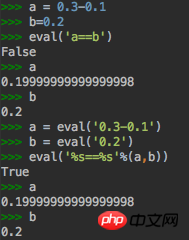
As shown in the figure, when Python2.7 uses eval to calculate floating point expressions,
eval('0.3-0.1==0.2') # 输出为False
eval('%d - %d == %d'%(0.3, 0.1, 0.2)) # 输出为True
eval('%s - %s == %s'%(0.3, 0.1, 0.2)) # 输出为False
eval('%s - %s == %s'%('0.3', '0.1', '0.2')) # 输出为FalseThis is very confusing. I can’t find the answer online. Please give me guidance!
renew:
I have another question,
a=0.3-0.1, print(a) outputs 0.19999999999999998; b=0.2,
But print('%s==%s'%(a,b) ) but the output is 0.2==0.2,
Why does a change from 0.19999999999999998 to 0.2 when formatting the string?
phpcn_u15822017-06-22 11:54:25
Generally, it cannot be used directly in computers. == Compares whether two floating point numbers are equal.
Because floating point values have errors in computers.
python has decimal and fraction 2 modules for high-precision floating point calculations.
Example
>>> from fractions import Fraction
>>> Fraction('0.3')-Fraction('0.1') == Fraction('0.2')
True
>>> from decimal import Decimal
>>> Decimal('0.3')-Decimal('0.1') == Decimal('0.2')
True
>>> 仅有的幸福2017-06-22 11:54:25
This has nothing to do with eval, it is mainly a matter of accuracy. This will be encountered in all programming languages. If you try 0.3-0.1 == 0.2, it will directly return False. Baidu JavaScript 0.2-0.1 problem, and then take a look at "Principles of Computer Composition" 》The initial data representation.
https://stackoverflow.com/que... This is a highly voted answer.
为情所困2017-06-22 11:54:25
eval('0.3-0.1==0.2') # 输出为False, 是因为0.3-0.1=0.19999999999999998
eval('%d - %d == %d'%(0.3, 0.1, 0.2)) # 输出为True, 是因为你%d传入是整数,相当于0-0=0
eval('%s - %s == %s'%(0.3, 0.1, 0.2)) # 输出为False, 参考1
eval('%s - %s == %s'%('0.3', '0.1', '0.2')) # 输出为False, 参考1