提示说:不要把「Do not place android context classes in static fields, this is a memory leak.」
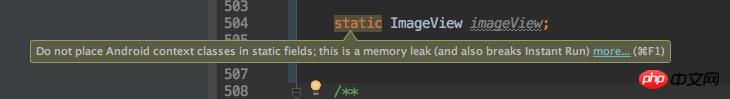
我知道activity context 不应该被放到static fields里面因为它在app生命周期内一直存在,而且如果它通过构造函数传递给其他class的话,其他class也会一直不被回收。
但为什么ImageView不能是static(我发现SwipeRefreshLayout也不行)?是因为ImageView包含context?Button和TextView之类的view就没有这种问题。
迷茫2017-04-18 09:08:00
To fill the layout in the Activity, you can use the following methods:
1.view view = View.inflate(context, R.layout.test,null );
2.View view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.test,null);
It can be found that no matter which way, the filled View holds a reference to the context, which is a reference to the Activity.
If the filled view at this time is statically modified, then the static object will continue to hold a reference to the Activity , causing the Activity to be unable to be destroyed, and all controls in the Activity to be completely destroyed and recycled, ultimately causing memory leaks.
PS: Why use static View? Are there any special business requirements?
PHP中文网2017-04-18 09:08:00
static variables exist separately in the memory block. The control (in your question refers to ImageView) holds a reference to the Activity. In this case, the Activity cannot be completely destroyed because it is in the memory. There is always a reference (pointer understanding) in it, causing the Activity to not be recycled, and naturally there will be a memory leak!
It is recommended not to use static modified controls in Android!
阿神2017-04-18 09:08:00
View needs to hold Context (otherwise the functions of setXXX(int resid)class cannot be realized)
I don’t know why Button/TextView doesn’t warn
怪我咯2017-04-18 09:08:00
Static variables cannot be automatically recycled
You set a view as a static variable, and the view holds a reference to the activity. Now even the activity is leaked
阿神2017-04-18 09:08:00
Because the static life cycle is very long and longer than the current activity
怪我咯2017-04-18 09:08:00
Let’s put it this way, this is the basis of Java. After the class file is compiled into bytecode, the static variable will be initialized when the method area is loaded, and the static variable will always exist, while the activity without static modification will When new, apply for space in the heap. When the activity is useless, gc will traverse according to gc-root to see whether the activity is referenced. Due to the context被持有,ImageView view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.test,null); of the activity, gc cannot recycle, causing memory leaks. When until The virtual machine ends the process (that is, the app stops),