XML tree structure
XML documents form a tree structure that starts at the "root" and expands to the "leaves."
An XML document example
XML document uses a simple self-descriptive syntax:
<note>
<to>Tove</to>
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
</note>
First line is an XML declaration. It defines the version of XML (1.0) and the encoding used (ISO-8859-1 = Latin-1/Western European character set).
The next line describes the document's root element (like saying: "This document is a note"):
The next four lines describe the four child elements of the root (to, from, heading and body):
<from>Jani</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body>
The last line defines the end of the root element:
You can assume, from this example, that the XML document contains a Jani Note to Tove.
XML is very self-descriptive, don’t you agree?
XML documents form a tree structure
XML documents must contain the root element. This element is the parent element of all other elements.
The elements in an XML document form a document tree. The tree starts at the root and expands to the very bottom of the tree.
All elements can have sub-elements:
subchild>
</child>
</root>
The terms parent, child, and sibling are used to describe the relationship between elements. Parent elements own child elements. Child elements at the same level become siblings (brothers or sisters).
All elements can have text content and attributes (similar to HTML).
Example:
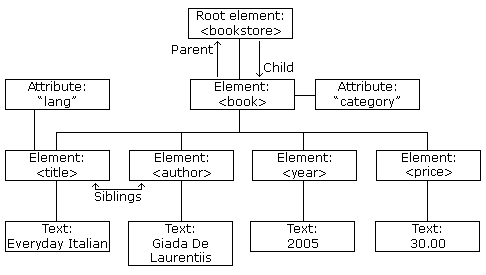
The above image represents a book in the following XML:
<book category="COOKING">
<title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title>
<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>30.00</price>
</book>
<book category="CHILDREN">
<title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="WEB">
<title lang="en">Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
The root element in the instance is <bookstore>. All <book> elements in the document are contained within a <bookstore>.
The<book> element has 4 child elements: <title>, <author>, <year>, <price>.








