async function a() {
var result = await b()
res.json(result)
}var fse = require('fs-extra')
function b() {
var fpath = '/data.json'
// 异步读取文件
fse.readJson(fpath, (err, data) => {
if(err) console.log(err)
return data
})
}In the above code, result is undefined, that is, the data after reading the file is not obtained. How should I modify it so that the result can get the content of data.json?
PHPz2017-05-19 10:48:58
In this case, it is recommended that you use stream and your b function does not return a Promise. It is recommended to understand the relationship between async/await and Promise and two processing methods
1.
var data = fs.createReadStream('/data.json')
data.pipe(res)2.
function b () {
var fpath = '/data.json'
return new Promise((resolve, reject) =>{
readJson(fpath, (err, data) => {
if (err) reject(err)
resolve(data)
})
})
}给我你的怀抱2017-05-19 10:48:58
async function a() {
var result = await b()
res.json(result)
}
var fse = require('fs-extra')
function b() {
var fpath = '/data.json'
// 异步读取文件
fse.readJson(fpath, (err, data) => {
if(err) console.log(err)
return data
})
}
I was reading an article when I just saw this code
6 Reasons Why JavaScript's Async/Await Blows Promises Away (Tutorial)
Think carefully about whether your function b uses the fse extension to read the file or uses a callback. . (The development history is callback function->promise->Async/Await). 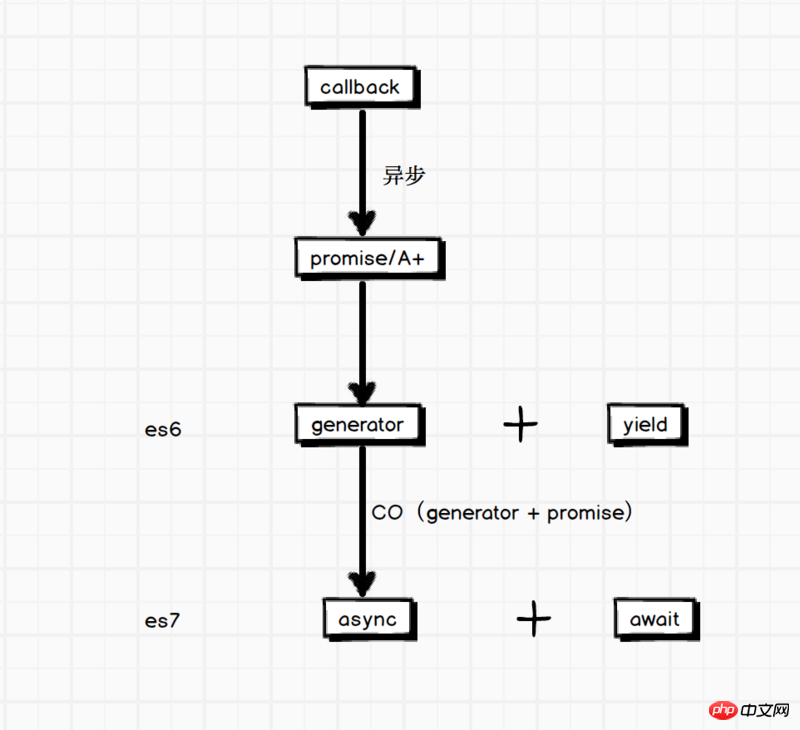
That is to say, async/Await does not support callback functions. If you must use async in function a, you can modify b to support returning a promise.
var fse = require('fs-extra')
async function a() {
var result = await b();
console.info(result);
}
const b= ()=> {
let p= new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
var fpath = 'data.json'
// 异步读取文件
fse.readJson(fpath,(err,data)=>{
if(err){
console.info(err);
reject(err);
}
resolve(data);
});
});
return p;
}
console .info(a());After using Promise packaging, you can use the latest features of await.
Just started to learn, please give me some advice
Reference:
What is Promise
Node.js latest technology stack - Promise