
int a= new int[3][2][4]; a[0][2][1]= 33; a[0][1][2]= 73; a[0][1][1]= 88;
A three-dimensional array of size 3 levels * 2 rows * 4 columns is created, but values are assigned to some positions only. Since none of the other elements does have any value assigned, default values will be assigned.
Operations on Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional Array in Java can perform several operations.
Example #1
Let Us See the Matrix Addition of Two Arrays.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String args[])
{
int row, col, c, d;
//input the number of rows and columns
Scanner <u>in</u> = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows of matrix");
row = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the number of columns of matrix");
col = in.nextInt();
//initialization of two matrices and sum matrix
int firstmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int secondmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int summat[][] = new int[row][col];
//adding elements to first matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the first matrix");
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
firstmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//adding elements to second matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the second matrix");
for (c = 0 ; c < row ; c++)
for (d = 0 ; d < col ; d++)
secondmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//sum of the two matrices
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
summat[c][d] = firstmat[c][d] + secondmat[c][d];
System.out.println("Sum of the two given matrices is:");
//printing the sum matrix
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
{
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
System.out.print(summat[c][d]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:

If subtraction needs to be performed, replace ‘+’ with ‘-‘ in the code.
Example #2
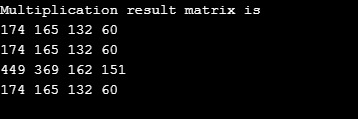
Let us see how Matrix Multiplication Works.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to perform matrix multiplication
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
static int N = 4;
// multiply matrices a and b, and then stores the result in c
static void mul(int a[][],
int b[][], int c[][])
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
c[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j]; //multiply a and b matrices
}
}
}
//main method
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int a[][] = { {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2},
{9, 7, 2, 3}};
int b[][] = {{ 9, 7, 2, 3}, {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2}};
// Store the result in c
int c[][] = new int[N][N] ;
int i, j;
mul(a, b, c); //calling the mul method
System.out.println("Multiplication result matrix" + " is ");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.print( c[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
Arrays are homogenous data structures that can store similar types of elements. It can be of single-dimensional or multidimensional. In this document, multidimensional arrays are discussed with explaining the syntax structure, initialization, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multidimensional Array in Java. Here we discuss 2 types of the multidimensional array in java, how to declare, how to initialize and operation in it. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- Multidimensional Array in C
- 2D Arrays in Java
- 2D Arrays in C#
- Multidimensional Array in PHP
以上是Java 中的多維數組的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

