就像JAVA一样,
test(new String[] {"1", "2"});
static void test(String[] args) {
}黄舟2017-04-17 14:41:42
Although C cannot pass arrays as parameters, you can still create an "unnamed" array when passing parameters like this:
#include <stdio.h>
void print_string(char str[])
{
puts(str);
}
int main()
{
print_string((char []) {"anonymous"});
return 0;
}怪我咯2017-04-17 14:41:42
cLanguage can only pass a pointer, which is the first address of the array~
void a(int* array);
void b(int array[]); When a function is declared, int* array and int array[] are equivalent, and array can only be a pointer.
The first two are exactly the same and can also be written as:
void d(int const* array);This is the same, the array is passed as a const pointer in c.
In the example below, you can see that arr points to the same address.
#include <stdio.h>
void arr_p(int* arr){
printf("%d\t%d\n", arr, &arr[0]);
}
void arr_a(int arr[]){
printf("%d\t%d\n", arr, &arr[0]);
}
void arr_10(int arr[10]){
printf("%d\t%d\n", arr, &arr[0]);
}
int main(){
int arr[20]={0};//20个元素
arr_p(arr);
arr_a(arr);
arr_10(arr);//这里并不会检查数组是否超过10个元素
printf("%d\t%d\n", arr, &arr[0]);
getchar();
return 0;
}As for the example of @拉丝Master, I tried it in vs2010 and it showed a syntax error. Maybe, is there something I didn't do right? 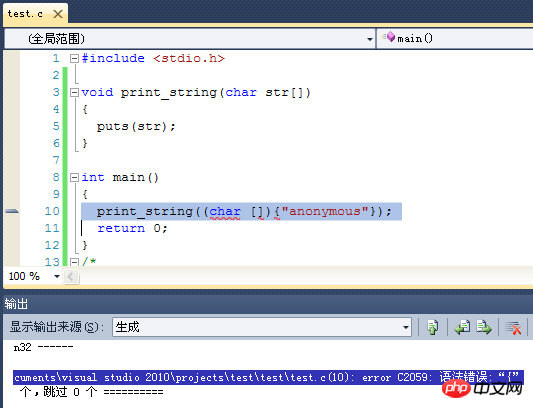
Also, if you want to complain, there are no points for likes in comments. There is no need for the author to be stingy enough to even cancel this~ :D
ringa_lee2017-04-17 14:41:42
int sum(int* arr){
// Do something
return 0;
}
int a[5] = {1,3,2,4,5};
sum(a);迷茫2017-04-17 14:41:42
The argv (argument vector) used by C programs to receive parameters by default is a string array.
char *argv[] = {"str1", "str2"};
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
fprintf(stderr,"argc: %d\n",argc);
int i;
for(i=0;i<argc;i++) {
fprintf(stderr,"argv[%d]: %s\n",i,argv[i]);
}
return 0;
}
编译: gcc ab.c -o ab
运行: ./ab -c10 -n500 http://127.0.0.1/index.php
结果:
argc: 4
argv[0]: ./ab
argv[1]: -c10
argv[2]: -n500
argv[3]: http://127.0.0.1/index.php
argc是参数个数,*argv[]是参数数组,用来接收命令行参数.