一、简介
XML(eXtensible Markup Language)指可扩展标记语言,被设计用来传输和存储数据,已经日趋成为当前许多新生技术的核心,在不同的领域都有着不同的应用。它是web发展到一定阶段的必然产物,既具有SGML的核心特征,又有着HTML的简单特性,还具有明确和结构良好等许多新的特性。
python解析XML常见的有三种方法:一是xml.dom.*模块,它是W3C DOM API的实现,若需要处理DOM API则该模块很适合,注意xml.dom包里面有许多模块,须区分它们间的不同;二是xml.sax.*模块,它是SAX API的实现,这个模块牺牲了便捷性来换取速度和内存占用,SAX是一个基于事件的API,这就意味着它可以“在空中”处理庞大数量的的文档,不用完全加载进内存;三是xml.etree.ElementTree模块(简称 ET),它提供了轻量级的Python式的API,相对于DOM来说ET 快了很多,而且有很多令人愉悦的API可以使用,相对于SAX来说ET的ET.iterparse也提供了 “在空中” 的处理方式,没有必要加载整个文档到内存,ET的性能的平均值和SAX差不多,但是API的效率更高一点而且使用起来很方便。
二、详解
解析的xml文件(country.xml):
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<data>
<country name="Singapore">
<rank>4</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>59900</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/>
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>68</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/>
<neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/>
</country>
</data>
1、xml.etree.ElementTree
ElementTree生来就是为了处理XML,它在Python标准库中有两种实现:一种是纯Python实现的,如xml.etree.ElementTree,另一种是速度快一点的xml.etree.cElementTree。注意:尽量使用C语言实现的那种,因为它速度更快,而且消耗的内存更少。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
try:
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
except ImportError:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
这是一个让Python不同的库使用相同API的一个比较常用的办法,而从Python 3.3开始ElementTree模块会自动寻找可用的C库来加快速度,所以只需要import xml.etree.ElementTree就可以了。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#!/usr/bin/evn python
#coding:utf-8
try:
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
except ImportError:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import sys
try:
tree = ET.parse("country.xml") #打开xml文档
#root = ET.fromstring(country_string) #从字符串传递xml
root = tree.getroot() #获得root节点
except Exception, e:
print "Error:cannot parse file:country.xml."
sys.exit(1)
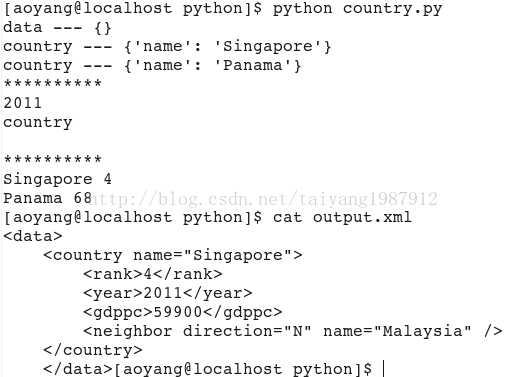
print root.tag, "---", root.attrib
for child in root:
print child.tag, "---", child.attrib
print "*"*10
print root[0][1].text #通过下标访问
print root[0].tag, root[0].text
print "*"*10
for country in root.findall('country'): #找到root节点下的所有country节点
rank = country.find('rank').text #子节点下节点rank的值
name = country.get('name') #子节点下属性name的值
print name, rank
#修改xml文件
for country in root.findall('country'):
rank = int(country.find('rank').text)
if rank > 50:
root.remove(country)
tree.write('output.xml')
运行结果:
参考:https://docs.python.org/2/library/xml.etree.elementtree.html
2、xml.dom.*
文件对象模型(Document Object Model,简称DOM),是W3C组织推荐的处理可扩展置标语言的标准编程接口。一个 DOM 的解析器在解析一个XML文档时,一次性读取整个文档,把文档中所有元素保存在内存中的一个树结构里,之后你可以利用DOM 提供的不同的函数来读取或修改文档的内容和结构,也可以把修改过的内容写入xml文件。python中用xml.dom.minidom来解析xml文件,例子如下:
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding=utf-8
from xml.dom.minidom import parse
import xml.dom.minidom
# 使用minidom解析器打开XML文档
DOMTree = xml.dom.minidom.parse("country.xml")
Data = DOMTree.documentElement
if Data.hasAttribute("name"):
print "name element : %s" % Data.getAttribute("name")
# 在集合中获取所有国家
Countrys = Data.getElementsByTagName("country")
# 打印每个国家的详细信息
for Country in Countrys:
print "*****Country*****"
if Country.hasAttribute("name"):
print "name: %s" % Country.getAttribute("name")
rank = Country.getElementsByTagName('rank')[0]
print "rank: %s" % rank.childNodes[0].data
year = Country.getElementsByTagName('year')[0]
print "year: %s" % year.childNodes[0].data
gdppc = Country.getElementsByTagName('gdppc')[0]
print "gdppc: %s" % gdppc.childNodes[0].data
for neighbor in Country.getElementsByTagName("neighbor"):
print neighbor.tagName, ":", neighbor.getAttribute("name"), neighbor.getAttribute("direction")
运行结果:

