1.子窗體
在設計網站的時候,我們需要設計一些模態的子窗體,像是
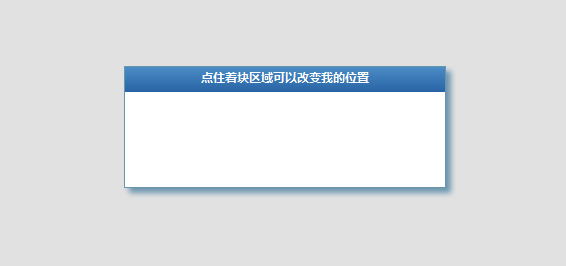
這一步驟很容易實現,只要div css就ok了,請看程式碼:
複製程式碼
程式碼如下:
.modal-background
{
background-color: #999999; 999999; left: 0;
opacity: 0.3;
position: fixed;
right: 0;
. >}
.modal-window
{
background-color: #FFFFFF;
border: 1px solid #6B94AD;
family : 'Microsoft YaHei';
font-size: 12px;
height: 120px;
left: 50%;
. 60px;
opacity: 1;
position: fixed;
top: 50%;
{
height: 25px;
height: 25px;
background-image: -moz-linear-gradient (top, #4A8CC5, #2963A5); /* Firefox */
background-image: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, left bottom, color-stop(0, #4A), left top, left bottom, color-stop(0, #ApCC5(0),1855 , #2963A5)); /* Saf4 , Chrome */
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#4A8CC5', endorstr='#2963AstartColorstr='#4A8CC5', endorstr='#2963AstartColorstr='#4A8CC5', endorstr='#2963A */
}
.modal-window .head center
{
🎜>
加上上述html和css就可以輕易達到上述模態窗體的效果。其中left: 50%;top: 50%; margin-left: -160px; margin-top: -160px;是為了實現這個模態窗體的居中效果。
🎜>
在第二行程式碼中追加了.list-window這個樣式類別來覆蓋.modal-window類別中的大小和位置,但同時保證模態視窗居中顯示
複製程式碼
margin-top:-200px;
}
如圖

