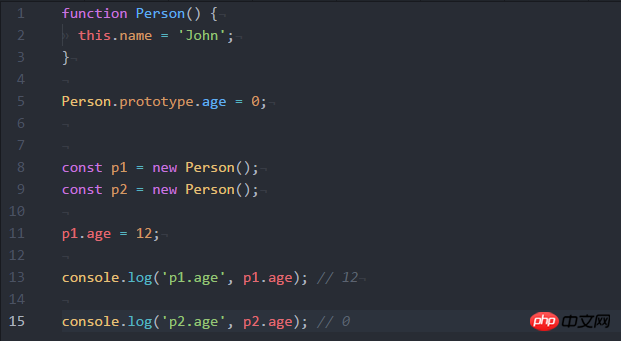
As shown above, the __proto__ of instances p1 and p2 point to the same prototype object Person.prototype,
Execute p1.age=12, why p1.age does not change to 12, but remains the original 0
漂亮男人2017-06-30 10:00:00
p1.age will not change the value of the prototype. p2 has no age attribute. It will look up along the prototype chain and find the age in Person, so p2.page is equal to Person.prototype.age
阿神2017-06-30 10:00:00
Because p1.age modifies the attributes on p1 instead of the attributes on the prototype.
世界只因有你2017-06-30 10:00:00
p1.age = 12 will only assign a value to the age of p1, but not to the age of Person, so the age of p2 is not assigned, so it is still 0 on the prototype
为情所困2017-06-30 10:00:00
p1.age = 12 actually adds an attribute age with a value of 12 to p1. When accessing p1.age, this attribute will be accessed directly without going to the prototype chain to find age. , if you want to realize that p1 and p2 are changed, you can write like this p1.__proto__.age = 12