《C++ Primer》第五版,中文版。p50。
需要注意的是,一个指针指向某对象,同时另一个指针指向另外对象的下一地址,此时也有可能出现这两个指针值相同的情况,即指针相等。
之前在 CSDN 问答上问的:http://ask.csdn.net/questions/256146
“另外对象的下一地址”指的是不是尾后迭代器?
有人提到是相邻的导致相等。是否是下面的代码表达的意思:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int a[] = { 1,2 };
int i = 4;
int main()
{
int *p = end(a);
if (p == &i) cout << "equ" << endl;
return 0;
}
巴扎黑2017-04-17 13:50:47
Regarding your question, I don’t know if I understand the meaning of the description correctly. Look at the picture below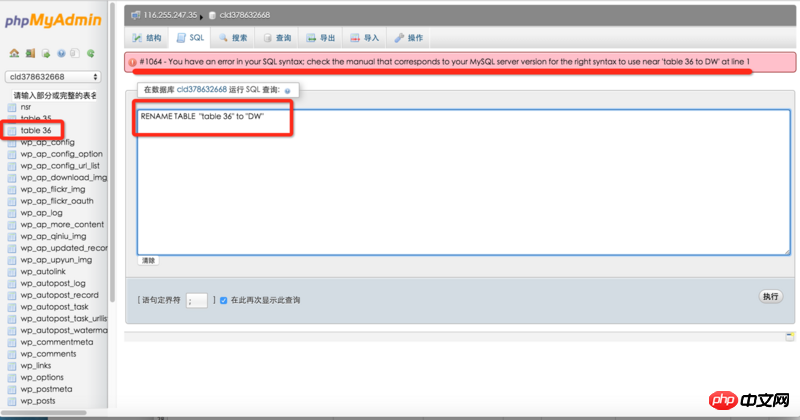
This is very simple, it is possible to be equal. When object C and object B are one object, they are equal.
I’ll lend you the code
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int a[] = { 1,2 };
int main()
{
int* p1 = &a[1]; //指针p1指向对象a[1]
int* p2 = &a[0] + 1; //指针p2指向对象a[0]的下一个
if(p1 == p2){
cout<<"p1("<<p1 <<") = p2("<<p2<<")\n";
}
return 0;
}大家讲道理2017-04-17 13:50:47
因为内存是连续的, after the file pointer p completes traversing the array, it actually points to a memory address behind the array. The next memory address happens to be the address of i. So they are exactly equal. I think the following two pictures will solve your doubts:
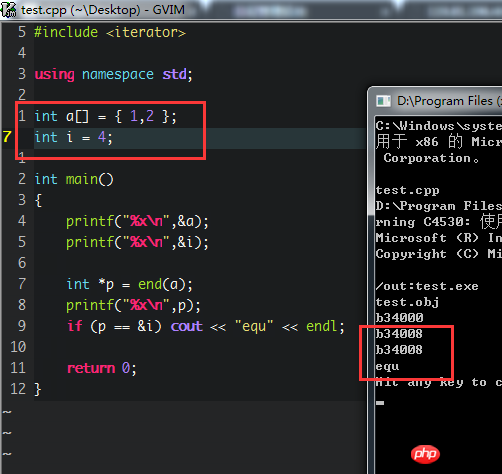
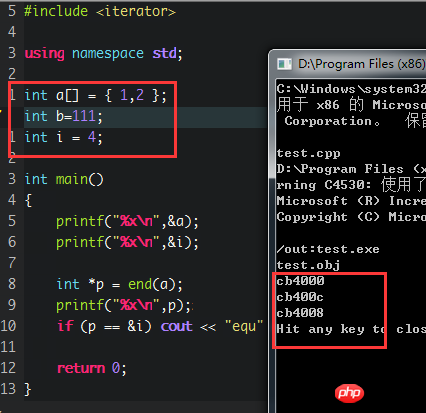
Calculate the memory address yourself, an integer is 4 bytes. Did it happen to correspond?