以下是flex布局: 相同的样式,应用在 p布局 和 和 ul布局上的效果,竟然会出现截然不同的效果!!谁能够解释??
代码:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
<style>
body,p,ul{font-size:100%;margin:auto;padding:0px;}
ul{list-style-type:none;}
.flex{width:800px;height:300px;border:1px solid blue;
display:flex;
display:-webkit-flex;
flex-flow:row wrap;
-webkit-flex-flow:row wrap;
justify-content:center;
-webkit-justify-content:center;
align-items:flex-start;
-webkit-align-items:flex-end;
}
.flex>*{
background-color:;
flex-grow:1;
flex-shring:1;
flex-basis:auto;
flex:1 1 auto;
-webkit-flex:1 1 auto;
text-align:center;
}
.flex>*:nth-of-type(1){background-color:blue;height:50px;line-height:50px;}
.flex>*:nth-of-type(2){background-color:red;height:100px;line-height:100px;}
.flex>*:nth-of-type(3){background-color:green;height:150px;line-height:150px;}
</style>
<p class='flex'>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
</p>
<ul class='flex'>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
现象图:
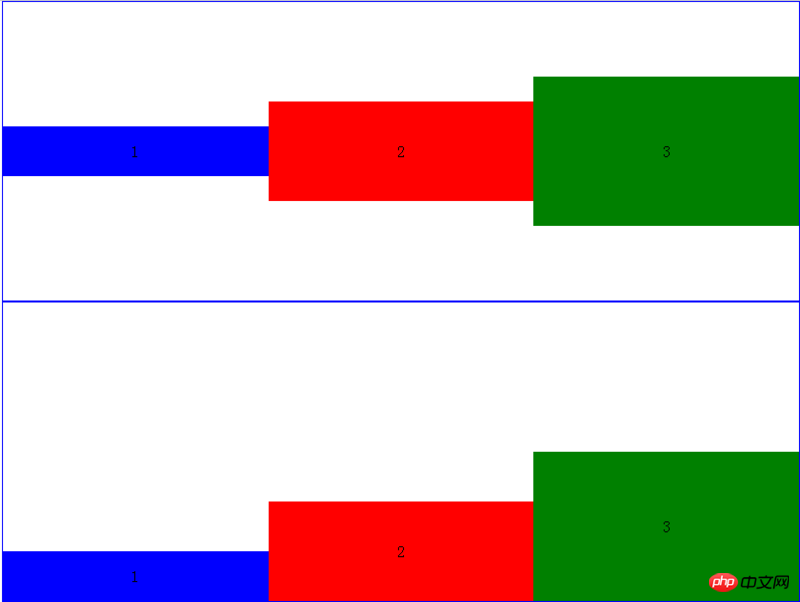
上面一张是p 的效果图 , 下面一张是 ul 的效果图。
个人觉得主要原因是:align-itmes:flex-start 不起作用!
align-items:flex-start 在阮一峰的介绍中:

所以,我得出的结论:p中的三个子p应该和ul中三个子li标签的表现一致,也就是,顶在上面。
可为什么却出现了如此截然不同的现象??
求解释.......
迷茫2017-04-17 11:40:10
The
1 image child element is p, with style margin: auto. The
2 picture sub-element is li.
ps: I originally thought that margin: auto vertical centering was only for absolutely defined elements, but it turns out that flex is also applicable.
伊谢尔伦2017-04-17 11:40:10
The last two lines in your own code css style.flex{} align-items:flex-start;-webkit-align-items:flex-end; so your li will be at the bottom;
Supplementary:
<style type="text/css">
.wrap1{
display:flex;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border:1px red solid;
margin:0 auto;
}
.a{
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
margin:auto;
background-color: blue;
}
.wrap2{
display:flex;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border:1px red solid;
margin:0 auto;
align-items:flex-start;
}
.b{
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
margin-left: 20px;
background-color: green;
}
.wrap2 p:nth-child(1){
margin-top:20px;
}
.wrap2 p:nth-child(2){
margin-top:50px;
}
.wrap2 p:nth-child(3){
margin-top:70px;
}
</style>
<p class="wrap1">
<p class="a"></p>
<p class="a"></p>
<p class="a"></p>
</p>
<p class="wrap2">
<p class="b"></p>
<p class="b"></p>
<p class="b"></p>
</p>Run the above code and you will find that first: after the parent element sets flex, the margin: atuo attribute of the child element not only affects the left and right directions, but also affects the up and down directions. Second: After setting align-items:flex-start, the arrangement of child elements will be affected by its own margin.