可以看得出來,這一步的實現是非常簡單的,掌握幾個關鍵行的css屬性就"完虐"這個模態子窗體,各類其它的模態子窗體可以舉一反三咯。
2.當滑鼠點住子窗體的頭部時,如何實現子窗體的拖曳移動呢?當引入jQ後,我們只需要很少的腳本就搞定這個小功能。不信我們看
var left, this $this;
var left, this $this;
$this; (document).delegate('.modal-window .head', 'mousedown', function (e) {
left = e.clientX, top = e.clientY, $this = $(this).css(' cursor', 'move');
this.setCapture ? (
this.setCapture(),
this.onmousemove = 必須this.onmouseup = mouseUp
) : $(document).bind("mousemove", mouseMove).bind("mouseup", mouseUp);
});
function mouseMove(3); > var target = $this.parents('.modal-window');
var l = Math.max((e.clientX - left Number(target.css('margin-left').replace(/px $/, '')) || 0), -target.position().left);
var t = Math.max((e.clientY - top Number(target.css('margin-top') .replace(/px$/, '')) || 0), -target.position().top);
l = Math.min(l, $(window).width() - target.width () - target.position().left);
t = Math.min(t, $(window).height() - target.height() - target.position().top);
left = e.clientX;
top = e.clientY;
target.css({ 'margin-left': l, 'margin-top': t });
}
function mouseUp (e) {
var el = $this.css('cursor', 'default').get(0);
el.releaseCapture ?
(
) : $(document).unbind("mousemove", mouseMove).unbind("mouse 🎜>
這段程式碼非常簡短,能否在各種瀏覽器中很流暢的運作。
其實它的實作原理非常簡單,大致分為三步:
②當滑鼠沒有彈起時(沒有mouseup)時,若滑鼠在窗體內移動時,啟動mouseMove函數,透過計算滑鼠移動的距離來及時整個窗體的位置移動。
③當滑鼠彈起(mouseup)時,呼叫mouseUp事件,將document上綁定的mousemove事件和mouseup事件解除綁定。
整個過程的原理是:當滑鼠mousedown時,滑鼠的移動事件轉移到document上來,透過滑鼠在document上的移動事件來處理整個窗體。
另外,在mouseMove中有個小技巧,就是全域的left,top變數記錄上一次滑鼠停止時的位置,然後下一次移動時滑鼠的位置與left,top變數進行對比來決定滑鼠移動了多少距離,來對整個模態子窗體做出對應的位置移動即可。
經過這段程式碼的分析,發現老鼠移動窗體乃至document上的任何元素都是相當easy的
比如,如果想要透過拖曳來改變窗體的大小,一樣我們只需要在mouseMove事件處理函數中調整窗體的大小就ok了,是不是又發現自己有多學會了一招,又精進了一小步呢?
有人會問setCapture和releaseCapture分別是做什麼的呢?其實這是為了相容IE,只有IE才有這兩個函數,在此鄙視IE。 setCapture可以讓目前元素捕捉滑鼠的所有事件,如果不使用它們,可能不相容IE瀏覽器哦。
 超越瀏覽器:現實世界中的JavaScriptApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
超越瀏覽器:現實世界中的JavaScriptApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript在現實世界中的應用包括服務器端編程、移動應用開發和物聯網控制:1.通過Node.js實現服務器端編程,適用於高並發請求處理。 2.通過ReactNative進行移動應用開發,支持跨平台部署。 3.通過Johnny-Five庫用於物聯網設備控制,適用於硬件交互。
 使用Next.js(後端集成)構建多租戶SaaS應用程序Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
使用Next.js(後端集成)構建多租戶SaaS應用程序Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM我使用您的日常技術工具構建了功能性的多租戶SaaS應用程序(一個Edtech應用程序),您可以做同樣的事情。 首先,什麼是多租戶SaaS應用程序? 多租戶SaaS應用程序可讓您從唱歌中為多個客戶提供服務
 如何使用Next.js(前端集成)構建多租戶SaaS應用程序Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
如何使用Next.js(前端集成)構建多租戶SaaS應用程序Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM本文展示了與許可證確保的後端的前端集成,並使用Next.js構建功能性Edtech SaaS應用程序。 前端獲取用戶權限以控制UI的可見性並確保API要求遵守角色庫
 JavaScript:探索網絡語言的多功能性Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript:探索網絡語言的多功能性Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript是現代Web開發的核心語言,因其多樣性和靈活性而廣泛應用。 1)前端開發:通過DOM操作和現代框架(如React、Vue.js、Angular)構建動態網頁和單頁面應用。 2)服務器端開發:Node.js利用非阻塞I/O模型處理高並發和實時應用。 3)移動和桌面應用開發:通過ReactNative和Electron實現跨平台開發,提高開發效率。
 JavaScript的演變:當前的趨勢和未來前景Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
JavaScript的演變:當前的趨勢和未來前景Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AMJavaScript的最新趨勢包括TypeScript的崛起、現代框架和庫的流行以及WebAssembly的應用。未來前景涵蓋更強大的類型系統、服務器端JavaScript的發展、人工智能和機器學習的擴展以及物聯網和邊緣計算的潛力。
 神秘的JavaScript:它的作用以及為什麼重要Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
神秘的JavaScript:它的作用以及為什麼重要Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScript是現代Web開發的基石,它的主要功能包括事件驅動編程、動態內容生成和異步編程。 1)事件驅動編程允許網頁根據用戶操作動態變化。 2)動態內容生成使得頁面內容可以根據條件調整。 3)異步編程確保用戶界面不被阻塞。 JavaScript廣泛應用於網頁交互、單頁面應用和服務器端開發,極大地提升了用戶體驗和跨平台開發的靈活性。
 Python還是JavaScript更好?Apr 06, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python還是JavaScript更好?Apr 06, 2025 am 12:14 AMPython更适合数据科学和机器学习,JavaScript更适合前端和全栈开发。1.Python以简洁语法和丰富库生态著称,适用于数据分析和Web开发。2.JavaScript是前端开发核心,Node.js支持服务器端编程,适用于全栈开发。
 如何安裝JavaScript?Apr 05, 2025 am 12:16 AM
如何安裝JavaScript?Apr 05, 2025 am 12:16 AMJavaScript不需要安裝,因為它已內置於現代瀏覽器中。你只需文本編輯器和瀏覽器即可開始使用。 1)在瀏覽器環境中,通過標籤嵌入HTML文件中運行。 2)在Node.js環境中,下載並安裝Node.js後,通過命令行運行JavaScript文件。


熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

Dreamweaver Mac版
視覺化網頁開發工具

MantisBT
Mantis是一個易於部署的基於Web的缺陷追蹤工具,用於幫助產品缺陷追蹤。它需要PHP、MySQL和一個Web伺服器。請查看我們的演示和託管服務。

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
將Eclipse與SAP NetWeaver應用伺服器整合。

VSCode Windows 64位元 下載
微軟推出的免費、功能強大的一款IDE編輯器

PhpStorm Mac 版本
最新(2018.2.1 )專業的PHP整合開發工具