参考:https://docs.python.org/2/library/xml.dom.html
3、xml.sax.*
SAX是一种基于事件驱动的API,利用SAX解析XML牵涉到两个部分:解析器和事件处理器。其中解析器负责读取XML文档,并向事件处理器发送事件,如元素开始跟元素结束事件;而事件处理器则负责对事件作出相应,对传递的XML数据进行处理。python中使用sax方式处理xml要先引入xml.sax中的parse函数,还有xml.sax.handler中的ContentHandler。常使用在如下的情况下:一、对大型文件进行处理;二、只需要文件的部分内容,或者只需从文件中得到特定信息;三、想建立自己的对象模型的时候。
ContentHandler类方法介绍
(1)characters(content)方法
调用时机:
从行开始,遇到标签之前,存在字符,content的值为这些字符串。
从一个标签,遇到下一个标签之前, 存在字符,content的值为这些字符串。
从一个标签,遇到行结束符之前,存在字符,content的值为这些字符串。
标签可以是开始标签,也可以是结束标签。
(2)startDocument()方法
文档启动的时候调用。
(3)endDocument()方法
解析器到达文档结尾时调用。
(4)startElement(name, attrs)方法
遇到XML开始标签时调用,name是标签的名字,attrs是标签的属性值字典。
(5)endElement(name)方法
遇到XML结束标签时调用。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#coding=utf-8
#!/usr/bin/python
import xml.sax
class CountryHandler(xml.sax.ContentHandler):
def __init__(self):
self.CurrentData = ""
self.rank = ""
self.year = ""
self.gdppc = ""
self.neighborname = ""
self.neighbordirection = ""
# 元素开始事件处理
def startElement(self, tag, attributes):
self.CurrentData = tag
if tag == "country":
print "*****Country*****"
name = attributes["name"]
print "name:", name
elif tag == "neighbor":
name = attributes["name"]
direction = attributes["direction"]
print name, "->", direction
# 元素结束事件处理
def endElement(self, tag):
if self.CurrentData == "rank":
print "rank:", self.rank
elif self.CurrentData == "year":
print "year:", self.year
elif self.CurrentData == "gdppc":
print "gdppc:", self.gdppc
self.CurrentData = ""
# 内容事件处理
def characters(self, content):
if self.CurrentData == "rank":
self.rank = content
elif self.CurrentData == "year":
self.year = content
elif self.CurrentData == "gdppc":
self.gdppc = content
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建一个 XMLReader
parser = xml.sax.make_parser()
# turn off namepsaces
parser.setFeature(xml.sax.handler.feature_namespaces, 0)
# 重写 ContextHandler
Handler = CountryHandler()
parser.setContentHandler(Handler)
parser.parse("country.xml")
运行结果:

4、libxml2和lxml解析xml
libxml2是使用C语言开发的xml解析器,是一个基于MIT License的免费开源软件,多种编程语言都有基于它的实现,python中的libxml2模块有点小不足的是:xpathEval()接口不支持类似模板的用法,但不影响使用,因libxml2采用C语言开发的,因此在使用API接口的方式上难免会有点不适应。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding=utf-8
import libxml2
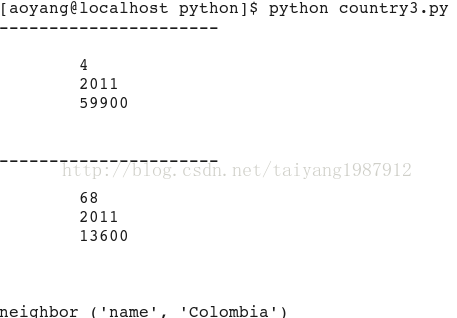
doc = libxml2.parseFile("country.xml")
for book in doc.xpathEval('//country'):
if book.content != "":
print "----------------------"
print book.content
for node in doc.xpathEval("//country/neighbor[@name = 'Colombia']"):
print node.name, (node.properties.name, node.properties.content)
doc.freeDoc()
lxml是以libxml2为基础采用python语言开发的,从使用层面上说比lxml更适合python开发者,且xpath()接口支持类似模板的用法。
在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding=utf-8
import lxml.etree
doc = lxml.etree.parse("country.xml")
for node in doc.xpath("//country/neighbor[@name = $name]", name = "Colombia"):
print node.tag, node.items()
for node in doc.xpath("//country[@name = $name]", name = "Singapore"):
print node.tag, node.items()

