Java程式從給定堆疊中刪除重複項
- WBOY原創
- 2024-08-28 12:01:04593瀏覽
在本文中,我們將探討兩種在 Java 中從堆疊中刪除重複元素的方法。我們將比較使用巢狀循環的簡單方法和使用HashSet的更有效方法。目標是示範如何最佳化重複刪除並評估每種方法的效能。
問題陳述
寫一個Java程序,從堆疊中刪除重複的元素。
輸入
Stack<Integer> data = initData(10L);
輸出
Unique elements using Naive Approach: [1, 4, 3, 2, 8, 7, 5] Time spent for Naive Approach: 18200 nanoseconds Unique elements using Optimized Approach: [1, 4, 3, 2, 8, 7, 5] Time spent for Optimized Approach: 34800 nanoseconds
要從給定堆疊中刪除重複項,我們有兩種方法 -
- 簡單的方法:建立兩個巢狀循環來查看哪些元素已經存在並防止將它們加入結果堆疊回傳。
- HashSet 方法:使用 Set 來儲存唯一元素,並利用其 O(1) 複雜度 來檢查元素是否存在。
產生和克隆隨機堆疊
以下是 Java 程式首先建立一個隨機堆疊,然後建立它的副本以供進一步使用 -
private static Stack initData(Long size) {
Stack stack = new Stack < > ();
Random random = new Random();
int bound = (int) Math.ceil(size * 0.75);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
stack.add(random.nextInt(bound) + 1);
}
return stack;
}
private static Stack < Integer > manualCloneStack(Stack < Integer > stack) {
Stack < Integer > newStack = new Stack < > ();
for (Integer item: stack) {
newStack.push(item);
}
return newStack;
}
initData 幫助創建一個具有指定大小和範圍從 1 到 100 的隨機元素的 Stack。
manualCloneStack 透過從另一個堆疊複製資料來幫助產生數據,並使用它來比較兩種想法之間的表現。
使用 Naïve 方法從給定堆疊中刪除重複項
以下是使用 Naïve 方法從給定堆疊中刪除重複項的步驟 -
- 啟動計時器。
- 建立一個空堆疊來儲存唯一元素。
- 使用 while 迴圈迭代並繼續,直到原始堆疊為空彈出頂部元素。
- 使用 resultStack.contains(element) 檢查重複項,看看該元素是否已在結果堆疊中。
- 如果該元素不在結果堆疊中,則將其新增至結果堆疊中。
- 記錄結束時間並計算總花費時間。
- 回傳結果
範例
以下是使用 Naïve 方法從給定堆疊中刪除重複項的 Java 程式 -
public static Stack idea1(Stack stack) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
Stack resultStack = new Stack < > ();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int element = stack.pop();
if (!resultStack.contains(element)) {
resultStack.add(element);
}
}
System.out.println("Time spent for idea1 is %d nanosecond".formatted(System.nanoTime() - start));
return resultStack;
}
對於樸素方法,我們使用
<code>while (!stack.isEmpty())</code>處理第一個循環遍歷堆疊中的所有元素,第二個循環是
<code>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">resultStack.contains(element)</pre>
檢查元素是否已經存在。 使用最佳化方法(HashSet)從給定堆疊中刪除重複項
以下是使用最佳化方法從給定堆疊中刪除重複項的步驟 -
- 啟動計時器
- 建立一個 Set 來追蹤看到的元素(用於 O(1) 複雜度檢查)。
- 建立一個暫存堆疊來儲存唯一元素。
- 使用 while 迴圈進行迭代,繼續直到堆疊為空。
- 從堆疊中移除頂部元素。
- 為了檢查重複項,我們將使用 seen.contains(element) 來檢查該元素是否已經在集合中。
- 如果該元素不在集合中,則將其新增至可見堆疊和臨時堆疊中。
- 記錄結束時間並計算總花費時間。
- 回傳結果
範例
以下是使用 HashSet 從給定堆疊中刪除重複項的 Java 程式 -
public static Stack<Integer> idea2(Stack<Integer> stack) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
Stack<Integer> tempStack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int element = stack.pop();
if (!seen.contains(element)) {
seen.add(element);
tempStack.push(element);
}
}
System.out.println("Time spent for idea2 is %d nanosecond".formatted(System.nanoTime() - start));
return tempStack;
}
為了最佳化方法,我們使用
<code>Set<Integer> seen</code>要在 Set 中儲存唯一元素,請在存取隨機元素時利用 O(1) 複雜度 來減少檢查元素是否存在的計算成本。
同時使用這兩種方法
以下是使用上述兩種方法從給定堆疊中刪除重複項的步驟 -
- 初始化數據,我們使用initData(Long size)方法建立一個充滿隨機整數的堆疊。
- 克隆堆疊,我們使用 cloneStack(Stack stack) 方法 建立原始堆疊的精確副本。
- 使用initData產生初始堆疊。
- 使用 cloneStack 複製此堆疊。
- 應用 樸素方法從原始堆疊中刪除重複項。
- 應用最佳化方法從克隆堆疊中刪除重複項。
- 顯示每種方法所花費的時間以及兩種方法產生的獨特元素
範例
以下是使用上述兩種方法從堆疊中刪除重複元素的 Java 程式 -
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Stack;
public class DuplicateStackElements {
private static Stack<Integer> initData(Long size) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Random random = new Random();
int bound = (int) Math.ceil(size * 0.75);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
stack.add(random.nextInt(bound) + 1);
}
return stack;
}
private static Stack<Integer> cloneStack(Stack<Integer> stack) {
Stack<Integer> newStack = new Stack<>();
newStack.addAll(stack);
return newStack;
}
public static Stack<Integer> idea1(Stack<Integer> stack) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
Stack<Integer> resultStack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int element = stack.pop();
if (!resultStack.contains(element)) {
resultStack.add(element);
}
}
System.out.printf("Time spent for idea1 is %d nanoseconds%n", System.nanoTime() - start);
return resultStack;
}
public static Stack<Integer> idea2(Stack<Integer> stack) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
Stack<Integer> tempStack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int element = stack.pop();
if (!seen.contains(element)) {
seen.add(element);
tempStack.push(element);
}
}
System.out.printf("Time spent for idea2 is %d nanoseconds%n", System.nanoTime() - start);
return tempStack;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> data1 = initData(10L);
Stack<Integer> data2 = cloneStack(data1);
System.out.println("Unique elements using idea1: " + idea1(data1));
System.out.println("Unique elements using idea2: " + idea2(data2));
}
}
輸出
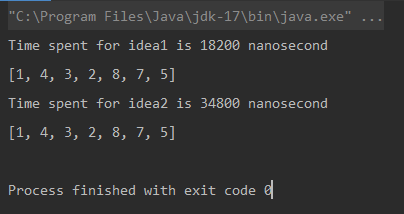
比較
* 測量單位是奈秒。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> data1 = initData(<number of stack size want to test>);
Stack<Integer> data2 = manualCloneStack(data1);
idea1(data1);
idea2(data2);
}
| Method | 100 elements | 1000 elements |
10000 elements |
100000 elements |
1000000 elements |
| Idea 1 | 693100 |
4051600 |
19026900 |
114201800 |
1157256000 |
| Idea 2 | 135800 |
681400 |
2717800 |
11489400 |
36456100 |
As observed, the time running for Idea 2 is shorter than for Idea 1 because the complexity of Idea 1 is O(n²), while the complexity of Idea 2 is O(n). So, when the number of stacks increases, the time spent on calculations also increases based on it.
以上是Java程式從給定堆疊中刪除重複項的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