三、总结
(1)Python中XML解析可用的类库或模块有xml、libxml2 、lxml 、xpath等,需要深入了解的还需参考相应的文档。
(2)每一种解析方式都有自己的优点和缺点,选择前可以综合各个方面的性能考虑。
(3)若有不足,请留言,在此先感谢!
 Python:編譯器還是解釋器?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python:編譯器還是解釋器?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython是解釋型語言,但也包含編譯過程。 1)Python代碼先編譯成字節碼。 2)字節碼由Python虛擬機解釋執行。 3)這種混合機制使Python既靈活又高效,但執行速度不如完全編譯型語言。
 python用於循環與循環時:何時使用哪個?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
python用於循環與循環時:何時使用哪個?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseeAforloopWheniteratingOveraseQuenceOrforAspecificnumberoftimes; useAwhiLeLoopWhenconTinuingUntilAcIntiment.forloopsareIdealForkNownsences,而WhileLeleLeleLeleLeleLoopSituationSituationsItuationsItuationSuationSituationswithUndEtermentersitations。
 Python循環:最常見的錯誤May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python循環:最常見的錯誤May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMpythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyingListsDuringteritation,逐個偏置,零indexingissues,andnestedloopineflinefficiencies
 對於循環和python中的循環時:每個循環的優點是什麼?May 13, 2025 am 12:01 AM
對於循環和python中的循環時:每個循環的優點是什麼?May 13, 2025 am 12:01 AMforloopsareadvantageousforknowniterations and sequests,供應模擬性和可讀性;而LileLoopSareIdealFordyNamicConcitionSandunknowniterations,提供ControloperRoverTermination.1)forloopsareperfectForeTectForeTerToratingOrtratingRiteratingOrtratingRitterlistlistslists,callings conspass,calplace,cal,ofstrings ofstrings,orstrings,orstrings,orstrings ofcces
 Python:深入研究彙編和解釋May 12, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:深入研究彙編和解釋May 12, 2025 am 12:14 AMpythonisehybridmodeLofCompilation和interpretation:1)thepythoninterpretercompilesourcecececodeintoplatform- interpententbybytecode.2)thepythonvirtualmachine(pvm)thenexecutecutestestestestestesthisbytecode,ballancingEaseofuseEfuseWithPerformance。
 Python是一種解釋或編譯語言,為什麼重要?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python是一種解釋或編譯語言,為什麼重要?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AMpythonisbothinterpretedAndCompiled.1)它的compiledTobyTecodeForportabilityAcrosplatforms.2)bytecodeisthenInterpreted,允許fordingfordforderynamictynamictymictymictymictyandrapiddefupment,儘管Ititmaybeslowerthananeflowerthanancompiledcompiledlanguages。
 對於python中的循環時循環與循環:解釋了關鍵差異May 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM
對於python中的循環時循環與循環:解釋了關鍵差異May 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM在您的知識之際,而foroopsareideal insinAdvance中,而WhileLoopSareBetterForsituations則youneedtoloopuntilaconditionismet
 循環時:實用指南May 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
循環時:實用指南May 12, 2025 am 12:07 AMForboopSareSusedwhenthentheneMberofiterationsiskNownInAdvance,而WhileLoopSareSareDestrationsDepportonAcondition.1)ForloopSareIdealForiteratingOverSequencesLikelistSorarrays.2)whileLeleLooleSuitableApeableableableableableableforscenarioscenarioswhereTheLeTheLeTheLeTeLoopContinusunuesuntilaspecificiccificcificCondond


熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
這個專案正在遷移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的過程中,你可以繼續在那裡關注我們。 MinGW:GNU編譯器集合(GCC)的本機Windows移植版本,可自由分發的導入函式庫和用於建置本機Windows應用程式的頭檔;包括對MSVC執行時間的擴展,以支援C99功能。 MinGW的所有軟體都可以在64位元Windows平台上運作。

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

Atom編輯器mac版下載
最受歡迎的的開源編輯器





